Notes - Mr. Houtz
advertisement

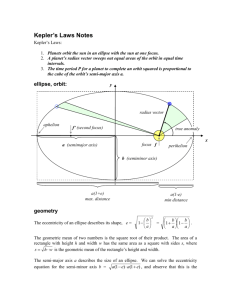
Science Starter Answer the following in your notebook: 1. When is the Earth closest to the Sun? 2. Does the speed of the Earth’s revolution change? 3. How can we tell if we are moving faster? Today’s Agenda • Science Starter • History of Astronomy • Lab Simulation • Vocabulary Review Activity • Haley’s Comet Summarizer Lesson Essential Question How do planets move through space? Historical Models of our Solar System and Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion Geocentric Model • Earth is center of our Solar System • Aristotle- Over 2000 years ago • Unexplained on how planets appear to move backwards • Ptolemy- Planets move in small circles or epicycles Heliocentric Model • Sun is center of our Solar System • Copernicus- Over 450 years ago (1543 ad) • First to suggest heliocentric theory and vaguely mapped out the planets orbiting the sun in a circular orbit. Galileo • Supporter of Copernicus’s Heliocentric theory • House arrest • Observed moons orbiting Jupiter and theorized objects can revolve around other planets not just Earth Solar System precisely measured • Tycho Brahe- studied Solar System and made very accurate recordings of his observations • Tycho’s assistant, Kepler, used information for the details of orbits Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion 1st Law - Law of Ellipses Each planet orbits the Sun in a path called an ellipse or elongated circle Ellipse is a closed curve whose path is determined by 2 points or foci within the ellipse Focus 1 is the Sun and Focus 2 is an imaginary point Eccentricity • Degree of elongation or shape of planet’s orbit • Ratio between the foci and length of major axis • Circular =0 • Very elongated =1 2nd Law – Law of Equal Areas • An imaginary line between the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times as the planet travels around the ellipse. Keplers’ nd 2 Law- Law of Equal Areas • This also means that as the planet comes closer to the Sun in its orbit, it travels faster. • So, the planets speed is slowest when it is the farthest from the Sun Challenge Question What time of the year is Earth moving faster in its orbit? Challenge Question What time of the year is Earth moving faster in its orbit? Winter (closer to the sun) 3rd Law – Law of Periods • Mathematical relationship • P 2 = a3 • a= semi-major axis (planets average distance from Sun measured in AU’s) • p= planet’s orbital period (time) • Simply means that the farther a planet is from the Sun, the longer it takes to orbit around the Sun Einstein (1879-1955) • Changed Newton’s gravitational theory based on findings of Mercury’s orbit. • Developed Theory of Relativity. It completely changed the way we study gravity and even changed our understanding of the universe. Kepler’s Lab Simulation • Each group will sign out a laptop (1 per group) • Each person at the group will have a lab sheet to fill out • Work together in your group to answer the questions and make sure everyone understands! • DO NOT VISIT OTHER SITES BEYOND THE SIMULATION!! (LOSS OF LAPTOP) • If you finish early: show Mr. Houtz your work, return your laptop, and grab a vocabulary activity from the front Kepler’s Lab Simulation • Suggested that you break up the work like so: 1. Computer Manager (signs out laptop) 2. Question Answerer (makes sure all group understands) 3. Task Manager (makes sure group is working at ALL times & follows the procedures) 4. Researcher (Keeps notes out to answer analysis questions, ask Mr. Houtz for help) Vocabulary Activity • Grab a vocabulary activity from the front of the classroom • The sheet has 4 activities for you to complete • You can use your notes or the book to answer (Ch.22-24) • Should be completed by the end of class Haley’s Comet Haley’s Comet follows the orbit path above, cycling once every 80 years. 1. When is Haley’s comet moving fastest & how do you know? (close or far from the sun) 2. Why does Haley’s comet not orbit the Sun in a circle? 3. How is Haley’s orbit similar to the Earth’s revolution?