Lewis diagrams for I..
advertisement

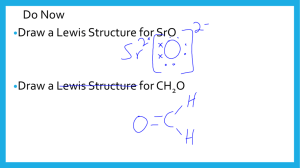
Lewis Diagrams For Ionic and Covalent Compounds First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. Sr First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F Strontium fluoride will be an ionic compound First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F Electrons will be transferred from the metal to the non-metal atoms. First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. 2+ F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. 2+ F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. 2+ F Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F 2+ Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F Fluoride ion 2+ Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F Fluoride ion 2+ Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F Fluoride ion – 2+ Sr F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F – 2+ Sr Lewis Diagram for Strontium Fluoride F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F Has a Stable Octet – 2+ Sr F Has a Stable Octet First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F – 2+ Sr Has no valence electrons left F First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F – 2+ Sr F Formula for strontium fluoride is First, we’ll consider the ionic compound strontium fluoride. – F – 2+ Sr F Formula for strontium fluoride is SrF2 Now we’ll do another example. This time we’ll draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K I need to gain 1 e– here. I need to gain 1 e– here. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K I can lose this one valence e–. S K I need to gain 1 e– here. I need to gain 1 e– here. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K The compound formed will be ionic. Electrons will be transferred, NOT shared. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K The compound formed will be ionic. Electrons will be transferred, NOT shared. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K The compound formed will be ionic. Electrons will be transferred, NOT shared. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. K S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K A potassium cation + S K A potassium cation Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + S K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + 2– S A sulphide anion K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + 2– S The Lewis Diagram for Potassium Sulphide K Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + 2– S K There are 2 potassium ions for every sulphide ion, so the formula for potassium sulphide is K2S. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + 2– S K There are 2 potassium ions for every sulphide ion, so the formula for potassium sulphide is K2S. Draw the Lewis diagram for the ionic compound potassium sulphide. + K + 2– S K There are 2 potassium ions for every sulphide ion, so the formula for potassium sulphide is K2S. Lewis diagrams can also be used to show the formation of covalent compounds. Lewis diagrams can also be used to show the formation of covalent compounds. In this example, we’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Hydrogen can He either lose, or share its valence e–. H Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. When hydrogen forms a compound with selenium, the compound, in the gaseous form, is found to be covalent. We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. When hydrogen forms a compound with selenium, the compound, in the gaseous form, is found to be covalent. So in this case hydrogen shares its valence electron rather than losing it. We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H A hydrogen atom with one valence e– We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. A Se atom with 6 valence e–’s Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H This electron will be SHARED, not lost! We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se I need to gain 1 e– here. H H I need to gain 1 e– here. We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se Another hydrogen atom H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H The entire atoms will move, rather than just their electrons. We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. These 2 valence e–’s are shared between Se and H Se H H These 2 valence e–’s are shared between Se and H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. A COVALENT bond Se H H A COVALENT bond We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. A stable octet Se H H We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. This H feels the same electron arrangement as Helium Se H H This H feels the same electron arrangement as Helium We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H The Lewis Diagram for hydrogen selenide We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H These shared electron pairs can be replaced by lines We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H Like this! We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H Each one of these lines is called a single covalent bond We’ll show how the covalent compound hydrogen selenide is formed. Se H H The Lewis Diagram for hydrogen selenide Se H H In this example, we’ll see how Lewis diagrams can be used to show how the covalent compound of phosphorus and chlorine forms. The compound is called phosphorus trichloride. Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Lone pair Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl Unpaired e– P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl Unpaired e– P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl The formula for this compound is PCl3, and its name is phosphorus trichloride Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl The formula for this compound is PCl3, and its name is phosphorus trichloride Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl The formula for this compound is PCl3, and its name is phosphorus trichloride Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl The phosphorus atom has a stable octet Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl The 3 chlorine atoms each have a stable octet Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl There are 3 covalent bonds in which a pair of electrons is shared Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl These shared electron pairs can be replaced by single lines. Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl These shared electron pairs can be replaced by single lines. Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Cl P Cl Cl Using Lewis diagrams, show how phosphorus trichloride forms from its atoms. Cl P Cl Cl Cl P Cl Cl Lewis Diagram of Phosphorus Trichloride, PCl3 Lewis Diagrams Showing Double and Triple Covalent Bonds Oxygen is a Diatomic Element Its formula is O2 Oxygen is a Diatomic Element Its formula is O2 Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O Unpaired electrons O Unpaired electrons Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O 2 pairs of electrons are being shared Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O The Lewis Diagram for an oxygen molecule, O2 Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Each shared pair of electrons is replaced by a line Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O Each shared pair of electrons is replaced by a line Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O This is called a double covalent bond Oxygen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is O2 O O O The Lewis Diagram for an oxygen molecule, O2 O Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element Its formula is N2 Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 lone pair N N lone pair Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N 3 unpaired 3 unpaired electrons electrons N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N The Lewis Diagram for a molecule of N2 Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N Has a stable octet N Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N Has a stable octet Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N These 3 pairs of electrons are shared Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N We have 3 parallel lines Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N A triple covalent bond Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N A triple covalent bond Nitrogen is a Diatomic Element. Its formula is N2 N N N N The Lewis Diagram for a molecule of N2