Philosophers and Writers of the Greek Golden Age
advertisement

Philosophers and Writers of
the Greek Golden Age
CH 6 Section 2
Section 1 review
• What did the Greeks use to make their
statues more lifelike?
• The Greeks used more ______ _______
than the Egyptians in their art
The Rise of Philosophy
• One of the Greeks greatest achievements was
the development of Philosophy
• Philosophy- is the study of the basic questions
of reality and human existence
• {Philosopher means “Lover of wisdom”}
• The Greeks used philosophy to better
understand the world around them
• {Early philosophers were called Cosmologists
because they studied the nature of the universe}
Philosophy continued…
• According to Greek tradition the first philosopher
was Thales of Miletus
• He and others like him wanted to understand the
universe
• They set up formal rules of logic for
philosophical arguments
• Democritus developed atomic theory by using
logic and mathematics
• Atomic theory stated that everything is made up
of tiny bits of matter called atoms
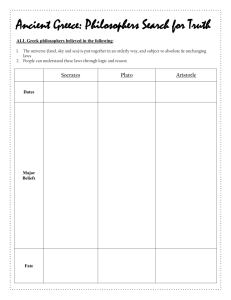
Socrates
Bill and Ted’s Socrates
Socrates
• One of the most important thinkers of the new
era
• He taught that education was the key to
personal growth
• {Socrates insisted that students think for
themselves}
• He asked questions that forced students to test
their own values and ideas
• Socrates way of teaching through questions
became known as the Socratic method
• His questions often made public officials look
foolish
• He made many enemies who accused him of
corrupting the youth
• He criticized democracy, saying unskilled people
should not hold positions of power
• He was brought to trial by his enemies and did
little to defend himself
• He was found guilty and executed
• He was forced to drink a poison called hemlock
Plato
• Later generations learned of Socrates writings
through Plato
• He was a young aristocrat and one of Socrates
students
• He founded the Academy a special school in
Athens for teaching philosophy
• He wrote dialogues or imaginary conversations
between several people
• These dealt with government, education, justice
and religion
• Most featured Socrates teaching and asking
questions
Plato continued
• {Plato believed that the soul and body were
separate but would reunite through
reincarnation}
• {Plato also wanted a govt. ruled by an
aristocracy or an intellectual upper class}
• The ideal rulers were philosophers not just the
wealthy
Aristotle
• One of Plato's students at the academy
• Aristotle founded his own school in Athens in
335 BC
• He believed that every field of study needed to
be studied logically
• He collected as many facts as possible and
organized them into systems
• {Aristotle believed that logical study led to truth}
• He investigated every field of study known to his
time
• He analyzed Greek drama to understand what
made a good or bad play
Math Medicine and Science
• The Greeks covered all fields of knowledge
including math and science
• {Pythagoras was a philosopher that believed
the world could be explained through math}
• He was best remembered for his theorem for the
right triangle
Natural Science
• Greek philosophers did not specialize in any one
field of study which kept them from fully
developing scientific knowledge until much later
• Aristotle laid the foundations of anatomy, botany,
and zoology
• The Greeks, in contrast to the Egyptians,
believed the natural world could be explained in
terms of natural law
• They also held that rules that govern our
universe could be identified, observed and
defined
Greek Science
Hippocrates
• Considered to be the founder of medical science
• It is believed that Hippocrates wrote between 60
and 70 medical studies
• He helped to collect medical knowledge in a
useable form
• {His work sums up Greek science because it
bases treatment on reason not magic}
• He thought that disease comes from natural
causes not a punishment from the gods
• He taught that rest, fresh air, and proper diet
made the best cures
Herodotus
• The Greeks became the first people to take the
writing of history seriously
• Herodotus the first historian of the western world
• He traveled to Babylonia, Phoenicia, and Egypt
and included his views of the countries and their
people in his histories
• He was careful to note if he had seen something
himself or someone had told him about it but did
exaggerate at times
• He is often called the father of history
Greek Theater
Drama
• These are plays containing action or conflict of
emotion
• The Greeks wrote plays in poetic form
• Male actors played the women's roles
• A group of singers, called the chorus, described
the scene and commented on the action
• Their theaters were carved into hillsides
• The flat bottom of the Greek theater is known as
the Orchestra
• Plays were often performed in connection with
religious festivals they would have competitions
between playwrights
What theater looks like with people
Tragedies
• This is when the main character struggles
against fate or events
• Main characters are usually punished for
displaying Hubris
• {Hubris is the sin of Pride}
• Oedipus Rex, written by Sophocles, was called
the perfect example of tragedy by Aristotle
• Euripides was a realist playwright
• He questioned many of the old ideas and beliefs
and in his plays showed the pain and misery of
war
Comedies
• These made fun of ideas and people
• Comedies included both tragic and humorous
figures
• Aristophanes was known for his wit and would
poke fun at Socrates for his theories about
education
• Un like tragedies, the main characters usually
solved their problem
Section Review
• What is another name for a lover of
wisdom?
• What were lovers of wisdom originally
known as?
• Who was Socrates student?
• Who believed that logical study led to
truth?
• Another name for the sin of pride
Speaking of Comedies