Document
advertisement

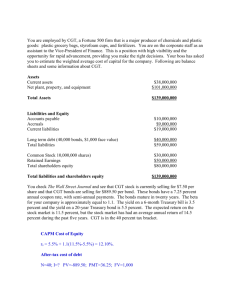
FINANCE FOR EXECUTIVES Managing for Value Creation Gabriel Hawawini Claude Viallet ESTIMATING THE COST OF CAPITAL 1 EXHIBIT 10.1: Risk and Return for the Sun Cream and Umbrella Investments. 2 EXHIBIT 10.2: SMC Stock Monthly Returns versus the S&P 500 Monthly Returns. 3 EXHIBIT 10.3: Beta Coefficients of a Sample of U.S. Stocks. Southwest Air Texas Instrument Compaq Computer Whirlpool Corp. AMR Corp. Motorola, Inc. Maytag Corp. BancOne Corp. Abbott Laboratories Air Gas Baxter International General Electric Viacom, Inc. Turner Broadcasting Ford Motor Company General Motors 1.60 1.60 1.40 1.40 1.35 1.30 1.30 1.25 1.20 1.20 1.15 1.15 1.10 1.10 1.05 1.05 Source: Value Line Investment Survey, 1996. 4 Anheuser-Busch McDonald’s Walgreen Co. Coca-Cola Pepsi-Cola AT&T McGraw-Hill GTE Bell Atlantic Quaker Oats Ameritech Continental Edison Amoco Corp. Energy Corp. Texas Utilities American Water Works 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.95 0.95 0.90 0.85 0.80 0.80 0.80 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.70 0.65 0.65 EXHIBIT 10.4: Average Annual Rate of Return on Common Stocks, Corporate Bonds, U.S. Government Bonds, and U.S. Treasury Bills, 1926 to 1995. TYPE OF INVESTMENT AVERAGE ANNUAL RETURN Common stocks (S&P 500) AVERAGE RISK PREMIUM DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RETURN OF INVESTMENT AND RETURN OF TREASURY GOVERNMENT BILLS BONDS 12.2% 8.5% 7.0% Corporate bonds 5.7% 2.0% 0.5% Government bonds 5.2% 1.5% — Treasury bills 3.7% — — Source: Ibbotson Associates, Inc., 1996 Yearbook. 5 EXHIBIT 10.5: The Capital Asset Pricing Model. 6 EXHIBIT 10.6a: Estimation of the Cost of Equity Based on the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) for a Sample of Companies Listed on the London Stock Exchange (1996). GOVERNMENT BOND RATE MARKET RISK PREMIUM COMPANY INDUSTRY REUTERS Agency 6% 7% PEEK Electronics 6% 7% BRITISH AEROSPACE Aerospace 6% 7% INCHCAPE Trading 6% 7% GLAXO HOLDINGS Health 6% 7% LUCAS INDUSTRIES Motor 6% 7% MARKS & SPENCER Stores 6% 7% BRITISH TELECOM Phone network 6% 7% SAVOY HOTELS Hotels 6% 7% 7 EXHIBIT 10.6b: Estimation of the Cost of Equity Based on the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) for a Sample of Companies Listed on the London Stock Exchange (1996). COMPANY BETA COEFFICIENT ESTIMATED COST OF EQUITY WITH THE CAPM REUTERS 1.73 6% + (7%)(1.73) = 18.1% PEEK 1.52 6% + (7%)(1.52) = 16.6% BRITISH AEROSPACE 1.34 6% + (7%)(1.34) = 15.4% INCHCAPE 1.30 6% + (7%)(1.30) = 15.1% GLAXO HOLDINGS 1.27 6% + (7%)(1.27) = 14.9% LUCAS INDUSTRIES 1.21 6% + (7%)(1.21) = 14.5% MARKS & SPENCER 0.88 6% + (7%)(0.88) = 12.2% BRITISH TELECOM 0.73 6% + (7%)(0.73) = 11.1% SAVOY HOTELS 0.40 6% + (7%)(0.40) = 8.8% 8 EXHIBIT 10.7: SMC’s Managerial Balance Sheet. INVESTED CAPITAL OR NET ASSETS CAPITAL EMPLOYED Cash Long-term debt $10,000,000 1 $90,000,000 90,000 bonds at par value $1,000 Working capital $50,000,000 requirement Owners’ equity $90,000,000 2,500,000 shares $25,000,000 at par value $10 Net fixed assets $120,000,000 Total $180,000,000 1 SMC 9 has no short-term debt. Retained earnings Total $65,000,000 $180,000,000 EXHIBIT 10.8a: The Estimation of a Firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), Including an Application to Sunlight Manufacturing Company (SMC). STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 1: Estimate the firm’s relative proportions of debt (D) and equity (E) financing: D E+D E and E+D HOW TO • Use the firm’s market values of debt and equity. • The market value of debt is computed from data on outstanding bonds using the bond valuation formula (equation 10.1). • The market value of equity is the share price times the number of shares outstanding. • If the firm’s securities are not publicly traded use the market value rations of proxy firms. 10 EXHIBIT 10.8b: The Estimation of a Firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), Including an Application to Sunlight Manufacturing Company (SMC). STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 2: Estimate the firm’s aftertax cost of debt: k D(1 – Tc). HOW TO • If the firm has outstanding bonds that are publicly traded, use equation 10.1 to estimate k D. • Otherwise, use the credit spread equation (equation 10.2) or ask the bank. • Use the marginal corporate tax rate for Tc . 11 EXHIBIT 10.8c: The Estimation of a Firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), Including an Application to Sunlight Manufacturing Company (SMC). STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 3: Estimate the firm’s cost of equity: KE. HOW TO • Use the capital asset pricing model (equation 10.11). • The risk-free rate is the rate on government bonds. • The market risk premium is 7% (historical average) . Step 4: 12 Calculate the firm’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). • Use the beta of the firm’s stock. If the firm’s shares are not publicly traded, estimate beta from proxies. D E • WACC = k D(1 – Tc) + KE E+D E+D EXHIBIT 10.9a: Proxies for Buddy’s Restaurants. EQUITY BETA1 DEBT-TO-EQUITY RATIO1,2 D E At market value ASSET BETA3 McDonalds 1.01 0.17 0.92 Wendy’s International 0.92 0.23 0.81 CKE Restaurants 1.15 0.22 1.02 Average values 1.03 0.21 0.92 1 Data from Alcar, June 1996. = debt; E = equity. 3 Calculated according to equation 10.7 with a corporate tax rate of 40 percent. 2D 13 EXHIBIT 10.9b: Proxies for Buddy’s Restaurants. DEBT RATIO1,2 D E+D At market value At book value EQUITY RATIO1,2 E E+D At market value At book value McDonalds 0.14 0.41 0.86 0.59 Wendy’s International 0.19 0.36 0.81 0.64 CKE Restaurants 0.18 0.47 0.82 0.53 Average values 0.17 0.41 0.83 0.59 1 Data from Alcar, June 1996. = debt; E = equity. 3 Calculated according to equation 10.7 with a corporate tax rate of 40 percent. 2D 14 EXHIBIT 10.10a: The Estimation of a Project’s Cost of Capital when the Project Risk Is Different from the Risk of the Firm, Including an Application to the Buddy’s Restaurants Project. STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 1: Estimate the project’s relative proportions of debt (D) and equity (E) financing: D E+D E and E+D using proxy firms. HOW TO • Use the proxies’ market values of debt and equity. • The market value of debt is computed from data on outstanding bonds using the bond valuation formula (equation 10.1). • The market value of equity is the share price times the number of shares outstanding. • Take the mean of the proxies’ ratios. 15 EXHIBIT 10.10b: The Estimation of a Project’s Cost of Capital when the Project Risk Is Different from the Risk of the Firm, Including an Application to the Buddy’s Restaurants Project. STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 2: Estimate the project’s aftertax cost of debt: kD(1 – Tc). HOW TO • If the proxies have outstanding bonds that are publicly traded, use equation 10.1 to estimate their cost of debt kD. • Otherwise, use the credit spread equation (equation 10.2) or ask the bank. • Take the mean of the proxies’ cost of debt. • Use the marginal corporate tax rate for Tc . 16 EXHIBIT 10.10c: The Estimation of a Project’s Cost of Capital when the Project Risk Is Different from the Risk of the Firm, Including an Application to the Buddy’s Restaurants Project. STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 3: HOW TO Estimate the project’s • Use the capital asset pricing model (equation 10.11). cost of equity: k E. • The risk-free rate is the rate on government bonds. • The market risk premium is 7% (historical average). • Un-lever the proxies’ equity betas using equation 10.7 to get their unlevered asset betas. • Re-lever the mean of the proxies’ asset betas at the project’s target debt-to-equity ratio using equation 10.6 to get the project’s equity beta. • Apply the CAPM to the project’s equity beta to get the project’s cost of equity kE. 17 EXHIBIT 10.10d: The Estimation of a Project’s Cost of Capital when the Project Risk Is Different from the Risk of the Firm, Including an Application to the Buddy’s Restaurants Project. STEPS TO FOLLOW Step 4: 18 Calculate the project’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). HOW TO • WACC = k D(1 – Tc) E D + KE E+D E+D EXHIBIT 10.11: Company-Wide Cost of Capital and Projects’ Expected Rates of Return. 19