Philosophers and Documents
advertisement

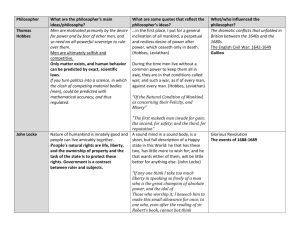
Philosophers and Documents Influences on American Government Terms to Know Philosophers - people who seek wisdom and/or knowledge. Democracy – a system of government in which power is shared by all citizens. Direct Democracy – a form of government in which laws are made directly by the citizens. Republic – citizens who elect people to represent them in government and make laws. Power is controlled by the people. (Indirect Democracy). Thomas Hobbes Thomas Hobbes 1588 - 1679 English Philosopher Wrote his political thoughts in a book called Leviathan in 1651. Thomas Hobbes *Belief: People lived in a state of nature (anarchy). Life was dangerous and violent until people chose a leader to rule them. People must agree to a social contract or convent. Under this people give a monarch absolute power, only keeping certain rights that protect their lives. John Locke John Locke 16321704 An English writer of philosophy and political thought. John Locke *Belief: People have certain rights that the state should protect. People give up certain rights but kept others. The rights they kept included: Life, Liberty (political equality/freedom), and Property. He felt rulers should protect these rights. John Locke cont… *Belief: in freedom of Press, Education Reform, and Religious Tolerance. *People had the right to overthrow a ruler who violated the contract. Social Contract between rulers and those ruled. “Consent of the governed.” Jean-Jacques Rousseau Jean-Jacques Rousseau 1712-1778 French author who wrote The Social Contract, published in 1762. Jean-Jacques Rousseau *Belief: People are born good but that environment, education, and laws corrupt them. Fair laws and wise governments are based on Popular Sovereignty - created, ruled, and subjected by the people. François-Marie Arouet aka Voltaire François-Marie Arouet aka Voltaire 1694-1778 A French writer Francois-Marie Arouet aka Voltaire *Belief: Freedom of speech and religion. Quoted as saying, “I disapprove of what you say, but will defend to the death your right to say it.” Baron de Montesquieu Baron de Montesquieu 16891755 In 1748 he published The Spirit of Laws tried to describe the perfect government. Baron de Montesquieu . *Belief: He felt that the British government was close to ideal. (perfection) Baron de Montesquieu cont… The power should be shared among three branches: Legislative – makes and passes the laws. Executive - enforces the laws. Judicial - interprets and applies the laws. *Checks and Balances* - Influenced the framers of the U.S. Constitution. Early Documents Magna Carta Mayflower Compact English Bill of Rights The Magna Carta 1215 The First System of Checks and Balances. The most important document in British history. Signed by King John on June 15, 1215. Created so that Kings wouldn’t abuse their power, and would be subject to the laws of the land just as common people were. Also, establishes the rights of the people; such as Trial by Jury. It is the cornerstone of constitutional government. Magna Carta • • • • Big Ideas: Limited Government Rights Rule of Law Due Process The Mayflower Compact 1620 The First Document on Self-Governing. Created by 41 Men on the Mayflower sailing to Plymouth, Massachusetts. They fled England in search of greater Religious Tolerance. It was a social contract that bound them to obey the authority of whatever government was established on land. Mayflower Compact Big Ideas: • Self Government • Rule of Law English Bill of Rights 1689 Limited Royal Power of the Parliament. Outlined the civil and political rights and liberties (freedoms) of the people. Signed into law by King William III in 1689. Transformed the country of England from one controlled by the Monarchy to one of free citizens with unalienable rights. English Bill of Rights • • • • Big Ideas: Limited Government Rights Due Process Rule of Law