5th Grade Cells Lesson Plan: Plant & Animal Cells
advertisement

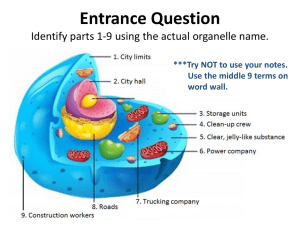
Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Name: Chelcie Tuell Date: October 10, 2014 Lesson Title: Cells Grade Level: 5th Length of Lesson (Minutes): 60 minutes Common Core State Standards or State Standards (Include the number and the entire standard. Highlight relevant portion emphasized in this lesson.) Standard 1: Cells GLE 0507.1.1 Distinguish between the basic structures and functions of plant and animal cells. 90507.1.1 Label drawings of plant and animals cells. 90507.1.2 Compare and contrast the basic structures and functions of plant and animal cells. SPI 0507.1.1 Identify the major parts of plant and animal cells such as, the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, and cytoplasm. SPI 0507.1.2 Compare and contrast basic structures and functions of plant and animal cells. Central Focus of Unit/Learning Segment (The single instructional theme or essential question across the planned learning segment that is aligned with content standards and relevant learning objectives.) All living things are made of cells that perform functions necessary for life. Lesson Objectives (Observable statements that specify what students will be able to do at the conclusion of a lesson. Such objectives should be aligned with relevant content standards and should include verbs that allow for measurement of students’ achievement of the desired outcome.) The learner will: Label drawings of plant and animals cells. Compare and contrast the basic structures and functions of plant and animal cells. Identify the major parts of plant and animal cells such as, the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, and cytoplasm. Language Demands Language Function & Key Learning Task (Identify a language function central to the learning segment and a key learning task that provides students with the opportunity to practice using it. A language function is the purpose for using language in the learning task or what students will use the language to do; it’s typically represented by an action verb in the lesson objective. Examples include, but are not limited to: analyze, argue, categorize, compare/contrast, describe, explain, interpret, justify predict, question, retell, summarize…) Compare and contrast the basic structures and functions of plant and animal cells. Content/Academic Vocabulary (List and define the content vocabulary taught in the lesson.) 1. Cell- basic, functional unit found in all organisms Function- activities required of a specific thing DNA - the storage of information about how the organism will look and function Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Photosynthesis- process by which plants make their own food using energy from the sun. Matter- he substance of which a physical object is composed; especially: the material substance that occupies space, has mass, and makes up the observable universe Magnify- to enlarge in fact or in appearance Microscope- an optical instrument consisting of a lens or a combination of lenses for making enlarged or magnified images of minute objects Building block- a unit of construction or composition Nucleus- the center of the cell, and directs all the cellular activities. Cell membrane- the outside covering of the cell, very similar to our skin! Cytoplasm- the jelly-like substance that fills the inside of the cell. Organelle- small structures that help carry out day-to-day operations of the cell. Chromosome- one of the rod-shaped or threadlike DNA-containing bodies of a cell nucleus that contain all or most of the genes of an organism and can be seen especially during cell division Cell wall- the firm nonliving layer that encloses and supports the cells of most plants, bacteria, fungi, and algae Vacuole- a cavity in bodily tissues or in the cytoplasm of a cell that is usually filled with fluid Plastid- any of various small bodies (as chloroplasts) that occur in the cytoplasm of cells of photosynthetic organisms (as plants) and that often serve as centers for special activities (as storage of starch) Centriole- one of a pair of minute bodies that are located next to the nucleus of a cell, are important in cell division, and consist of a cylinder-shaped central part surrounded by a circle of nine tiny tubes Discourse & Syntax (Describe how students will use one or both of the following. Include language that you will expect students to use verbally and in written form.) Discourse (how students talk and verbally communicate in knowledge construction in ways specific to discipline) o Singing and discussing the Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap o Discussing what each ingredient stands for in the Edible Cell activity. o Q&A and discussion during the Cells Jeopardy Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Syntax (set of written conventions specific to discipline for organizing symbols, words, & phrases together into structures, for example, sentences, formulas, staffs in music, etc.) o Lyrics to the Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap Supports (What opportunities AND supports will you provide for students to use the language function, practice and apply content language/academic vocabulary, and integrate discourse and syntax? Describe how you & students will use these supports. (i.e., graphic organizer, anchor chart, foldable, chart, model, word wall, and strategies such as think, pair, share, etc.). Consider how you will use/differentiate these supports to meet the needs of learners with different levels of language learning.) “Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap” YouTube video and song mp3 Language Function, Academic Vocabulary, and Discourse: Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap Assembling their edible cells, Cells Jeopardy review game. Syntax: Cells, Cells Parts of the Cell Rap song lyrics Materials/Resources (What do you need for this lesson?) Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap song lyrics “Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap” YouTube video and song mp3 Document camera or other form of projection Computer with internet access Cells Jeopardy Paper Towels Sugar Cookies White Icing (Cytoplasm) Plastic knives Pull n’ Peel Twizzlers (Cell Wall) Mini Reese’s Cups (Nucleus) Green Mike and Ikes (Chloroplast) Red Mike and Ikes (Mitochondria) Yellow Mike and Ikes (Animal Vacuole) Circus Peanuts (Plant Vacuole) Glue Interactive Science Notebook Assessment/Evaluation Criteria Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Formative Assessment (A range of assessment procedures used by teachers during the learning process in order to modify teaching and learning activities to improve student achievement occurring throughout the lesson.) The teacher will observe the students while they are: Singing the cells song Completing edible cells Participating in the review game. The teacher is looking to see that all students are listening, paying attention, and staying on the task at hand. Summative Assessment (Summative assessments occur at the end of the lesson to determine what students know and do not know. What evidence will you collect and how will it document individual student learning/mastery of lesson objectives? Include evaluation criteria such as a checklist, rubric, answer key, % earned for mastery, etc. Attach copies of any documents that will be used as evidence.) Students will demonstrate mastery of the lesson if they correctly complete the edible cell activity within 3 tries. Also, students will demonstrate mastery by answering the Jeopardy review game questions correctly. Academic Feedback (Based on your formative and summative assessments, How will you monitor and/or give academic feedback? How will students use the academic feedback? What opportunities are you giving students to use academic feedback?) Formative feedback will be provided throughout the duration of the lesson. Classroom discussion and oral Q&A will take place during the “Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap,” edible cell activity, and Cells Jeopardy review game. Summative feedback Instruction (Include a suggested time for each major activity in the plan below.) Be sure to include both form formative and summative assessment within your instructional plan. This plan should be highly detailed and carefully sequenced with information so that another teacher could implement your plan. The plan explains both student and teacher actions. Set/Hook/Motivator (This brief section at the beginning of the lesson grabs the students’ attention and focuses their thoughts on the learning objectives by utilizing knowledge of students’ academic, social, and cultural characteristics.) 15 minutes As an engagement into the lesson, the teacher will play the “Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap” YouTube song and video. After listening to the song, the lyrics to the Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap song will be passed Higher-Order Thinking Questions Identify high order thinking questions that cannot be answered with a yes or no. The word cell has many different contexts. What are some of the contexts and meanings of the word “cell?” List all the similarities and differences of plants and animals that you can think of. What is the function of a cell Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template out to students by the teacher and discussion over the parts of the cell will ensue. The lyrics are to be glued into students’ interactive science notebooks and serve as a form of notes. (Engagement Theory, Social Learning Theory, Multiple Intelligences, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Marzano’s Questioning Strategies, Zone of Proximal Development, Scaffolding, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills.) Instructional Procedures (This is the body of the lesson plan; it is the way in which information is shared with students and the methods used to help them assume a level of mastery of that material.) 30 minutes There are two main types of cells- animal and plant, and each has different structures that carry out different functions. This edible cells activity accesses the student’s understanding of the differences between plant and animal cells. * Teacher is to check and consult for known student allergies and has the right to change candies if needed. *For the cell membrane, have students spread the icing on the cookie but leave a thin line all the way around to represent the cell membrane! in our body? What is meant by the phrase “a cell is a building block?” Why is a plant cell different from an animal cell? Give specific examples. What is an organelle? What three structures do plants cells have that animal cells do not? Name and describe them. What two structures do animal cells have that plant cells do not? Name and describe them. What in the real-world acts like a . . . nucleus? Golgi apparatus? Etc. How does structure relate to function? Is this true of other things, besides cells? Examples? Instructions: 1.) Setup List what each item represents on the board Prepare a bowl of each organelle 2.) Provide instructions Assign animal or plant to each student Tell students what each item represents (including the cell membrane) They are to pick out their own materials Once they have finished, students are to raise their hands until the teacher can check their work. 4.) Let students select their own materials What is the connection between the organelle’s function and the cell’s function, and what would happen if a cell didn't have this organelle? Which organelle in a cell do you think is the most important? Why? Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Send them to the materials table in groups of 3-4 5.) Check their work If they do not have it right give them two chances to correct it Once all students have finished, discuss the animal and plant cells. What is conducive to each type of cell? When all students have everything correct, they can eat their EDIBLE CELL! (Social Learning Theory, Multiple Intelligences, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Marzano’s Questioning Strategies, Constructivism, Zone of Proximal Development, Scaffolding, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills.) Closure (The closure provides an opportunity for STUDENTS to demonstrate that they’ve met the learning objectives for the lesson by actively engaging in a short task. Examples of tasks include exit tickets, think-pair-share, use of clickers, etc. The closure can include your summative assessment.) 10 minutes Students will be divided into three teams and play a version of the TV shows Jeopardy on cells. This review game is on animal and plant cells and questions include labeling cell parts, functions of cell parts, identifying cells and questions on how cells make systems. (Engagement Theory, Social Learning, Multiple Intelligences, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Marzano’s Questioning Strategies, Zone of Proximal Development, Scaffolding, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills.) Adaptations to Meet Individual Needs (How will you adapt the instruction to meet the needs of individual students?) Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template High-Level Learners: (Scaffolding, Multiple Intelligences, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills, Engagement Theory, Social Learning Theory, Zone of Proximal Development) Encourage the student(s) to assist peers that may be struggling. Encourage the student(s) to find current cell research online. Have the student(s) log related science news articles in his/her interactive notebook and reflect on the articles’ course-related topics. Assign a specific technology to investigate and report (for example, the student could study the Scanning Electron Microscope and present the subject to the class in a minilesson; the student could also study and compare other technologies that are revolutionizing the study of life science and medicine, such as transmission electron microscopes, acoustic microscopes, scanning tunneling microscopes, magnetic resonance and other imaging technologies, computerized axial tomography and ultrasound.) On-Level Learners: See Instruction section above. Struggling Learners: (Scaffolding, Multiple Intelligences, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills, Zone of Proximal Development) Assign specific, more precise tasks in team productions, focusing on individual strengths of the student. Provide a checklist that breaks down individual tasks into component parts. Allow additional time for completing assignments and working on online tutorials. Allow the student to complete exams orally. Request assistance of resource aides English Language Learner: (Scaffolding, Multiple Intelligences, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills, Social Learning Theory, Zone of Proximal Development) Ask the ELL support teacher to help the student develop a glossary of terms in both English and the student’s first language. Enlist the help of bilingual students to help with translating and interpreting concepts. Allow for partner or group work. Allow for visual representations to reduce the language load. Allow for realia for tactile and multidimensional connections between learned material and the object of the lesson. Write vocabulary terms on a chart as they are introduced. Allow the student to write material in the student’s first language for later translation. Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Other individual needs of the students/class you are teaching? The VARK Modalities and Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences are used to enhance student learning. Not all students learn the same way so this lesson is using different learning styles to enhance each student’s experience. Management/Safety Issues (Are there any management and/or safety issues that need to be considered when teaching the lesson? What supports and behavioral management strategies are you providing to your students to facilitate a smooth and structured lesson. Provide classroom-wide strategies as well as those needed for specific students .) During each activity, the teacher will observe the students to make sure that the class is listening, paying attention, and staying on task. If the students are not on task, the teacher will redirect their attention to the objective. If a student or students continue to be off task and distracting to others, the teacher will modify the behavior by having students deduct money from their “personal money” behavior system. (Behaviorism, Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development.) During transitions between activities, the teacher will remind students that they are to be behaving like “model” students. They are not to run, horseplay, or touch each other. Students are to be respectful of one another, as well as of the teacher, and use manners when transitioning. (Behaviorism, Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development.) Students are to be listening and paying attention during the parts of the cell discussion. They are not to talk while the teacher or peer is talking and they are to raise their hand to answer a question or make a comment. This will allow all students to share their thoughts and ideas, and help cut down on other unrelated conversations. (Behaviorism, Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development.) Due to different abilities, some students may finish the edible cell activity before others. It will be important for the teacher to remind students to be respectful, patient, and quiet to the other students who need more time to finish. (Multiple Intelligences, VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills.) The teacher is: To check and consult for known student allergies and has the right to change candies if needed for the edible cell activity. Monitoring discussion and implementation during the edible cells activity. Serving as a judge during the Cells Jeopardy review game Rationale/Theoretical Reasoning Rationale (Describe suggestions and research-based best practices for teaching the specific content in your lesson. This should not be generic information that could be applied to any lesson .) This lesson is meant to help students understand the different organelles of a cell and how important each organelle's functions are for the purpose of the cell. Students will be able to show the different organelles of a cell, their functions, and that importance of the function in the cell. Though it may not be evident right away, understanding the study of cells means that students understand living things, and that we have interactions with various living organisms on a daily basis. Students have the chance to compare two types of cells (plant and animal), which can be very similar in some regards, but also very different in other ways. Understanding why plants cells are composed the way they are ties in what they can physically see in plants. Contrary to this, animal cells are comprised a specific way, one in which students can relate to, Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template because it explains further mechanisms of life they can observe, and learn about in the future. On a global scale, specific cell processes within animal cells, like humans, explain skin color, eye color, hair color, and other visible traits, as well as diseases and conditions like cancer, or color blindness, or cystic fibrosis. These things that are relatable to students, make the importance of understanding what is going on at a microscopic level within the cells, that much more important. Theory (Include a description of the theory and how it specifically applies to your lesson. Theorists such as Piaget, Vygotsky, Dewey, Gardner, etc.) This lesson includes: Engagement Theory Social Learning Multiple Intelligences Bloom’s Taxonomy Marzano’s Questioning Strategies Constructivism Behaviorism Zone of Proximal Development Scaffolding VARK Modalities/ Fleming and Mills Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development Common Misconceptions or Difficulties (What are some common areas in which students are likely to have misconceptions or difficulties pertaining to the specific content that you are teaching?) Students may: Not make the connection between humans and animal cells. Say that different types of cells look different, but will focus on the differences in cell shape, not cell organelle type and frequency. Confuse the organelles (i.e. an animal cell has a cell wall, etc.). Confuse the functions of the organelles. Confuse the real-world analogies. References (List the sources used in this lesson for activities, vocabulary, rationale, theory, misconceptions, etc.) Cells, Cells- Parts of the Cell Rap http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zafJKbMPA8 Cells Jeopardy https://jeopardylabs.com/play/cells-jeopardy-game Cell Structure and Function - Science and Literacy Lesson Set (Common Core) http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Cell-Structure-and-Function-Science-and-LiteracyLesson-Set-Common-Core-910386 Cells Gr. 5-8 http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Cells-Gr-5-8-337796 Merriam-Webster Student Dictionary http://www.wordcentral.com/home.html Differentiating Cells Lesson Plan http://www.usc.edu/org/cosee-west/LACSSP Lesson Plans/files/Grade 7 Lessons/Differentiating Cells Grade 7/Lesson Plan-Differentiating Cells.doc. Interactive Cell Animations http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template Cell to Cell Unit Plan http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/education/k12/project-design/unitplans/cell-to-cell.html?wapkw=cell+to+cell Lesson Plan: Plant and Animal Cell Structure https://secureweb.education.ucsb.edu/webdata/instruction/tepweb/Student_Teaching/LessonPla nning/SST_LP_Examples_09%20copy/Science/LP_SCI_LMCA.PDF Cytology: https://sites.google.com/site/allaboutbeccawren/performance-based-standards-forcolorado/educ-485/ii-unit-topic-and-rationale Reflections/Future Modifications (To what extent did the class learn what you intended them to learn? Describe student progress toward mastery of objectives. What trends can you identify?) (How did students use the language function, vocabulary, syntax, and discourse that you identified in the Language Demands section of this lesson plan?) (What will be your next steps instructionally? What goals do you have for immediate and long-term re-teaching and instruction based on feedback you provided to students with varied needs?) (What did you learn about your students as learners? What have you learned about yourself as a teacher?) (Provide principles from research and/or theory specific to the content of your learning segment and students’ needs to support your statements.) Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template "Cells, Cells" Original Rap by Ms. Quitmeyer- Legal name now changed to: Emily Crapnell Today's the day were gonna learn about the cell If I teach it okay, you'll know it very well So listen up 6th graders-no room left for haterslets talk about the building blocks of life- cells that make us. Chorus: Cells, cells they're made of organelles Try to pull a fast one, the cytoplasm gels The nucleus takes over controllin' everything The party don't stop 'till the membrane blocks the scene Inside the vacuole we can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, cells, they're made of organelles First things first, there's two different typesanimal and plant cells that make up all life. The little things that make up microscopic cells, The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some informationHow do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -ChorusThe cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds the organelles- don't worry, plasm-has 'em! In the middle of the cell you'll find the big brain, The nucleus surrounded by nuclear membrane Don't forget the vacuole filled up with water It's a basic need for life when this rap keeps getting hotter! -ChorusThe mitchondria's something every cell needs, Breaking down the food and releasin' energy. There's a place inside the cell where chemicals are stored, the squiggly golgi bodies, releasin' even more. Yo hangin' in the cell is endoplasmic reticulum, synthesizin' enzymes for respiration, and um... If you still think that this rap is whack, remember ribosomes making proteins gettin' jacked! -ChorusLookin at the plant cell, weird and green two more parts is all it takes you see? Cell wall knows what's up when it comes to keepin' structure Strong with cellulose, this cell can't get much tougher. C-H- L-O- R-O -- Plast, These little green machines are havin' a blast Photosythenisizing- filled with chlorophyll -they hit the cell club, runnin' up a high bill-Chorus- Tennessee Tech University Lesson Plan Template