Chapter 7 World Geography
advertisement

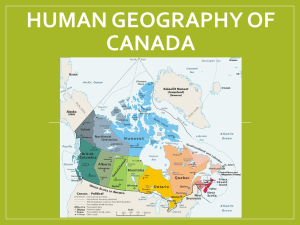
Human Geography of Canada Developing a Vast Wilderness History and Government of Canada Objective The student will examine Canadian expansion and development and be able to describe Canadian government. Places and Terms province Dominion of Canada confederation parliamentary government parliament prime minister The First Settlers and Colonial Rivalry Canada’s vast size & cold climate affected it’s development. Early people migrated after the last Ice Age, many being the ancestors of the Inuit (Eskimos) 16th & 17th Century: Colonization by France & Britain. Coastal fisheries & fur trade important to both countries. Britain and France in Canada Two Cultures Roman Catholic French Lower Canada (Quebec) Protestant English Upper Canada (Ontario) Britain and France in Canada Establishing the Dominion of Canada 1867: British North America Act A loose confederation of Ontario & Quebec as well as Nova Scotia & New Brunswick Had self-government but remained part of British Empire with Ottawa as the capital Expansion of Dominion was rapid Continental Expansion 1872: Construction of transcontinental railroad Not long after the completion of the railroad gold was found in Yukon which brought people from all over the world to seek their fortune As a result of the transcontinental railroad many towns developed. Governing Canada Canada was recognized as an independent nation by Britain in 1931 Parliamentary Government Legislative & Executive functions are combined into “parliament” Canada is independent but it’s symbolic head of state remains the British Monarch Majority party’s leader in parliament becomes “Prime Minister” Review Questions Why did France and Britain fight? Why was the Dominion of Canada formed? What brought immigrants to Canada in the late 1800s? How is it determined who heads the government? Human Geography of Canada Developing a Vast Wilderness Economy and Culture of Canada Objective The student will identify economic power and examine cultural diversity in Canada. Places and Terms First Nations métis (may-TEES) reserve Economy and Culture of Canada Fur trade was a major economic activity in early Canada First Nations Canada’s native peoples began fur trade with European Fisherman during the 16th century Economy and Culture of Canada Primary Industries: Farming, logging, mining, & fishing Only 5% of land suitable for farming Biggest export: Forest products Three ocean coastlines give ample access to fishing industry North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA signed in (1994) allowed the United States and Canada to trade goods easily. These two countries share the largest open border in the world. Economy and Culture of Canada Canada is officially a bilingual country English speaking majority French speaking minority Only in Quebec is French spoken in the majority Economy and Culture of Canada Sports and Recreation Canadians enjoy sports such as skating, ice hockey, fishing, skiing, golf, and hunting are popular. The First Native peoples developed the game of lacrosse. Human Geography of Canada Developing a Vast Wilderness Subregions of Canada Objective The student will examine the subregions of Canada. Places and Terms Atlantic Provinces Quebec Ontario Prairie Provinces British Columbia Nunavut Subregions of Canada Canada is divided into ten provinces and three territories Atlantic Provinces include Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, & St. John Subregions of Canada Core Provinces include Quebec and Ontario, which sustain three out of every five Canadian residents Prairie Provinces are part of the Great Plains of North America. Pacific Provinces include British Columbia and the three territories Nunavut was carved out of the eastern half of the Northwest Territories and is home to many of Canada’s Inuit Map Activity Using a piece of computer paper draw Canada and label all ten provinces and three territories. Label the following areas – Ottawa, Toronto, Quebec, St. Lawrence, Newfoundland, Winnipeg, Calgary, Vancouver, Edmond, Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and Hudson Bay Reference pages 154, 157, and Atlas – p.11 Ask teacher for markers, map pencils, or other supplies