Kingdom
advertisement

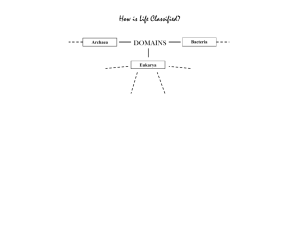
HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Answer the following question, you do not have to write the question: 1. A multicellular, heterotrophic organism with cell walls containing chitin belongs to which kingdom? KINGDOM FUNGI 2. A unicellular, photosynthetic organisms with cell walls containing peptidoglycan belongs to which kingdom? KINGDOM EUBACTERIA 3. A unicellular autotrophic organisms living in volcanic vents belongs to which kingdom? KINGDOM ARCHEABACTERIA 4. A eukaryotic, single-celled organism found in a sample of pond water belongs to which kingdom? KINGDOM PROTISTA Essential Question: How would you determine if an organism is in the Plantae kingdom? The Animal kingdom? Standard: compare the characteristics of taxonomic groups including plantae and animalia (B8C) Domain Eukaryota Domain Eukaryota Kingdom maturing fish eggs zygotes human cheek cells human muscle tissue Organisms from the Kingdom Plantae are multicellular eukaryotic organisms. Plants have characteristics that make them different from other eukaryotic organisms. One of the main differences is that they are autotrophic, meaning they are able to make their own food using simple inorganic substances. They do this through a process known as photosynthesis, in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of a plant cell. Plants are multicellular and, unlike animals, their cells have rigid cell walls made from cellulose. Some species of plants reproduce sexually Kingdom Plantae and some reproduce asexually. In asexual reproduction, such as budding, an exact copy of the parent is produced. Plant sexual reproduction can be assisted by animals, as is the case with flowers and honeybees. As the bees go from flower to flower collecting nectar, they carry pollen, plant sex cells, with them and pollinate other plants. Pollination is the first step in plant sexual reproduction. The Kingdom Plantae is divided into 11 Phyla. For example, Phylum Bryophyta are mosses - small, soft plants that don’t have flowers. They absorb water and nutrients through their leaves, which are 1 cell thick. Animals are a group of multicellular eukaryotic organisms. The word animal comes from the Latin word animalis meaning “having breath.” Animals are different from other eukaryotes in a number of ways. First, animal cells lack the rigid cell wall that plants, fungi, and algae have. Instead, animal cells are surrounded only by a cell membrane. Second, animals are heterotrophic, meaning that they must ingest other organisms in order to survive. Heterotrophs are the consumers in the food chain. Third, all animals are motile, or able to move, at least during one stage of their life cycle. Nearly all animals undergo some form of sexual reproduction, where specialized sex cells form and fuse together to form zygotes, which develop into individuals. Some animals are also capable of asexual reproduction, through budding or forms of cloning. The Kingdom Animalia is divided into approximately 40 Phyla including Phylum Chordata, which includes all the vertebrate animals, or animals with a backbone and spinal column. Humans, as well as fish, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and other mammals, belong to the Phylum Chordata. Other phyla include Phylum Arthropoda, to which crabs, spiders, and insects belong; and Phylum Nematoda, which are the roundworms. Kingdom Plantae Animalia Cell Type? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote) Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicelluar? Multicellular Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph? Autotroph Heterotroph Cell Wall? Yes, cellulose No, (cell membrane) Example Pine tree, moss Penguin, Sponge Before the end of class… 1. Label/color code your plant and animal cells 2. Color code your chart Autotroph or Heterotroph: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote: • Color heterotrophic boxes • • Color eukaryotic boxes blue Color prokaryotic boxes yellow. Unicellular vs Multicellular: • • • Color unicellular boxes purple Color multicellular boxes orange Color the both boxes half purple and half orange. • • red Color autotrophic boxes green Color the both boxes half red and half green. Cell Wall: • • • Color the yes boxes grey Color the no boxes light blue Color the both boxes half grey and half light blue.