The Greeks - The Irving Wiki
advertisement
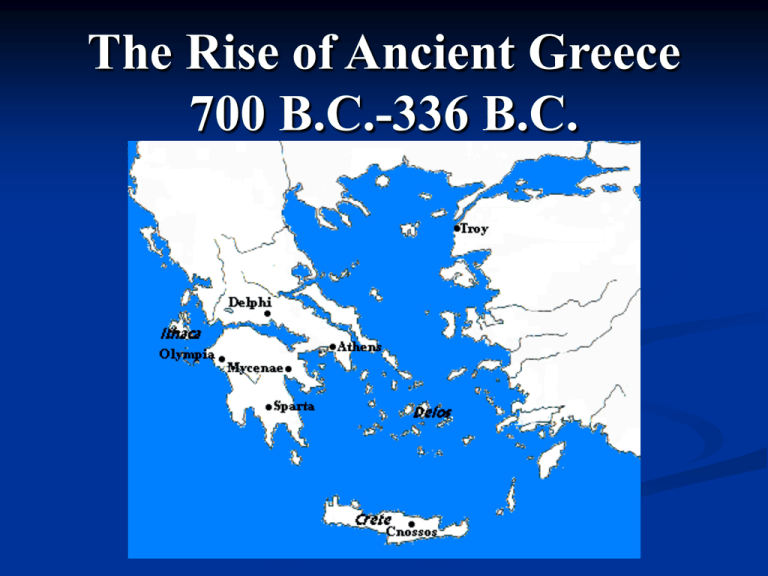
The Rise of Ancient Greece 700 B.C.-336 B.C. Religion Polytheistic: worshiped many gods Humanized deities Zeus: chief god Sky and weather Polis Independent city-state Formed colonies to grow grain for the Polis Population Citizens Vote & own property Expected to serve in the government and military The minority Non-Citizens Slaves, foreign-born, & women The majority Athens and Sparta Sparta Oligarchy: rule by a few wealthy people Women had more freedom and rights than in other city-states. Military Society Invasion over colonization 200,000 slaves, 10,000 Spartans Athens Democracy: rule by all citizens Constitution (507 B.C.): made all free, Athenian-born men citizens Focused on education and public service Culture, art, and philosophy flourished Greek Philosophers What is philosophy? Socrates (470 B.C.-399 B.C.) Absolute truth Socratic Questioning Sentenced to death for corrupting the youth of Athens. “The School of Athens” by Raphael (1510) Plato & Aristotle Plato’s “Allegory of the Cave” Plato Wrote The Republic Community over the individual Rule by philosopher-kings “World of appearance” perceived by the senses. “Real world” understood through logic and reason. Aristotle Valued knowledge from the senses Logic Example: The Syllogism If A then B A Therefore B Wars of Classical Greece (500-338 B.C.) Hoplites (Greek Soldiers) in a Phalanx formation Persian Empire: strongest military power Persian Wars (499B.C.-479 B.C.) Persians sought expansion into Europe. Greek city-states cooperated and forced Persians back to Asia. Who fought in the next war? Peloponnesian War (431 B.C.- 404 B.C.) Athenian Empire vs. Spartan-led alliance Weakens all city states Led to an invasion of Greece Macedonia Conquers Greece 338 B.C. North of Greece in the Balkan Peninsula. Greek Influenced Culture Greek-influenced Greek-style army language. Alex Alexander the Great Ruled the Macedonian empire from 336 B.C. to 323 B.C. Extended empire south to Egypt and east to the Indus river. Political unity of Alexander’s empire ended with his death. Led to the Hellenistic (“to imitate Greeks”) Era Works Cited "Ancient Greece Map." 7 Aug. 2009 <http://www.salem.k12.va.us/staff/kbaer/3rd%20grade/graphics /greece/Ancient%20Greece.gif>. Brown, Robert W. Lecture Notes: Ancient Civilizations. 2006. University of North Carolina at Pembroke. 27 May 2009 <http://www.uncp.edu/home/rwb/lecture_ancient_civ.htm>. Farah, Mounir A., and Andrea B. Karls. World History: The Human Experience. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999. 104-51. Hanson, Hardy. Thucydides' History of the Peloponnesian War . 2007. Brooklyn College. 27 May 2009 <http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/classics/hansen/thucinfo.ht m>. "Mount Olympus." 7 Aug. 2009 <http://static.lonelyplanet.com/worldguide/images/BN3589_8.j pg>. "Ostracon." Positive Liberty. Oct. 2004. Positive Liberty. 7 Aug. 2009 <http://www.positiveliberty.com/2004/10>. "The Security Systems of Athens and Sparta." Discovery Education. 2009. Discovery Education. 7 Aug. 2009 <http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guid AssetId=14EC5B6D-2F40-4F8F-80F00522E5DBD2F0&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=U S>. "This is Sparta." Wikimedia Commons. 25 Apr. 2009. Wikimedia Foundation. 7 Aug. 2009 <http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:TH IS_IS_SPARTA.jpg>. "This Is Sparta Map." My Space. 7 Aug. 2009 <www.myspace.com/tx_curry>. "Zeus." Ancient Greek Art: Zeus. Ed. Aaron Atsma. 2007. Theoi Project Copyright . 7 Aug. 2009 <http://www.theoi.com/Gallery/K1.1.html>. Show what you know. World History Themes Describe an example of each of the World History Themes as they relate to the Greeks. Display one graphically.