Plants: Study Guide Characteristics of Plants Describe the common
advertisement

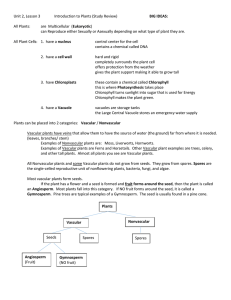
Plants: Study Guide Characteristics of Plants Describe the common characteristics of all plants. Describe the life cycle of all plants. Describe the process of photosynthesis. Describe the significance of chlorophyll in plants. Structure and Function in Plants List the characteristics of nonvascular and vascular plants. Identify three organs found in vascular plants and describe their function. Classification of Plants Explain reproduction in seedless plants. Describe reproduction in seed plants. List the major groups of plants. Plants and Energy Describe photosynthesis. Describe the role of chloroplasts and chlorophyll. Explain how plants get chemical energy from glucose through cellular respiration. Plant Reproduction Describe the phases of plant life cycles. Compare sexual reproduction in seedless and seed plants. Identify the roles of the parts of a flower in reproduction. Plant Responses Identify the types of stimuli that plants respond to. Relate transpiration to a plant’s ability to maintain in internal balance of water. Describe two types of plant tropisms. Describe the triggers and the benefits of winter dormancy for some plants. Characteristics of Plants Plants are multicellular eukaryotes. Most plants are producers. Plant cells have cell walls. Plant life cycles include two stages. During photosynthesis, plants use energy from sunlight to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that plants use to capture energy from sunlight. Structure and Function in Plants Nonvascular plants lack a vascular system and rely on diffusion to transport water and nutrients. Vascular plants have a vascular system to transport water and nutrients. Most vascular plants have roots, stems, and leaves. Roots supply plants with water and minerals from soil. Stems support the plant. Leaves make food for the plant, prevent water loss, and allow for gas exchange. Classification of Plants In plants, fertilization results in a zygote, which develops into and embryo. All nonvascular plants and some vascular plants are seedless. They depend on water to allow their sperm to swim and fertilize eggs. Most vascular plants produce seeds, which consist of the embryo and a protective coating. Seed plants also produce pollen. The major groups of plants are seedless nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Plants and Energy During photosynthesis, plants use the energy in sunlight to make glucose, which stores energy in its chemical bonds. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll, a green pigment. Plants release the energy in the bonds of glucose through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration also produces carbon dioxide and water. Plant Reproduction Plant life cycles include two phases: the sporophyte and the gametophyte. Seedless plants require standing water for sperm to swim to eggs during reproduction. Seed plants produce pollen, which is passed from male to female reproductive structures. In flowering plants, reproduction involves the stamen, pistil, and seeds. Plant Responses Plants respond to internal and external stimuli. During transpiration, water vapor is released into the air through stomata. Stomata can be opened or closed to conserve water. A tropism is a change in the direction of plant growth in response to a stimulus. Hormones control tropisms. Phototropism is a change in plant growth in response to light. Gravitropism is growth in response to gravity. Dormancy is a slowing of plant growth triggered by shorter days and longer nights. This helps plants survive winter.