How Can You Prevent Cardiovascular Disease?
advertisement

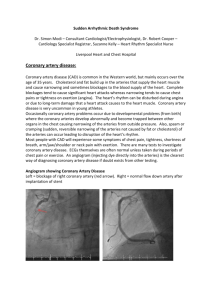
Cardiovascular Disease By: Vicky Zakrzewski Audience: EVERYONE How It Occurs! •Blood Vessels gets clogged and flow to the heart or brain is blocked. Lack of oxygen supply to heart or brain. Affecting Factors •Poor diet •Lack of Exercise •Heredity What Are Strokes? •Blood clot, blood vessel, or ruptured artery blocking blood flow to the brain •Brain requires certain delivery of oxygen and glucose from the blood stream •Cerebrovascular accident (stroke) occurs when this delivery is disrupted a) can result in cell damage (brain damage) Types Of Strokes Ischemic Stroke - Blood clot or blockage to brain. a) Most common 75% of all strokes Hemorrhagic Stroke - Brain fills up with blood putting to much pressure on the brain a) 25% of strokes Who Gets Strokes? •Cardiovascular disease •Over age 55 •Male •Family History •Blood Pressure •High Cholesterol •Diabetes •Cigarettes Symptoms •Dizziness, Trouble Walking, Loss of Balance and Coordination •Slurred Speech •Paralysis one side of body •Blurred Vision •Severe headache Life After Stokes •Combat physical and emotional struggles •Brain damage can result in paralysis of bodily functions •Relearn Basic everyday skills a) b) c) Eating Walking Dressing Heart Attacks! •More than 1 million people suffer from a heart attack each year. What is it? •Myocardial Infarction •“Myo”- muscle; “Caridial”- heart; “Infarction” - lack of blood causes death of tissue Typical Causes •Coronary artery supplies heart with blood •Coronary Artery Disease causes coronary artery to narrow •Fat cells, proteins, inflammatory cells, and more clog the artery •Forms plaque •Plaque breaks and platelets come to form a blood clot •Clot prevents blood flow to the heart causing the heart to suffocate without oxygen Result Permanent death of heart tissue. Other Causes •Coronary Artery Spasm more unlikely cause •Silent heart attacks are typically caused by Diabetes a) A heart attack is produced without prior symptoms a) Symptoms •Discomfort, Pressure •Pain in chest, back, arm, under the sternum, jaw throat •Feeling of heartburn or indigestion, fullness, or choking •Dizziness, sweating, nausea, vomiting •Extreme shortness of breath, weakness, or anxiety. •Rapid or irregular heartbeats WebMd.com/heartdisease/guide/heart_disease_heart_attacks Related Illnesses •Coronary Artery Disease •Diabetes •Cardiovascular Disease Treatment Medicines and procedures to help open coronary arteries and make it easier for heart to pump. Lifestyle Changes Post-Heart Attack •Quit smoking •Lose weight •Eat healthy diet •Increase physical activity •Prescriptions to help control blood cholesterol, blood pressure, and chest pain •Cardiac Rehabilitation •Most patients may return to all normal activities within the first few weeks Risk of a Repeat Heart Attack •Heart attack victims are at greater risk of a repeat heart attack Symptoms are different the second time •Heart attack vs. Angina •Repeat heart attacks feel much more severe than angina •Angina is the body’s warning sign that the heart is working too hard a) Choking feeling under the sternum a) High Blood Pressure! Aka Hypertension What is High Blood Pressure? Definition: Blood pressure that is persistently higher than normal. Over time, if the force of the blood flow is often high, the tissue that makes up the walls of arteries gets stretched beyond its healthy limit. This creates problems in several ways: •Vascular weaknesses •Vascular scarring • Increased risk of blood clots •Increased plaque build-up • Tissue and organ damage from narrowed and blocked arteries •Increased workload on the circulatory system Statistics High blood pressure (hypertension) killed 56,561 people in the United States in 2006 About 74.5 million people in the United States age 20 and older have high blood pressure One in three adults has high blood pressure Risk Factors Uncontrollable: Controllable: Not completely proven yet: •Family History •Lack of Physical Activity •Smoking/ Second hand smoke •Gender •Poor diet (especially if high in salt) •Stress •Age •Overweight/ Obesity •Sleep Apnea •Drinking too much alcohol Symptoms High Blood Pressure is often called “the silent disease” because there are no symptoms until it reaches an advanced state. There's a common misconception that people with high blood pressure will experience symptoms such as nervousness, sweating, difficulty sleeping or facial flushing. Getting Tested Healthcare professionals use a medical instrument called a sphygmomanometer, which in layman's terms is known as a blood pressure monitor. This bicep cuff monitor yields the most accurate reading among various types of monitors. Understanding Blood Pressure Results Read as "117 over 76 millimeters of mercury" Systolic The top number measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (when the heart muscle contracts) Diastolic The bottom number measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats (when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood) Blood Pressure Chart This chart reflects blood pressure categories defined by the American Heart Association. * Your doctor should evaluate unusually low blood pressure readings. Blood Pressure Category Normal Systolic mm Hg (upper #) Diastolic mm Hg (lower #) less than 120 and less than 80 Prehypertension 120 – 139 or 80 – 89 High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Stage 1 140 – 159 or 90 – 99 High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Stage 2 160 or higher or 100 or higher Hypertensive Crisis (Emergency care needed) Higher than 180 or Higher than 110 Examples of Cardiovascular Treatments Lifestyle Changes Can help a patient suffering from: I. Coronary Heart Disease, Heart Attacks & Congestive Heart Failure a) Reduce amount of salt intake b) Eat Healthier c) Exercise d) Keep blood pressure under control e) Stop Smoking f) Limit Alcohol Medicine Treatments •Blood Thinners •Hypertension •Antiarrythmatics •Cholesterol Lowering •Rate Control •Vasodilators Special Procedures Defibrillation: I. When a electronic device gives an electric shock to the heart to help establish normal contraction rhythm. a) AED devices are now in schools Cardioversion: I. Used in emergency situations to electrically or chemically shock the heart out of abnormal heart rhythms. a) Mostly associated with low blood pressure, faintness, loss of consciousness and difficulty breathing Surgical Treatments Stents: Tube placed in an artery to help keep the passageway open. Transplants: When a doctor removes a diseased or defected heart and replaces it with a donor heart. •The success rate varies and the person receives the heart can have many complications. Bypass Surgeries: Arteries from another region of the patients body are moved to the area of the heart in order to improve blood supply and flow. How Can You Prevent Cardiovascular Disease? Lower Your Blood Pressure! A person’s blood pressure should be < 120/80 Ways To Lower Your Blood Pressure Lose weight Eat heart healthy foods Exercise daily Reduce salt Quit smoking Decease alcohol Be Active! A. Aerobic exercises B. Strength training exercises Keep A Healthy Diet! • • • • • • • Keep saturated fats low Eat less or no trans fats Stay away from sugars and processed foods Reduce cholesterol Get at least 50% carbohydrates a day Eat foods high in fiber Eat more fruits and vegetables Get More Sleep! Reduce Stress! Stay Positive! For more info check out http://www.webmd.com/heartdisease/guide/diseases-cardiovascular