October 20 Chapter 6 slides BAF3M
advertisement

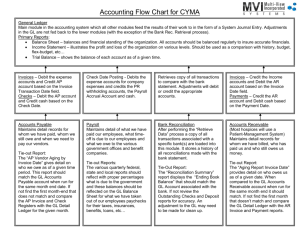
Unit 3 : Chapter 6 The Journal and Source Documents •Chapter 6 Quiz will be on October 24 (Friday) 1 Transactions occur. 4 Trial Balance 2 Transactions are recorded in the journal in order by date. 5 Adjusting Entry 3 The accounting entries are transferred to the ledger accounts. (or T accounts) 6 Balance Sheet and Income Statement •When a bookkeeper first records the journal entry, they have to read and interpret the information in source documents. (More than 90% of journal entries are made from source document) • Some business transactions are started by non-accounting people such as owner, salespeople, department supervisors, managers and other authorized people. There are many types of source documents : 1. Cash Sales slip 2. Sales Invoice 3. Point of Sale Summaries 4. Purchase Invoice 5. Check copies 6. Cash Receipts Daily Summary 7. Bank Advices or (Bank Memo) •People use credit cards and debit cards to pay for items. •A point of sale terminal is a computerized sales register which allows a business and its customers to exchange funds electronically. (More details in chapter 9) • At the end of each day, an accounting clerk can use POS terminal to print POSS at least two source documents. •An example is Fig 6.6 Page 187 •You can see that PSS reveals the sales activities of three cards: VISA, Master card and debit cards. •Journal Entry for POS summaries is: Dr Bank Cr 743.18 Sales POS summary Oct 30 743.18 Note: Cheque copy itself is not sufficient proof that the payment is proper. A bill or receipt is also needed to support the accounting entry for a cash purchase. Otherwise we have no idea what this check is for. Source Document Transaction Description Journal Entries Debit Credit Cash Sales Slip POS Summaries A sale of goods (or services) for cash. Bank Sales or Revenue Sales Invoice A sale of goods (or services) on account. Accounts Receivable Sales or Revenue Purchase Invoice Company purchased 1. An expense Accounts goods (or services) on account (small Payable account amount) Few times an asset account (big amount) can be debited. For example, machine Source Document Cheque Copy (Company wrote a cheque, meaning company paid cash) Transaction Description 1. Paying off of an account payable 2. Cash purchase of an asset 3. Cash payment for an expense 4. Owner draws out money for personal use Cash Receipts Cheques received Daily Summary from customers (who (or check copies) purchased goods on account in the past) Journal Entries Debit Credit 1. A liability account 2. An asset account 3. An expense account 4. Drawings account Bank Bank Accounts Receivable Source Document Bank Debit Advice (by Bank Statement) Bank Credit Advice (by Bank Statement) Transaction Description Bank account decrease Bank account increase because company’s savings acct earned interest or customer paid back their debt by online payment Journal Entries Debit Interest expense or service charge Bank Credit Bank Interest earned (Revenue), or AR In addition to the source documents listed in previous slide, you may encounter the following source documents: ◦ Receipts such as donations ◦ Bills (=Invoice) such as hydro or telephone charge ◦ Email invoices vs mail invoices ◦ Online banking transactions ◦ Insurance certificates In addition to the source documents listed in previous slide, you may encounter the following source documents: ◦ Written memos from the owner ◦ Bank Statements – can contain most (if not all) of these information in reality. You have to learn how to read bank statements. ◦ Cash register tapes There is no fixed number of required copies of business documents. It depends on the business and the owner. You would need to keep at least one copy of the source document in general. I will take up one or two questions from yesterday. Review Questions: #10 to #12, #14, 16 and 18 (P193) Exercises #1, #4 and #5 (P193 and P195)