Porifera Intro - WordPress.com
advertisement

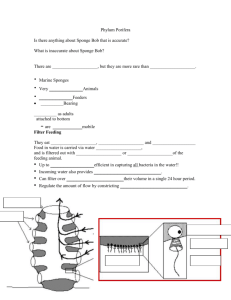
Warm up. Name that symmetry Answer: Bilateral Answer: Radial Answer: Radial Sea sponge Answer: Asymmetry! Asymmetry – non-symmetrical Phylum: Porifera "I drink no more than a sponge" Francis Rabelais Phylum Porifera • From Greek ‘poros’ meaning ‘passage’ or ‘pore’ Sponges have tiny openings all over their body • Therefore Porifera = “pore-bearers” • Most ancient and primitive of all animals • Estimated 5000-10000 species • Most sponges are marine, some live in freshwater Where are they on the tree of life? • You tell me? “I never wanted to be different; I just wanted to be me” • Sponges are different than other animals. • Originally thought to be plants because “sessile” • Have no: Mouth, head, muscles, nervous system, digestive tract, circulatory organs, true tissue layers, organ system. • Long thought to be an evolutionary dead end however recently believed to be at the base of the animal tree of life. Sessile: “fixed in one place” What do they have? Why are they an animal? • Collagen- all animals use collagen as an essential structural protein • Animal embryonic development • “Motility” of most cells within the sponge Motile Structure and Function in Porifera -The 4 Cells • Epidermal cells • Pore Cells • Collar Cells (choanocyte) • Amoebocytes Epidermal - Flat cells form the outer covering. - Respire and excrete via diffusion. Pore cells - Cylindrical cells which allow water and food to enter the sponge - The flow of water is driven by current and by collar cells Collar cells (choanocyte) - Inner cell layer of a sponge - Have a flagellum which draws water into the sponge -flagellum also drives food into the collar where they are ingested into the cell body Amoebocytes • amoeba-like cells that crawl around the jellylike inner layer of the sponge • Deliver food and O2 • Absorb nutrients and remove wastes • Make SPICULES which create sponge skeleton • Carry sperm to eggs n Activity • With a partner try and remember the 4 cell types • Draw the four cell types • Label their parts. • Write brief definition of what they do • Gallery walk (see other drawings get ideas how other people do their work) How does a sponge stay standing? • Spicules • Spongin Head to Head Spicules Spongin • Created by Amoebocytes • Made from either: -chalklike calcium carbonate (CaCO3) -or glasslike silica (SiO2) • Form the delicate skeleton of the sponge • Softer sponges (like the ones you can buy to use in the bath) are made up of fibrous proteins called spongin. • Some sponges contain both spicules and spongin Spicules Spongin Evolution of Spicules Other key words • Spongocoel – hollow body in the sponges interior. (think coelom) • Osculum- Opening where water exits the sponge • Spicules – the skeleton of the sponge (more later) How does a sponge eat? • ..\..\..\Lesson Videos\Biology 11\Sponge Feeding.mov.flv How does a sponge eat? • Sponges are filter feeders – they sift microscopic food particles from the water that passes through them • All digestion is intracellular • Food particles stick to the collar cells Collar cells either digest the food or pass them on to the ? (what else digests/delivers food) Amoebocytes The water flowing through a sponge serves as its respiratory, excretory, and circulatory system. • Sponges pump huge amounts of water through their body every day • Roughly one tonne water per ounce of food Reproduction Asexual reproduction • “Budding” – a small growth forms and falls off the sponge starting a new sponge • “regeneration” Sponges can regenerate from broken pieces • “Gemmules” sphere-shaped collections of amoebocytes surrounded by spicules. They leave sponge, settle, and wait for improved conditions Sexual reproduction • Hermaphrodites (both male and female sexual organs) • Most fertilization is hermaphroditic • “Broadcast” method of sperm release. Masses of sperm released into water • Amoebocytes carries sperm to egg when received. Gemmulles • “Little gems of life”? “Survival pods”? • Remember it your way. • Sphere-shaped collections of amoebocytes surrounded by spicules • leave sponge, settle, and wait for improved conditions Gemmules • Can survive extreme temperatures or drying out • Some are resistant to freezing • Full of amoebocytes which can grow into any type of cell necessary for survival • Why would sponges have evolved Gemmules? Here comes the Motility Flagellated larvae • • • • A sponges larvae have flagellum Leave via ? Osculum Drift/ swim to their new home • ..\..\..\Lesson Videos\Biology 11\Sponge Spawning.flv