Topic 11 Animal Physiology
advertisement
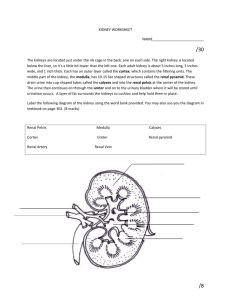
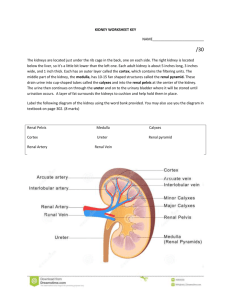
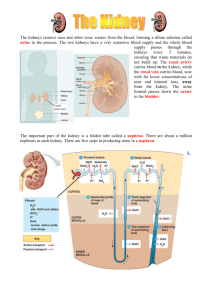
Topic 11 Animal Physiology 11.3 The Kidney and Osmoregulation Nature of Science • Curiosity about particular phenomena: Investigations were carried out to determine how desert animals prevent water loss in their waste. Excretion • The removal from the body of the waste products of metabolic pathways. Animals are either osmoregulators or osmoconformers. o Osmolarity solute concentration of a solution o Osmoregulators – maintain a constant internal solute concentration even when living in marine environments with very different osmolarities. (EXAMPLES: terrestrial animals, freshwater animals and some marine organisms like bony fish) o Osmoconformers – internal solute concentration tends to be the same as the concentration of the solutes in the environment. Example: sharks The Malpighian tubule system in insects and the kidney carry out osmoregulation and removal of nitrogenous wastes. o Osmoregulation – a form of homeostasis whereby the concentration of hemolymph (in insects) or blood (in animals) is kept in a certain range. o When animals break down amino acids, the nitrogenous waste produce is toxic and needs to be excreted (waste is uric acid in insects and urea in mammals) o Insects have tubes that branch off from their intestinal tract (Malpighian tubules). Cells lining the tubules actively transport ions and uric acid from the hemolymph into the lumen of the tubules. This draws water by osmosis from the hemolymph through the walls of the tubules into the lumen. The tubules empty their contents into the gut. SKILL: Drawing the Kidney The composition of blood in the renal artery is different from that in the renal vein. o Kidney function in both osmoregulation and excretion. o The composition of blood in the renal artery (how blood enters the kidney) is different from the renal vein (how blood leaves the kidney). Composition of Blood Renal Artery Renal Vein • Higher amounts of toxins • Higher amounts of excretory wastes (urea) • Higher amounts of salt and water. • Slightly higher amount of glucose. • Higher concentration of oxygen • Lower concentration of carbon dioxide • SAME concentration of plasma proteins. • Lower amounts of toxins • Lower amounts of excretory wastes (urea) • Lower amounts of salt and water. • Slightly lower amount of glucose. • Lower concentration of oxygen • Higher concentration of carbon dioxide • SAME concentration of plasma proteins. SKILL Drawing and labelling a nephron (see page 492 in text). Structures and functions of nephron • Bowman’s capsule – a cup-shaped structure with a highly porous inner wall, which collects the fluid filtered from the blood. • Proximal convoluted tubule – a highly twisted section of the nephron, with cells in the wall having many mitochondria and microvilli projecting into the lumen of the tube. • Loop of Henle – a tube shaped like hairpin, consisting of a descending limb that carries the filtrate deep into the medulla of the kidney and an ascending limb that brings it back out to the cortex. • Distal convoluted tubule – another highly twisted section, but with fewer, shorter microvilli and fewer mitochondria. Structures and functions of nephron • Collecting Duct – a wider tube that carries the filtrate back through the cortex and medulla to the renal pelvis. • Blood vessels – associated with the nephron – blood flows through them in the following sequence • Afferent arteriole – brings blood from the renal artery. • Glomerulus – a tight, knot-like, high pressure capillary bed that is the site of blood filtration • Efferent arteriole – a narrow vessel that restricts blood flow, helping to generate high pressure in the glomerulus. • Peritubular capillaries – a low-pressure capillary bed that runs around the convoluted tubules, absorbing fluid from them. • Vasa recta – unbranched capillaries that are similar in shape to the loops of Henle. • Venules – carry blood to the renal vein. Ultrafiltration • Separation of particles differing in size. • Happens in the glomerulus. • Blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole. And is under high pressure. Three parts of Ultrafiltration system 1. Fenestrations – openings between the cells in the wall of the capillaries. Allow fluid to escape, but not blood cells. 2. Basement Membrane – covers and supports the wall of the capillaries. Made of negatively charged glycoproteins, which form a mesh. Prevents plasma proteins from being filtered out, due to their size and negative charges. 3. Podocytes – cells that form the inner wall of the Bowman’s capsule. Have extensions that wrap around the capillaries of the glomerulus. **if particles pass through all three parts, they become part of the glomerular filtrate Proximal Convoluted Tubule • Filtrate enters PCT from Bowman’s capsule. • PCT selectively reabsorbs useful substances by ACTIVE TRANSPORT. • Most of the filtrate is reabsorbed and most of the this reabsorption happens in the PCT. By the end of the PCT, ALL glucose, amino acids, and 80% of the water have been reabsorbed. Methods used to reabsorb substances by PCT • Sodium ions – moved by active transport (protein pumps) • Chloride ions – attracted from filtrate into fluid outside tubule because of charge gradient set up by sodium ions (diffusion) • Glucose – co-transported out of filtrate by co-transporter proteins. (cotransported with sodium ions). • Water - osmosis Loop of Henle • The Loop of Henle maintains hypertonic conditions in the medulla. • Sodium ions are pumped out of the filtrate to the interstitial fluid. (only in ascending limb) • The wall of the ascending limb is impermeable to water, so the interstitial fluid is hypertonic relative to the filtrate. • The wall of the descending limb is permeable to water, but impermeable to sodium ions. As filtrate flows down the descending limb, the increased concentration in the interstitial fluid in medulla causes water to be drawn out of the filtrate. Loop of Henle • The length of the loop of Henle is positively correlated with the need for water conservation in animals. • The longer the loop of Henle, the more water will be reclaimed. Animals adapted to dry habitats will often have long Loops of Henle. (must have thicker medulla in order to accommodate longer Loops of Henle). ADH – antidiuretic hormone • ADH controls reabsorption of water in the collecting duct. • If the solute concentration of blood is too low, little water is reabsorbed as filtrate passes through distal convoluted tubule = large volume of urine produced and low concentration. • If the solute concentration of blood is too high, the brain detects it and causes the pituitary gland to secrete ADH. ADH makes the collecting duct permeable to water, so water will be reabsorbed here = small volume of urine produced and high concentraiton. Nitrogenous Waste • The type of nitrogenous waste in animals is correlated with evolutionary history and habitat. • When animals break down amino acids, nitrogenous waste in the form of ammonia is produced = TOXIC. So organisms must get rid of it. • Marine or freshwater fish – ammonia • Terrestrial organisms – urea or uric acid • Amphibians – ammonia as larva and urea as adults APPLICATIONS • Consequences of dehydration and overhydration. • Treatment of kidney failure by hemodialysis or kidney transplant. • Blood cells, glucose, proteins, and drugs are detected by urinary tests. ***READ APPLICATIONS on pg. 496 and 497 in text for HW.