File
advertisement
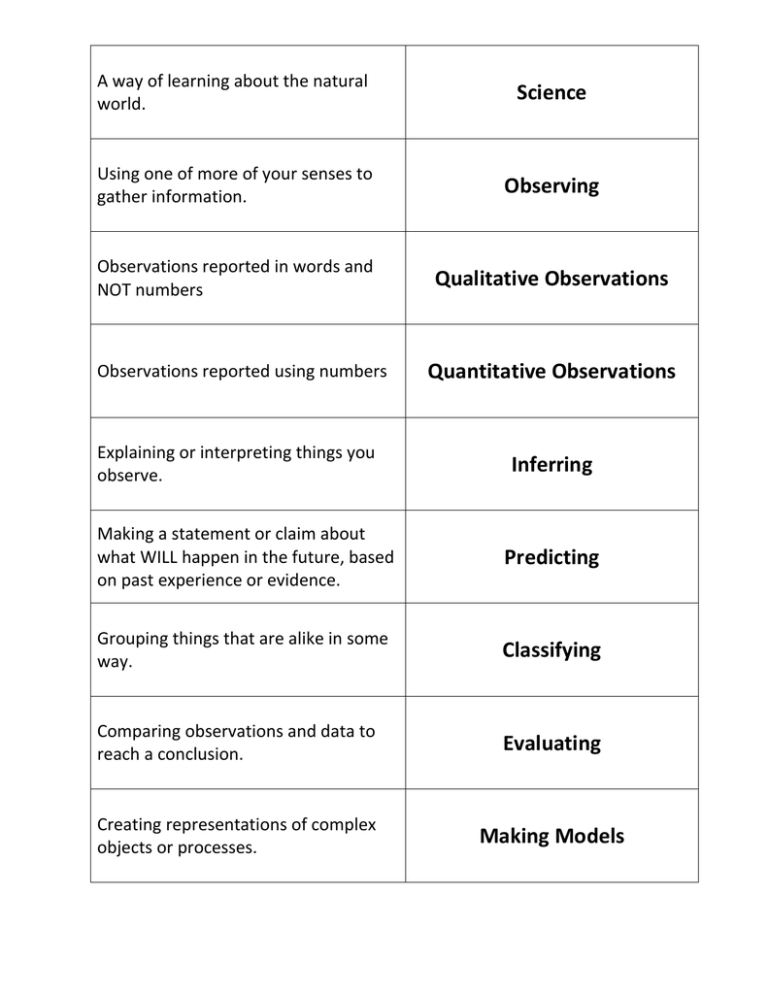
A way of learning about the natural world. Science Using one of more of your senses to gather information. Observing Observations reported in words and NOT numbers Qualitative Observations Observations reported using numbers Explaining or interpreting things you observe. Quantitative Observations Inferring Making a statement or claim about what WILL happen in the future, based on past experience or evidence. Predicting Grouping things that are alike in some way. Classifying Comparing observations and data to reach a conclusion. Evaluating Creating representations of complex objects or processes. Making Models Studying the natural world and proposing explanations based on evidence. (doing experiments to gather data and Scientific Inquiry explain how or why things happen in the world) An experiment in which only ONE variable is manipulated at a time. Controlled Experiment Possible answer to a scientific question, suggested solution to a problem. Hypothesis The “who or what” is being experimented on Test Subjects Test subjects used for comparison and do not get the independent variable Control Group The test subjects that are given the independent variable Experimental Group Any factor that can be changed in an experiment. Variable All the factors kept the same in an experiment to make a fair test Constants the variable changed by the experimenter to test a hypothesis, this given or done to the test subject Independent Variable The response measured from the test subject in an experiment Dependent Variable Facts, figures, and other evidence gathered through quantitative and qualitative observations. Data Testing multiple times within your experiment to get valid results. Repeated Trials Having another scientist conduct your experiment to see if he gets the same results. Replication A state of mind Attitude Wanting to learn new things. Curiosity Reporting observations and results truthfully. Honesty Coming up with inventive ways to solve problems or produce new things. Creativity Capable of accepting new and different ideas. Open-mindedness Having an attitude of doubt to help you distinguish between what is true and what is not. Rules that enable people to know right from wrong. Things that can influence what a scientist expects to find in his experiment; Can be personal, cultural, or experimental. Skepticism Ethics Bias Bias that comes from an individual’s likes and dislikes. Personal Bias Bias that stems from the culture in which one grows up Cultural Bias Making a mistake in the design of an experiment that makes one result more likely. Experimental bias Making decisions and drawing conclusions based on available evidence. Objective reasoning When personal feelings enter a decision or conclusion. Subjective reasoning