Asset Focused, Person Centered Model
advertisement

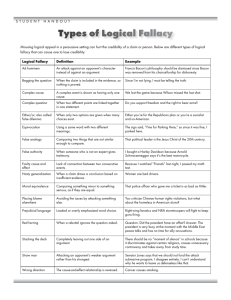
Asset Focused, Person Centered Model Strategies for a Rural Homeless Model Presenter: Brent L. Anderson Objectives of this class • To distinguish Asset Focused/Development Focused models from other models of care. • To learn how this basic philosophy has been used in various parts of society with success. Positive Youth Development, Asset Building Model, Clubhouse, Housing First, and others. • To explore how rural homeless programs may benefit from development focused strategies. Strategy strategy strategy strategy strategy strategy strategy “It is dangerous to know only one thing. This creates short sightedness. The principle of strategy is having one thing, to know ten thousand things.” ~Miyamoto Musashi strat·e·gy [strat-i-jee] Origin: 1680–90; < Greek stratēgía generalship, equivalent to stratēg ( ós ) military commander, general ( strat ( ós ) army + -ēgos noun derivative of ágein to lead) noun, plural strat·e·gies. 1. Also, strategics. the science or art of combining and employing the means of war in planning and directing large military movements and operations. 2. use or an instance of using this science or art. 3. skillful use of a stratagem: The salesperson's strategy was to seem always to agree with the customer. 4. a plan, method, or series of maneuvers or stratagems for obtaining a specific goal or result: a strategy for getting ahead in the world. Miyamoto Musashi (宮本 武蔵), c. 1584 – June 13, 1645 Miyamoto Musashi was a Japanese swordsman and rōnin. Musashi, as he was often simply known, became renowned through stories of his excellent swordsmanship in numerous duels, even from a very young age. He was the founder of the Hyōhō Niten Ichi-ryū (the school of the strategy) and the Niten-ryū (two sword fighting) style of swordsmanship and the author of The Book of Five Rings a book on strategy, tactics, and philosophy that is still studied today by military strategists, military schools, and business leaders. Strategy #1 Know the Person • Lets get to know you a little better. • Please fill out the provided form. [discussion] Development vs. Prevalent Models Development Model Medical Model Asset Focused, Person Centered, Rehabilitation Risk focused, Intervention, Recovery/cure • Power and control is given, shared, and/or negotiated. • Structures are flexible. Choices can be negotiated or created. • Staff are guides, mentors, advisers, consultants, cheerleaders. Power is shared equally or given away to the participant. Solutions are created with the participants. • Power and control is in the hands of the program/organization. • Structures are fairly rigid. If choices are give it is from a menu of options. • Staff are the experts, professionals, rule enforcers, coaches, teachers. Power lies with the expert. Cures, solutions and fixes are doled out. Development vs. Prevalent Models Development Model Medical Model Asset Focused, Person Centered, Rehabilitation Risk focused, Intervention, Recovery/cure Continued • Expectations are high, tolerances are low. Participants experience natural consequences for their chosen behaviors both positive and negative. “What can we help you achieve, what are your goals?” (power lies with the individual participant) Continued • Conformance and performance. Participants follow the prescribed program and rules and receive rewards. “You do [this] and we will give you [this].” (power lies with the professionals) Housing First • Housing First is an approach to ending homelessness that centers on providing people experiencing homelessness with housing as quickly as possible – and then providing services as needed. This approach has the benefit of being consistent with what most people experiencing homelessness want and seek help to achieve. Housing First programs share critical elements: • A focus on helping individuals and families access and sustain permanent rental housing as quickly as possible without time limits; • A variety of services delivered to promote housing stability and individual well-being on an as-needed basis; and • A standard lease agreement to housing – as opposed to mandated therapy or services compliance. TIME Video Why 'Housing First' Saves Homeless Lives and Public Money http://www.time.com/time/video/player/0,32068,1011477093001_2085601,00.html • Seemed counter intuitive on the surface. [why?] • Costs less than leaving people on the streets Street: $100,000+ per year vs. Housing First: $26,800 per year. [results] • Notice the comments made about conforming with the rules in the “services as usual” approach. [discuss] Strategy #2 Think Broadly –Openly - Logically Caution: Beware of the Either/Or Fallacy Either/Or Fallacy (also called "the Black-and-White Fallacy," "Excluded Middle," "False Dilemma," or "False Dichotomy"): This fallacy occurs when a writer builds an argument upon the assumption that there are only two choices or possible outcomes when actually there are several. Outcomes are seldom so simple. This fallacy most frequently appears in connection to sweeping generalizations: “Either we must ban X or the American way of life will collapse.” – Cont. to next page Strategy #2 Think Broadly –Openly - Logically Caution: Beware of the Either/Or Fallacy – Continued "We go to war with Canada, or else Canada will eventually grow in population and overwhelm the United States." "Either you drink Burpsy Cola, or you will have no friends and no social life. " Either you must avoid either/or fallacies, or everyone will think you are foolish.” People with Mental Illness • About five percent of American adults have a severe mental illness, according to the Center for Mental Health Services, part of the U.S. Dept. of HHS • Approximately one-third of the nation's homeless have a severe mental illness. • The National Alliance for Mental Illness says that the rate of success for treating a first episode of bipolar disorder is 80 percent; for major depression, 70 percent; and for schizophrenia, 60 percent. • Slightly more than one-fourth of the 1,000,000 hospital admissions in the United States in 1998 were for psychiatric care, according to the CMHS. Clubhouse Model • • • • • Better transitional employment results: longer on-the-job tenure is found to be highly correlated with Clubhouse attendance. Cost effectiveness: the cost of ICCD Clubhouses is estimated to be one-third of the cost of the IPS model; about one-half the annual costs of Community Mental Health Centers; and substantially less than the ACT model. Reduced hospital stays: membership in an ICCD Clubhouse has resulted in a significant decrease in the number of hospitalizations. Reduced incarcerations: criminal justice system involvement is substantially diminished during and after Clubhouse psychosocial program membership. Improved well-being: Compared with individuals receiving services as usual, ICCD Clubhouse members have been shown to be significantly more likely to report that they had close friendships and someone they could rely on when they needed help. A recent study has suggested that service systems should prioritize services that offer ongoing social supports like ICCD Clubhouses because they enhance mental and physical health by reducing disconnectedness. Video Clip Dead Poets Society Conformity [Discussion] Positive Youth Development • Engagement - People need opportunities to engage in meaningful activities, have a voice, take responsibility for their actions and actively participate in civic discourse. When people are not engaged in meaningful activities or in environments that honor their voice, they are at risk for feeling their existence has no meaning for others or themselves. Positive Youth Development • Connectedness - People need to belong. They need to be connected to a family and a community to thrive. A growing body of brain research indicates that humans are "hardwired to connect". Social connectedness enables us to experience an increased ability to formulate a greater sense of self identity and fosters security, hope, self-worth and an overall sense of purpose. Positive Youth Development • Preparedness - People need to develop competencies and skills. Competencies range from cognitive, social emotional, vocational and cultural. With these competencies people are in a better position to successfully overcome adversity, as well as to accomplish personal goals. Positive Youth Development • Safety & Basic Needs - People need their needs met (housing, food, medical, social, etc.) and to feel safe before they can set goals for future growth. Positive Youth Development • Voice - People need to be included as active participants in any initiative that affects them or their lives. They have to be equal partners in the process. Video Clip Dangerous Minds Questions • How might you uses some Development Strategies in your community?