6th Grade Life Science Standards: Cell Theory & Organization
advertisement

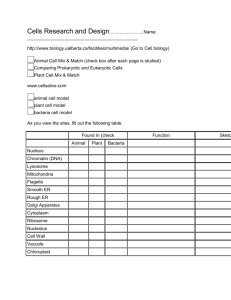
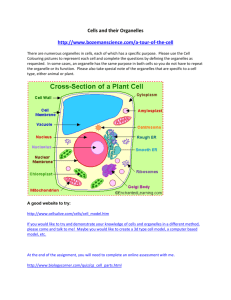
Big Idea: SC.6.L.14 A. All living things share certain characteristics. B. The scientific theory of cells, also called cell theory, is a fundamental organizing principle of life on Earth. C. Life can be organized in a functional and structural hierarchy. D. Life is maintained by various physiological functions essential for growth, reproduction, and homeostasis. Direct link to this page: http://www.cpalms.org/Standards/PublicPreviewIdea555.aspx BASIC INFORMATION Subject: NGSSS: Science Grade Level: 6 Body of Knowledge: Life Science Date Adopted or Revised: 02/08 RELATED Benchmarks (3) SC.6.L.14.1: Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to molecules and cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to organisms. SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.6.L.14.6: Compare and contrast types of infectious agents that may infect the human body, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. RELATED Access Points (14) Independent SC.6.L.14.In.a: Identify how the major structures of plants and organs of animals work as parts of larger systems, such as the heart is part of the circulatory system that pumps blood. SC.6.L.14.In.b: Identify that the cell is the smallest basic unit of life and most living things are composed of many cells. SC.6.L.14.In.c: Identify that cells carry out important functions within an organism, such as using energy from food. SC.6.L.14.In.d: Recognize that plant and animal cells have different parts and each part has a function. SC.6.L.14.In.e: Recognize that bacteria and viruses can infect the human body. Supported SC.6.L.14.Su.d: Identify ways to prevent infection from bacteria and viruses, such as hand washing. SC.6.L.14.Su.c: Recognize that animals, including humans, use energy from food. SC.6.L.14.Su.b: Recognize that there are smaller parts in all living things, too small to be seen without magnification, called cells. SC.6.L.14.Su.a: Identify the major internal organs of animals and external structures of plants and their functions. Participatory SC.6.L.14.Pa.a: Recognize that the human body is made up of various parts. SC.6.L.14.Pa.a: Recognize that the human body is made up of various parts. SC.6.L.14.Pa.b: Identify basic needs of plants and animals. SC.6.L.14.Pa.c: Recognize body parts related to basic needs, such as mouth for eating. SC.6.L.14.Pa.d: Recognize practices that keep the body free from infection, such as hand washing. RELATED RESOURCES (21) Virtual Manipulative, Educational Game , Teaching Idea Human Body Systems Interactive In this online interactive, studens are presented with a body system and a variety of organs. Students drag and drop all the organs that belong in that particular body system to a body who is missing his parts. Lesson Plan, Problem- MIT BLOSSOMS - Discovering Medicines, Using Robots and Solving Task, Video / Computers Audio / Animation Scientists who are working to discover new medicines often use robots to prepare samples of cells, allowing them to test chemicals to identify those that might be used to treat diseases. Students will meet a scientist who works to identify new medicines. She created free software that "looks" at images of cells and determines which images show cells that have responded to the potential medicines. Students will learn about how this technology is currently enabling research to identify new antibiotics to treat tuberculosis. Students will complete hands-on activities that demonstrate how new medicines can be discovered using robots and computer software, starring the student as "the computer." In the process, the students learn about experimental design, including positive and negative controls. Students should have some introductory knowledge about the following topics: (1) biology: students should have a basic understanding of infection and good hygiene, they should know what bacteria and cells are; (2) chemistry: the students should know what a chemical compound (molecule) is. They should have an understanding that medicines, also called “drugs”, are chemical compounds; (3) basic experimental design: students should understand the terms “samples” and “testing”. All hand-outs necessary for this video lesson can be downloaded below. Lesson Plan Check Out The Chicken Wing! Students will examine a chicken wing to discover the different tissues and organs that make it up. They will relate this to the concept that cells make up tissues, which make up organs, which make up organ systems in the organism. Lesson Plan, Problem- Discovering the Characteristics of Living Things Solving Task, This is a lab developed by Orange County Public School middle school Instructional science teachers. It is designed as an inquiry-based lab in which Technique students explore how living and non living things are different. They are given many situations, including demo, lab, outdoor exploration, and follow-up, to learn the characteristics of living things. Lesson Plan A Cell-A-Bration of Life Students will look at cells of plants and animals and identify the organelles. Lesson Plan Communicating About Communicable Disease In this "tried and true" investigation, students use a commercially available product (Glo-germ) and a blacklight to demonstrate how germs are spread. Glitter can be substituted. Students then write a public service announcement, including statistics, about the preventing the spread of a communicable disease. Lesson Plan, Worksheet, Assessment , Presentation /Slideshow , Video / Audio / Animation, Formative Assessment Cell Theory This lesson is designed to teach middle school students about cell theory. The activity involves using microscopes and looking at living, dividing, and non-living material. Lesson Plan, Project , Professional Development How Viruses Spread Teaches three ways viruses can spread: cough, sneeze, and touch. Educational Game , Video / Audio / Animation, Teaching Idea The Cell and its Organelles "The Cell and its Organelles educational game is based on the 1974 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, which was awarded for discoveries concerning the structure and organization of the vital components of a cell. The game revolves around the ultracentrifuge -a piece of laboratory equipment that separates organelles in a cell by virtue of their size, shape and density. By sheer bad fortune, Professor Megacell happens to fall into an ultracentifuge, which results in some of his organelles being shot out and he himself ending up hanging from a rotating fan on the ceiling. Your mission is to return his organelles to their correct position by firing different organelles at him using a slingshot. Each time you must read the hints to figure out the correct organelle to shoot. For example, if you see the hint "He looks like he has lost all his energy", you should shoot the mitochondria (the power plant of the cell that provides the energy to drive chemical reactions in the cell)." From: "The Cell and its Organelles - About". Nobelprize.org. 30 Jul 2012 http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/cell/about.html Project , Presentation Human Body Quest /Slideshow , Teaching This quest give students the ability to work with a cooperative group Idea and teach the class on specific body systems, while learning the content themselves. Teachers can choose what system each group presents and they can present them in front of the class using a PowerPoint presentation and the students listening can be writing notes. It can also be used as a culminating activity as well. Unit / Lesson Sequence, Educational Game Disease: Cause and Effect The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways that infectious diseases can be prevented. Lesson Plan Are We Like Robots? This lesson explores the similarities between how a human being moves/walks and how a robot moves. This allows students to see the human body as a system, i.e., from the perspective of an engineer. It shows how movement results from (i) decision making, i.e., deciding to walk and move, and (ii) implementing the decision by conveying the decision to the muscle (human) or motor (robot). Lesson Plan, Worksheet, Assessment , Presentation /Slideshow , Video / Audio / Animation, Image / Photograph, Formative Assessment Immunity Lesson Plan This lesson plan has power point to support it. The lesson requires students to complete a project comparing bacteria, fungus, and viruses. Lesson Plan, Homeostasis and Human Body Systems Educational Game , Formative Assessment ***All activities from this lesson, with the exception of free alternative activities, are adapted from Florida Science Fusion Grade 6 Teacher’s Manual and Lab Manual ©Holt McDougal*** This lesson addresses the structure and function of human body systems with emphasis on how organ systems collaborate to maintain homeostasis for an entire organism. Lesson Plan Agents of Infection This is a collaborative lesson design by Lori Kern and Dawn Barone. This lesson focuses on infectious agents (fungus, bacteria, virus and parasites). Students will be able experience a hands-on activity to reinforce the concepts addressed in this benchmark. Lesson Plan Cells 1: Make a Model Cell This lesson is the first of two-part series on cells. In Cells 1: Make a Model Cell, students will compare a plant and animal cell, and then make a model of a cell. They will select items to represent various cell structures and justify their choices by describing how the items they have chosen represent the actual parts of a cell. Prior to this lesson, students should have at least been introduced to cells, including the basic differences between plant and animal cells. Unit / Lesson Sequence Cell Structure and Function Cross Content Lesson Multi-day lesson plan from OCPS focusing on the structure and function of cells that incorporates science, reading and fine arts standards. Lesson Plan, Worksheet, ProblemSolving Task, Project , Video / Audio / Animation, Data Set, Student Center Activity Uncle Henry's Dilemma Uncle Henry's Dilemma is a problem solving lesson to determine the global location for the reading of Uncle Henry's will. The students will interpret data sets which include temperature, rainfall, air pollution, travel cost, flight times and health issues to rank five global locations for Uncle Henry's relatives to travel to for the reading of his will. This is an engaging, fun-filled MEA lesson with twists and turns throughout. Students will learn how this procedure of selecting locations can be applied to everyday decisions by the government, a business, a family, or individuals. Educational Game Cell Crossword Puzzle This cell crossword puzzle uses vocabulary from CELLS alive! If you have trouble, use the "Search this Site" engine in the lefthand menu. Lesson Plan Cell City/Anatomy of a Cell This lesson uses an analogy that has students compare the cell to a city. Problem-Solving Task, Travel Brochure for a Cell Teaching Idea Students produce a travel brochure that describes a plant or animal cell as if it were a large exhibit/amusement park. They must accurately describe/draw/explain organelles (attractions) and their functions. Big Idea: SC.6.L.15 A. The scientific theory of evolution is the organizing principle of life science. B. The scientific theory of evolution is supported by multiple forms of evidence. C. Natural Selection is a primary mechanism leading to change over time in organisms. Direct link to this page: http://www.cpalms.org/Standards/PublicPreviewIdea556.aspx BASIC INFORMATION Subject: NGSSS: Science Grade Level: 6 Body of Knowledge: Life Science Date Adopted or Revised: 02/08 RELATED Access Points (3) Independent SC.6.L.15.In.a: Classify animals into major groups, such as insects, fish, reptiles, mammals, and birds. Supported SC.6.L.15.Su.a: Sort common animals by their physical characteristics. Participatory SC.6.L.15.Pa.a: Match animals based on a given shared characteristic. RELATED RESOURCES (11) Problem-Solving Task, Creepy Critters Teaching Idea The lead scientist from a newly discovered planet similar to Earth sends you illustrations of the organisms and asks you to help develop a classification system. Your role is to study the illustrations and come up with a possible classification scheme based on the information provided about each organism. You'll be asked to explain to the scientific team how and why you organized the creatures this way. Lesson Plan Let’s Sort It Out Students will be introduced to the classification system using domains and kingdoms. They will sort cards with pictures of organisms on them into different groups and then revise if necessary after learning about the characteristics of the kingdoms. Teaching Idea Primate Dichotomous Key-SeaWord Classrooom Activity Students will research and evaluate ten primate species. The student will construct a dichotomous key to classify ten primate species into distinct categories. Lesson Plan, Unit / Lesson Sequence Introduction to Classification (1 of 3) This activity is geared for sixth graders as they are first introduced to the relevance of taxonomy and the Linnaean system of classification, along with the concept of Domains. It is part 1 of 3 lessons. Lesson Plan, Problem- Introduction to Classification (2 of 3) Solving Task This lesson is part 2 of 3 as an introduction to the Linnaean System of classification and the concept of Domains. Educational Game , Teaching Idea Animal Classification Game Learn about classes of animals and test your ability to identify animals as mammals, birds, reptiles and more in this interactive activity adapted from Sheppard Software. Lesson Plan Fun with Taxonomy and Dichotomous Keys Students will be introduced to the taxonomy of living things created by Linnaeus. They will learn how to use binomial nomenclature to create and solve dichotomous keys. Lesson Study Exploring Diversity and Evolution grades 6-8 This toolkit is designed to assist lesson study teams as they work to develop a unit on natural selection that conforms to the NGSSS for science and the CSSS for mathematics and English language arts. Problem-Solving Task, Teaching Idea Butterfly Sort This is a teaching idea where students develop a classification scheme for butterflies and moths based on observable traits. Through the development and discussion of classification schemes, students begin to make inferences about evolutionary relationships. This activity was used in the BIOSCOPES Diversity and Ecology Institute. Virtual Manipulative, Teaching Idea Mesquite - Phylogenetic Trees Students use software to create evolutionary trees by comparing and contrasting physical traits. This activity demonstrates the complexity of creating evolutionary trees when multiple traits are being analyzed. The use of the software simplifies the analysis without compromising the learning objectives. Virtual Manipulative, Teaching Idea Climbing The Tree of Life: Cladograms This is an activity where students create cladograms given a beginning point (species) and end point (species) using the Tree of Life website.