Physical Geography of Russia Chapter 14 Test Review

Physical Geography of Russia
Chapter 14 Test Review
World Geography
Which of the following statements about the fishing industry in Russia is TRUE?
a.
Salmon, herring, cod, and halibut support the fishing industry.
b.
The fishing industry is dependent solely on sturgeon.
c.
The demand for Russian caviar has declined.
d.
Russia's fishing exports double every year.
The __________ mark the traditional boundary between European Russia and Asian
Russia.
a. Verkhoyanski Mountains b. Ural Mountains c. Sayan Mountains d. Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are located between the _______ and ________ Seas.
a.
Black, Caspian c.
Baltic, Barents b.
Black, Baltic d.
Caspian, Barents
The Volga River connects Moscow with which body of water?
a. Pacific Ocean b. Mediterranean Sea c. Bering Sea d. Caspian Sea
Russia has a.
large forest lands but not much petroleum.
b.
huge reserves of mineral resources.
c.
small reserves of mineral resources.
d.
vast petroleum deposits but few minerals.
The ________ climate region dominates the landscape in Russia’s far north.
a. Subarctic b. Steppe c. Tundra d. humid continental
What is the Black Earth Belt?
a.
an area in which the ground is frozen most of the year b.
a region in which farming is difficult because of the infertile soil c.
an area in which factories are most important to the economy d.
an area of rich soil whose farms feed most of Russia
Russia’s largest climate region is the
_________ a.
arctic.
c.
highland.
b.
subarctic. d.
humid continental.
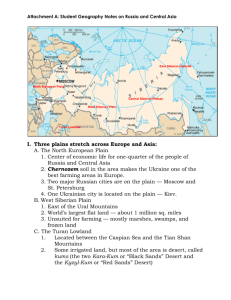
The majority of Russia’s people live a. on the Northern European Plain.
b. along the Lena River. c. on the West Siberian Plain. d. on the Central Siberian Plateau.
Russian coasts lie along the Pacific Ocean, a.
Arctic Ocean, Caspian Sea, Black Sea, and
Baltic Sea.
b.
Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Black Sea, and Baltic Sea.
c.
Arctic Ocean, Caspian Sea, North Sea, and
Black Sea.
d.
Arctic Ocean, North Sea, Black Sea, and
Baltic Sea.
Canals link the _________ River to the
_________ Sea, providing a water route to northern Europe.
a.
Lena, Laptev c.
Irtysh, Barents b.
Volga, Black d.
Volga, Baltic
When attacking Russia in 1941, German forces a.
were defeated in part by Russia's harsh winter.
b.
found Russians had burned their own villages to keep the Germans from finding food.
c.
were very well prepared for the harsh winder to come.
d.
were defeated with very little loss of life.
Russia’s steppe climate is characterized by a.
wet summers and long, cold winters with swirling winds and blowing snow.
b.
dry summers and short, mild winters with swirling winds and blowing snow.
c.
wet summers and short, mild winters with swirling winds and blowing snow.
d.
dry summers and long, cold winters with swirling winds and blowing snow.
Russia has few ocean ports that are a.
closed year-round.
b.
able to accept more than one type of ship.
c.
free from ice year-round.
d.
usable for ships constructed in the past 20 years.
The Caspian Sea is a.
a saltwater lake.
b.
a freshwater sea.
c.
the world's largest freshwater lake.
d.
a saltwater lake with an outlet to the ocean.
Which statement about Russia's size is
TRUE?
a.
Russia spans three continents.
b.
Russia spans seven time zones.
c.
Russia is both a country and an entire continent.
d.
Russia spans two continents.
Napoleon’s Grand Army of 600,000 men a.
moved south to escape the Russian winter.
b.
crossed the Volga River.
c.
were reduced to 40,000 men by
Russia's harsh winter and a lack of food.
d.
quickly defeated Russia's army.
The rivers in Siberia flow a.
north and are warmer at the source than at the mouth.
b.
south and are colder at the source than at the mouth.
c.
east and are about the same temperature at the source and the mouth.
d.
west and are frozen throughout the year.
Russia's taiga is the world's largest a. deciduous forest.
b. freshwater lake.
c. wheat belt.
d. coniferous forest.
The Volga-Don Canal connects a.
the Amur River and Siberia.
b.
Moscow to the Sea of Azov and the
Black Sea.
c.
Moscow to the Baltic Sea.
d.
St. Petersburg and the West Siberian
Plain.
The __________ River Valley is Siberia’s main food-producing area.
a.
Amur c.
Lena b.
Yenisey d.
Irtysh
____________ form a natural boundary between Russia and China.
a.
Plateaus c.
Mountain ranges b.
Canyons d.
Plains
Which of these Russian cities are located on the
Northern European Plain?
a. St. Petersburg and Moscow b. St. Petersburg and Omsk c. Moscow and Vladivostok d. Yakutsk and Moscow
The Black Sea provides Russia with a warmwater outlet to the Aegean and Mediterranean
Seas by way of ________, ________, and
________.
a.
the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, the Bosporus b.
the Sea of Marmara, the Dardanelles, the
Caspian Sea c.
Lake Baikal, the Dardanelles, the Bosporus d.
the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, the
Dardanelles
__________ from the ___________ moderates temperatures in western Russia.
a. Warmer air, Pacific Ocean b. Warmer air, Atlantic Ocean c. Cooler air, Pacific Ocean d. Cooler aid, Atlantic Ocean
The effect of extreme variations in temperature and very little precipitation within the interior areas of a landmass is called a. continentality.
b. chernozem.
c. global warming.
d. permafrost.
Why is the taiga important to Russia’s economy?
a.
Its rain forest could provide new drugs.
b.
It produces about one-half of the world’s softwood timber.
c.
Its lakes provide much of the country’s freshwater supply.
d.
It provides a home for many endangered species of animals.
In which areas of Russia does a humid continental climate exist?
a.
West Siberian Plain and southern Siberia b.
Northern European Plain and southern
Siberia c.
Central Siberian Plateau and Northern
European Plain d.
northern Siberia and West Siberian Plain
The Ural Mountains divide the Northern
European Plain from a. the West Siberian Plain.
b. the Caucasus Mountains.
c. the Central Siberian Plateau d. the Kamchatka Peninsula.
A permanently frozen layer of soil that lies beneath the surface of the ground is called a.
tiaga.
c.
permafrost.
b.
tundra.
d.
chernozem.
____________ , located in ___________, is the deepest freshwater lake in the world.
a. Lake Baikal, southern Siberia b. Lake Ladoga, eastern Russia c. Lake Baikal, northeastern Siberia d. Lake Ladoga, northwestern Russia
Why does the northern part of the Northern
European Plain contain many swamps and lakes?
a.
It is very flat and poorly drained.
b.
It is below sea level.
c.
It has a long rainy season.
d.
Global warming has increased temperatures.
Most of Russia’s longest rivers, which carry 84 percent of the country’s water, are located a. west of the Ural Mountains. b. north of the Caucasus Mountains.
c. in Siberia.
d. in Kaliningrad.
The Volga River is also known as the Matushka
Volga, or “__________.” a.
River of Life c.
Mother Volga b.
Massive Volga d.
Father Volga
Russian forests shrink at a rate of loss a.
three times lower than that of the
Amazon Basin.
b.
higher than that of the Amazon Basin.
c.
the same as that of the Amazon Basin.
d.
five times lower than that of the
Amazon Basin.
Why is it a challenge to transport crops in
Russia?
a.
There are great distances between the farms in the south and the cities in the north.
b.
The machinery gets too cold to operate.
c.
Freezing and thawing of the ground make roads very difficult to cross.
d.
Crops spoil before they arrive at their destination.
Why are Russian forests shrinking?
a. slash-and-burn farming b. global warming c. commercial logging and wildfires d. pest infestations
Dams built on the _________ have interrupted the migration of sturgeon.
a.
Lena River b.
Amur River c.
d.
Don River
Volga River
What is the average temperature of the
Russian tundra?
a. mild with no extremes b. cold but never freezing c. below freezing d. warm and usually sunny
Russia’s steppe climate region is found a.
between the Black and Caspian Seas and along the Russia-Kasakhstan border.
b.
on the Kamchatka Peninsula along the
Sea of Okhotsk.
c.
to the east of the Ural Mountains along the Ob’ River.
d.
in a band that extends across the
Northern European Plain.