Porifera (Sponges) Study Guide: Characteristics & Classes
advertisement

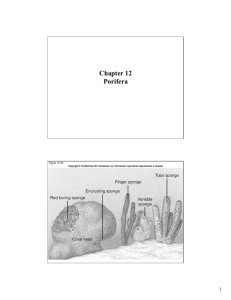
Porifera: Sponges Kingdom: Animal Phylum: Porifera (pore bearer) Class: Calcispongiae Class: Hexdtactinellida Class: Demospongiae General Characteristics ______________________ Simplest animal, has organized cells Put sponge through a sieve, cells would reform the sponge (few weeks) No head or anterior end, no mouth or gut cavity 5000 species, some in water 8500 ft deep Habitat Most live in ocean, very few freshwater Adults sessile (do not move on own), larvae are freeswimming ______________________: filters small particles of food from water as it passes by or through some part of the organism Digestion Water comes in through pores (flagella beat the water in) and out through top Small organisms trapped in spaces and digested Body Structure _____________________ All have central cavity (spongocoele) All have pores that open from the outside, pass through body wall and open in to the spongocoele All have a larger opening on the top (osculum) Body wall consists of two layers of cells with a jelly-like middle layer (mesoglia) o Skeleton is in the mesoglia and consists of spicules o Spiculues are calcium carbonate, silicon oxide fibers, and/or a skeleton of organic spongin fibers o “Sponges” are the spongin net after the living tissue has decomposed and washed away Gas Exchange Circulation of water through spongocoele provides gas exchange & waste removal Three Body Types Ascon: simple urn shape, pores open directly into the spongocoeole Sycon: pores open radial canalsspongocoele Leucon: pores incurrent canals flagellated chambers radial canals spongocoele (one or several) Porifera Classes Class: Calcispongiae Ascon shape Spiculues: calcium carbonate (basically bone) Class: Hexdtactinellida Sycon shape Spiculues: silicon oxide based (basically glass) Class: Demospongiae (commercial sponges) Leucon shape Spicules: sponging fibers Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Hermaphrodites (contain sperm & eggs) Internal fertilization release sperm carried by water to another sperm fertilization External fertilization release sperm & eggs into water fertilization Asexual Reproduction Fragments break off and make a new sponge (budding) Osculum Typical Sponge Features Large opening at the top, water & wastes expelled Sponges no bigger than a pen can move 20L of water through its body per day Pore Cell Surrounds each pore, bring water carrying food and oxygen into sponge’s body Epithelial cell “skin” cells, thin and flat, contract to touch or chemicals, close up pores, protect pores Collar Cell Line interior of sponges, has flagellum, draws water through the pores Amoebocytes Located between two cell layers Spicules Small, needlelike structures, located between layers, provide structure & protection