Phylum Porifera - Glasgow Independent Schools
advertisement

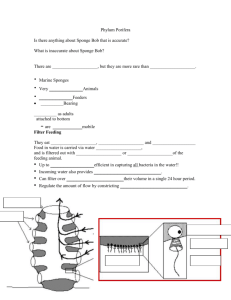
Phylum Porifera General Characteristics SPONGES! Simplest of all animals _________________ No true tissues or organs _________________________ Marine and Freshwater Saltwater are colorful Freshwater are dull green color General Characteristics Cont. • • • • Sponges are sessile as adults Free swimming larval stage called dipleurula Porifera means pore-bearing Water enters through pores bringing in food and oxygen • ____________________________ • Osculum- large opening at the top where excess water leaves WATER OUT Water Flow Through the Sponge WATER IN Osculum 3 Basic Cell Types 1. _______________ 2. Mesenchyme Cells 3. Choanocytes 3 Basic Cell Types • 1. Pinacocytes- flat cells that line the outer surface of the sponge. –May be slightly contractile –____________: a specialized type of pinacocyte; are tube-like in shape; contractile; and can regulate water circulation. 2. Mesenchyme Cells- move around in the mesohyl layer; are specialized for reproduction, secreting the skeleton, transporting/storing food. ____________: jelly-like layer just underneath the pinacocyte layer. • 3. Choanocytes- flagellated cells that line the inner chamber of the sponge; called collar cells. –Flagellum: flagella spins to create water currents to pull in water and food –Collar: __________________________ (plankton) from the water Choanocyte Choanocyte __________________________ Consists of either one or all of the following: Spicule: microscopic needle-like spikes that are made of Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or silica (glass). Spongin: a fibrous protein made of collagen Sponge Skeletons Silica Spicules Limestone Spicules SPONGIN Sponge Body Types • 3 Kinds–Ascon –__________ –Leucon Ascon • ____________________ • Are vase-like • Least common type of sponge ________________ • Sponge wall is folded into canals • Choanocytes line the radial canals to move water Leucon • Have an extensively branched canal system. • ___________________________ • Multiple ostia for water to exit • Increased surface area means more water can move through sponge Body Forms Summary Reproduction Sexual Reproduction- sponges are monoecious (male and female in the same body) Release sperm and eggs into the water from the Osculum Cross-Fertilization takes place in the ocean _____________________________ Reproduction Sponge Releasing Eggs & Sperm Reproduction Cont’ o Sponges can regenerate (regrow) lost body parts through mitotic cell division (asexual) o Sponges also reproduce asexually by ________________ Reproduction Cont’d gemmule Asexual Reproduction- involves the formation of gemmules ______________: resistant capsules that sponges release to survive unfavorable conditions. When conditions become favorable, the gemmules sprout into sponges. _____________________ • Phylum Porifera –3 Classes • Class Calcarea • Class Hexactinellida • Class Demospongiae Class Calcarea • • • • Spicules made of Calcium Carbonate Can have all three body forms __________________ Ex. Grantia Class Hexactinellida • ___________________________ • Can have syncon or leucon body forms –Often fused into an intricate lattice –Glass sponges Class Demospongiae • Spicules made of silica, spongin, or both. • ____________________ • Ex: common bath sponge