Unit 3: The Senses
advertisement

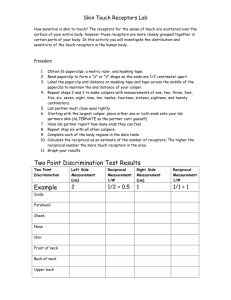
Unit 3: The Senses S Essential Questions Day 1: Sensations S Required Readings: S 9.1 S Learning Objectives: S Describe the roles of sensory receptors, neurons, nerves, and the cerebral cortex in sensations S Name the five basic types of sensory receptors S Compare the mechanisms of projection and adaptation of sensations Starter S There are 5 different bags on the back lab benches S Use your sense of hearing and touch to try to guess what is in the bag S Time: 10 minutes Activity 1 S 1. Place one finger in the middle [ROOM TEMPERATURE] container and leave in the water for 15 seconds. S 2. Place the finger from the middle container into the container with cooler [COLD] water. How does that finger feel? Warmer or colder? S 3. Move the finger from cooler water into the middle container; wait 30 seconds. How does that finger feel? Does it change over the course of 30 seconds? Does it feel warmer or colder than it did originally? S 4. Move the finger from the middle container into the warmer [HOT] water. How does that finger feel? Warmer or colder S Time: 10 minutes Activity 2 S What do you think would happen if you changed the order between the cups (i.e. hot to room to cold? Hot to cold? Cold to hot)? S Try it out after you have written a hypothesis S What does this activity tell you about our thermoreceptors and how sensations are interpreted by our nerves? S Time: 10 minutes Activity 3 S Your group will be given one of the sensory receptors: S Thermoreceptor, mechanoreceptor, pain receptor, chemoreceptor, or photoreceptor S Create a 6-segment story board for your sensory receptor S When completed, you will present it to the rest of the class S Time: 45 minutes Closing S What happens when turn off the lights in a room? S How/why does this happen? (Think about what happens to your pupils, cones (colour receptors) and rods (night vision receptors) S How long does it take you to adapt to the dark? S Time: 5 minutes Day 2 S Required Readings: S 9.2 S Learning Objectives: S Name and describe the locations of receptors involved in sensations of heat, cold, touch, pressure, and pain S Name and describe the location of receptors involved in maintaining posture and muscle tone S Explain the basis of referred pain Starter S Take shoes off S On the balance discs, do the following: S Balance with two feet S Balance with two feet with eyes closed S Balance on one foot, then the other S Balance on one foot with eyes closed S What do you notice? S Time: 15 minutes Activity 1 S We will complete the “Our Sense of Touch” experiment in your lab groups S Once you have finished the first part, go on to design your own experiment. Ok your idea with me before you investigate S Time: 60 minutes Closing S How can our touch receptors be masked? S What does this mean for real life applications? S Think about people’s jobs, people who are blind, activities you do, etc. S Which part of your body has the most touch receptors? S Which part of your body has the least touch receptors? S Why is this? S Time: 10 minutes Homework S Our sense of touch lab – October 2 S Read Section 9.3 S Test – Friday October 4 Day 3 S Required Readings: S 9.3 S Learning Objectives: S Describe the location, structure, and function of taste, hearing, vision, and equilibrium receptors S Describe the structure of the eye and the functions of its parts Video: The Senses Overview Starter S What are the 4 special senses? S What type of receptors are used to respond to stimuli for the 4 special senses? S Time: 5 minutes Activity 1 S What are the receptors for taste? S Draw a picture that shows where sweet, bitter, salty, and sour tastes are perceived on the tongue S Time: 10 minutes Activity 2 S Explain what happens as the person is smelling the flower S Time: 5 minutes Video: How do we hear a sound? Activity 3 S Create a flow chart to show how we hear a sound S Time: 15 minutes Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane Tympanic membrane vibrates, causes vibration of the stapes Impulses by the hair cells Vestibulocochlear nerve carries impulses to the hearing centers of the temporal lobes where the sensation is interpreted Oscillatory movement of perilymph causes vibrations in the vestibular and basilar membranes Activity 4 S Draw a picture to show how an image is formed by the eye S Time: 5 minutes Activity 5 S Work through Lab#8: Human Senses with your lab group S You don’t need to do #2D as we did it in the last lesson S Answer the questions as you go along S Hand in on Friday S Time: 45 minutes Closing S Sit with your group and discuss any new or interesting findings from the senses lab you just completed S Time: 5 minutes Homework S Read section 9.4 S 2 point discrimination lab - Wednesday S Human Senses lab - Friday S Test – Friday Day 4 S Required Readings: S 9.4 S Learning Objectives: S Describe the common disorders of hearing and vision