Chapter 1 Test Flashcards
advertisement

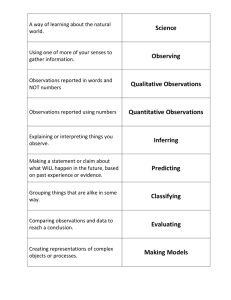
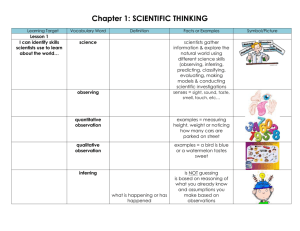
Chapter 1 Test Review science observing way of learning about the natural world using one or more of your senses to gather information quaNtitative observation deals with Numbers, or amounts qualitative observation deals with descriptions that cannot be expressed in numbers inferring when you explain or interpret the things you observe predicting making a statement or a claim about what will happen in the future based on past experience or evidence classifying the grouping together of items that are alike in some way evaluating comparing observations and data to reach a conclusion about them making models creating representations of complex objects or processes ex. math equations skepticism having an attitude of doubt balanced by open-mindedness ethics rules that enable people to know right from wrong personal bias bias that stems from person’s likes and dislikes cultural bias bias that stems from the culture in which a person grows up experimental bias mistake in the design of an experiment that makes a particular result more likely objective making decisions and drawing conclusions based on available evidence subjective making decisions and drawing conclusions where personal feelings have been entered deductive reasoning using general ideas and applying them to a specific observation (decreasing) inductive reasoning using specific observations to make generalizations scientific inquiry diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world hypothesis possible answer to a scientific question variable factor that can change in an experiment manipulated variable factor that is purposely changed to test a hypothesis responding variable factor that may change in response to a manipulated variable controlled experiment experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time data facts, figures, and other evidence gathered through observation scientific theory well-tested explanation for a wide range of observations scientific law statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time ex. “all objects in the universe attract each other” faulty reasoning honesty open-mindedness creativity many trials reasoning that can lead to faulty conclusions attitude used when reporting observations and results attitude that makes accepting new ideas possible attitude that helps scientists come up with inventive ways to solve problems needed before a hypothesis can be accepted as true conclusion summary of what is learned from an experiment graph tool that can help you interpret data 3 ways scientists communicate their results publish articles, talk at meetings, and interpret