total quality improvement - Southern University System
advertisement

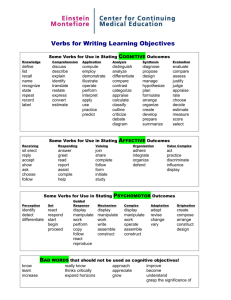
From Rules & Regulations to Continuous Improvement Presented by: Elaine Griffin, PhD, MHA, MBA, FACHE Lipscomb University Nashville, Tennessee And the benefits of CQI… Improved learning outcomes of the educational process (student learning outcomes) Increased student satisfaction Increased faculty and staff satisfaction Improved organizational performance Improved financial strength Objectives for this session… At the conclusion of this session, you will be able to: Answer the question, “Why quality?” Discuss the philosophy of CQI with its components: - Customers and requirements - Process focus - Continuous improvement Describe and explain the process focus of: - Quality planning - Quality measurement and reporting - Quality improvement - Cultural changes I. Philosophy of CQI Customers and requirements Continuous improvement Process focus II. Process focus and continuous quality improvement (CQI) Quality planning Quality measurement and reporting Cultural changes Quality improvement We’re going to spend our time on CQI Quality planning Quality measurement and reporting Quality improvement Cultural changes But first, let’s note some pressures on education… Competition for students Increased awareness by customers of educational quality Cost of education Continuous changes in job skills requirements to meet stakeholders’ needs Regulatory agencies and accrediting bodies More pressures… Pressure from all constituents to lower educational costs Pressure from all constituents to improve quality How do you define quality? Our definition: Customers (students) define what quality is for them. The product or service is quality if it meets the customer’s expectations or requirements Customer requirements for education Learning outcomes Service requirements Cost requirements Continuous improvement is a journey The goal is to provide services that meet our customers’ expectations It cannot be accomplished overnight It is accomplished over time by measuring the performance of our processes (everything is a process) We must take actions to improve our processes The journey requires… Identifying our current level of performance Setting goals for improvement Identifying new ways to improve work processes Pursuing goal achievement Celebrating Setting new goals to continuously improve Four components I. Quality planning II. Quality measurement and reporting III. Quality improvement IV. Cultural changes I. Quality planning Purpose of planning: to define a corporate-wide strategy to meet customer needs and achieve the vision Provides framework for innovation and creation of new services Concept of customers and requirements is further developed and put into action for organization as a whole Starts with mission, vision, values, and goals 1. Organization’s mission, vision, values, goals Mission: purpose for existence Vision: where organization wants to be in the future Values: principles by which organization conducts business Goals: what organization needs to accomplish in short run to achieve the vision 2. Department mission Each department adopts a mission, vision, values, and goals which contribute directly to the organization’s mission, vision, values, and goals Example: - University mission: To provide an undergraduate liberal arts education for any student, regardless of race, age, political preference, or religious preference - Department of Management mission: To educate students in the art and science of management and to prepare them for positions in the profession of management Another way to look at it… Organization mission, vision, values, goals Departmental mission, vision, values, goals Departmental mission, vision, values, goals Departmental mission, vision, values, goals Your turn to participate … Corporate vision: to become a premier nationally recognized university Finance: Student enrollment: Computer Center: Your department: Write the mission for your department Mission Vision Values Goals 3. Let’s summarize quality planning Integrates departmental operations into corporate mission and vision (alignment) Results: corporate-wide strategy on how to meet customer requirements Achieves vision of organization II. Quality measurement and reporting Includes: Performance measurement: indicators and goals Alignment of goals Department continuous improvement plan 1. Performance measurement: indicators and goals Must manage by facts Information obtained allows decisions based on objective data Indicators are used to measure performance Quality indicator measures the performance of a process which meets customer requirements Examples of indicators Student achievement Accurate billing Student registration process Retention rate Student satisfaction How do you select indicators? Guiding principle #1: MEASURE WHAT MATTERS Guiding principle #2: SET PRIORITIES - Required by agencies (legal, accreditation, state, strategic plan) Guiding principle #3: BE REASONABLE And next? When the measurement of an indicator demonstrates that a process needs improvement, then a goal may be established Goals give us a target or milestone at which to aim 2. Department continuous improvement plan (CIP) The departmental plan contains indicators for the end results or outcomes important for the department to measure, and goals for those outcomes where customer requirements are not being met 3. Let’s develop a plan… Answer these questions: What is my mission? How am I organized? Who are my stakeholders/constituents/students? With whom am I affiliated? Products and services offered (courses) How do I conduct my business (meetings, etc)? What have I promised (mission) and what are the major program outcomes/learning objectives for my stakeholders? What are the indicators used to determine performance? What is my current performance at meeting their expectations (program outcomes)? What is my goal for continuous improvement on this performance? Write your own plan… YOUR UNIVERSITY CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PLAN I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. X. DATE: DEPARTMENT: MISSION: ORGANIZATION: CONSTITUENTS: Internal constituents: External constituents: AFFILIATIONS: MEETINGS: STANDING COMMITTEES: PROGRAM OUTCOMES: PERFORMANCE INDICATORS: 1. Strategic plan 2. Continuous improvement 3. Other A little review… UNIVERSITY MISSION AND VISION UNIVERSITY INDICATORS/GOALS (CORPORATE CIP) DEPARTMENT INDICATORS/GOALS (DEPARTMENT/MAJOR CIP) Bachelor of Arts in Accounting Learning Objective or Outcome Quality Present (2006) For Each Major Indicators Performance CQI goal 1. Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret accounting principles MFT CPA exam GSS Internal exams 95th percentile Etc. Etc. 98th percentile 2. Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret managerial accounting principles MFT CPA exam GSS Internal exams 87th percentile 98th percentile 3. Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret auditing principles and processes MFT CPA exam GSS Internal exams 89th percentile 98th percentile 4. Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret cost accounting principles MFT CPA exam GSS Internal exams 85th percentile 98th percentile 5. Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret federal income tax principles MFT CPA exam GSS Internal exams 82nd percentile 98th percentile Percentile Major Field Test Scores 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Acc P Mg Ac P Aud P CA P FIT P 2002 S 2003 S 2004 S 2005 S 2006 S Semester Legend: Acc P = Accounting Principles; Mg Ac P = Managerial Accounting Principles; Aud P = Auditing Principles; CA P = Cost Accounting Principles; FIT P = Federal Income Tax Principles Percent of accounting graduates Job upon graduation 100 95 90 85 % w Job 80 75 70 2002 S 2003 S 2004 S Semester 2005 S 2006 S Percent satisfied with advising Student satisfaction with advising (Graduating Senior Survey: GSS) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Sat/advis 2003 S 2003 W 2004 S 2004 W 2005 S 2006 S Semester CIP Worksheet YOUR UNIVERSITY CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT REPORT DEPARTMENT: Department of Accounting OPPORTUNITY FOR IMPROVEMENT: Student achievement (Accounting Principles – Acc P) INDICATOR: Major field test (MFT) PRESENT LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE: 80th percentile (2002 S) GOAL: Incremental improvement until 98th percentile TEAM MEMBERS: Department of Accounting faculty, students, alumni, business representatives Date initiated Plan of action Internal or external constituent Source of data Resources required Estimated completion date Measure of effectiveness May 2003 Review curriculum Internal Accounting Curriculum Budgeted August 2003 Improved Acc P scores if successful Dec 2003 Identify root cause of low Acc P MFT scores Internal and external Students, scores, curriculum, faculty, teaching methods, etc. NA: budgeted May 2004 Improved Acc P scores if successful Make appropriate changes as determined Summary Form Degree Learning Objectives/ Outcomes How Measured Bachelor of Arts in Accounting Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret accounting principles MFT, CPA exam, GSS, Internal exams Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret managerial accounting principles MFT, CPA exam, GSS, Internal exams Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret auditing principles and processes MFT, CPA exam, GSS, Internal exams Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret cost accounting principles MFT, CPA exam, GSS, Internal exams Recognize, understand, and develop skills to perform and interpret federal income tax principles MFT, CPA exam, GSS, Internal exams Use of results: Describe how you used the data to make changes in the teaching process that ultimately led to increased student learning and improved scores Verbs for stating general instructional objectives Analyze Compute Interpret Perform Translate Apply Create Know Recognize Understand Appreciate Demonstrate Listen Speak Use Locate Think Write Comprehend Evaluate Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Complex, Logical, Judgmental Behaviors) Analyze Conclude Deduce Formulate Plan Appraise Contrast Defend Generate Structure Combine Criticize Evaluate Induce Substitute Compare Decide Explain Infer Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Language Behaviors) Abbreviate Edit Punctuate Speak Tell Accent Hyphenate Read Spell Translate Alphabetize Indent Recite State Verbalize Articulate Outline Say Summarize Whisper Call Print Sign Syllabify Capitalize Pronounce Write Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Mathematical Behaviors) Add Derive Group Number Square Bisect Divide Integrate Plot Subtract Calculate Estimate Interpolate Prove Tabulate Check Extrapolate Measure Reduce Tally Compute Extract Multiply Solve Verify Count Graph 4. In education, indicators frequently measure the following… Student achievement/effectiveness of educational process - was a planned, successful outcome achieved? Appropriateness of programming/curriculum - was the curriculum appropriate for desired outcomes? Student satisfaction - were students satisfied with advising, etc.? Retention rates - were retention rates acceptable? Graduation rates - were graduation rates acceptable? More education indicators… Customer (students, parents, community) satisfaction - were customers satisfied with products/services and outcomes of educational process? Enrollment management - did enrollment meet planning goals? Campus climate - does campus climate meet mission/goals for LU? Resource utilization - was product/service delivered in cost-effective manner? - was product/service a good value for the cost? - was product/service affordable? 5. Summary of quality measurement and reporting Uses objective data for continuous improvement purposes Provides opportunity to know and manage current performance Identifies opportunities to improve Prioritizes attention Requires departmental continuous improvement plan (CIP) - measures operational and management indicators - establishes departmental goals that support corporate goals - reports on progress towards goals III. Quality improvement Includes actions taken to improve processes that deliver products/services to customers Actions can be efforts of individuals or quality improvement teams/departments Here’s what we will discuss: - action for improvement - faculty/staff involvement - continuous quality improvement teams/departments 1. Action for improvement Here’s the process: - identify the opportunity to improve - analyze the problem - take action to resolve problem - actions can be made by individuals and teams - requires skills that may be new to many faculty and staff Skills and required concepts… Understanding stakeholders and their requirements Measurement by facts Process definition and analysis Root-cause identification Plan-Do-Check-Act on-going improvement cycle Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle (PDCA) 1. Plan what to do 4. Act to improve what you did Act Check 3. Check the results Plan Do 2. Do what you planned 2. Faculty/staff involvement in CQI Invaluable resources Know and use the processes/deliver the product and service Know how best to improve the processes Closest to the “customer” Need to know: - CQI philosophy - Department CIP plan - Problem solving skills - Customer relations skills 3. Quality improvement teams (QITs) Groups of faculty/staff who analyze problems and recommend actions to resolve problems Two kinds of teams: - functional (one department) - cross-functional (from different departments) 4. Summary of quality improvement Individuals or teams can make improvements Problem-solving skills include: - managing by facts - process analysis - root-cause identification and elimination - PDCA (plan, do, check, act) IV. Cultural changes Here are our topics for this one: Management commitment and leadership in process Organize for CQI Education and training Communication Our professional attitude and behavior Recognition Paradigm shift… The shift is from one of looking for assessment activities (narrow) to one of pursuing continuous improvement (inclusive) opportunities Requires a “higher” approach to the process 1. Management commitment and leadership responsibilities Knowledge of CQI Encourage innovation and risk-taking Remove barriers Speak about CQI and process Encourage participation Provide necessary resources Become a role model Let’s exercise… 1. 2. 3. List some barriers to CQI in the organization and in your area of responsibility 2. Organize for CQI Organize so everyone will know: 1. Who will develop the plan 2. Who will oversee implementation 3. How employees will be involved in development and implementation 4. What will be the responsibilities of: - the board - executive staff - deans/department directors - front-line employees 5. Communication channels 3. Education Management education CQI awareness training Problem-solving skills - management by facts - process analysis - root cause identification - PDCA Tools for CQI Tools and techniques… Brainstorming Multi-voting Selection matrix Checklist Graphs Pareto diagram Process flow chart Histogram Cause-and-effect diagram Problem statement Brainstorming Technique used to generate a large quantity of ideas in a short time It is useful because it encourages participation and contributions from all team members There is a right way and a wrong way Benchmarking Benchmarking is a process of comparing one’s performance on a specific achievement with that of another department/organization, etc. Usually compares one’s own performance with a “best in class” Can be useful in setting and reaching realistic goals Can be harmful if you select one that is just a mediocre department/company Check-sheet Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Wrong Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 Etc. A check-sheet is an easy-to-use form for collecting and processing data. It is used by teams to collect data and help identify and quantify problems. Checklist Registration checklist Yes No Student ID Admission number Meal plan Housing location Adviser assigned A checklist is a list of items or steps to be checked off or referred to in completing a process. It provides an organized way of proceeding. Bar graph 90 80 70 60 50 East West North 40 30 20 10 0 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr Bar graphs visually represent comparisons among groups of data. Quantities are shown by means of uniform-width bars (rectangles) whose length is proportional to the number being represented. Line graph 100 90 80 70 60 East West North 50 40 30 20 10 0 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr A line graph is a way to visually display data for trends or comparisons. Histogram 20 18 Admissions in 000’s 16 14 12 10 Admissions 8 6 4 2 0 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 A histogram is another type of bar chart. It is a graphic representation of the distribution of a set of data. It displays patterns that are difficult to see in a simple table of numbers. Pie chart 20.4 20.4 27.4 Section Section Section Section 90 A pie chart is used to visually show relative relative proportions or frequency of items. It can be used to show real numbers or percentages. 1 2 3 4 Pareto chart Number of complaints 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Santa overslept Sleigh broken Wrong toy Wrong address Reindeer ill Pareto analysis is a ranked comparison of factors that make up the subject being analyzed. It helps a team focus on the vital few problems or causes of problems that have the greatest impact on what the team is trying to improve. The 80-20 rule: 80% of the problems result from 20% of the causes Cause-and-effect diagram Machine Man Night technician Mean machine Day super Problem statement Floors are dirty Cleaning sol Process for cleaning Mops Materials Methods This technique is used to generate, organize, and display the factors that might contribute to a problem. Lines and arrows show relationship between problem and potential causes Process flow chart Registered for class Arrived on campus Picked up packet Found dorm room Went to class Confirmed student identity A process flow chart is a graphic representation of the sequence of steps in a process. It also helps clarify the relationship between steps. Problem statement It must: Be measurable Be specific State the pain of how customers are affected It must not: Imply blame Imply solutions Problem statement says in specific and concrete terms what the data have revealed and what the team will now focus on improving 10 – 4 exercise Used to quickly determine priorities among issues and/or ideas Each member given 10 points to “spend” Can vote on ideas as desired, but upper limit is 4 points on any particular item Ideas getting the most points are declared winners Top numbers established in advance, i.e., top 5, top 10, etc. 4. Communication Varied – newsletters, bulletin boards, e-mail, etc. Wide-spread Frequent Timely 5. Our professional attitude and behavior We have been working “in” our profession We must begin working “on” our profession We are responsible for the success of (fill in the blank) University Stakeholders expect the very best from us We are a million dollar business unto ourselves If this were your business, would you manage it differently? 6. Recognition Spontaneous and planned events Individual and team recognition Small wins and large wins CQI efforts and successes 7. Summary of cultural changes Management’s actions demonstrate leadership Organization’s structure must support CQI New skills are needed for faculty and staff to participate Information must be communicated We must manage our business as though it were our business Recognition should reinforce continuous improvement activities Summary of CQI process Quality planning Quality measurement and reporting Quality improvement Cultural changes And the benefits of CQI… Improved outcomes of the educational processes (student learning outcomes) Increased student satisfaction Increased external stakeholder satisfaction Improved organizational performance Improved financial strength Questions… Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Creative Behaviors) Alter Paraphrase Reconstruct Rephrase Rewrite Ask Predict Regroup Restate Simplify Change Question Rename Restructure Synthesize Design Rearrange Recognize Retell Systemize Generalize Recombine Reorder Revise Vary Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (General Discriminative Behavior) Choose Detect Identify Match Place Collect Differentiate Indicate Omit Point Define Discriminate Isolate Order Select Describe Distinguish List Pick Separate Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Social Behaviors) Accept Communicate Discuss Invite Praise Agree Compliment Excuse Join React Aid Contribute Forgive Laugh Smile Allow Cooperate Greet Meet Talk Answer Dance Help Participate Thank Argue Disagree Interact Permit Volunteer Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Study Behavior) Arrange Compile Itemize Mark Record Categorize Copy Label Name Reproduce Chart Diagram Locate Note Search Cite Find Lock Organize Sort Circle Follow Man Quote Underline Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Music Behavior) Blow Compose Hum Pluck Strum Bow Finger Mute Practice Tap Clap Harmonize Play Sing Whistle Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Physical Behaviors) Arch Bend Catch Climb Float Bat Carry Chase Face Grab Grasp Kick Pull Skip Swim Grip Knock Push Somersault Swing Hit Lift Run Stand Throw Hop March Skate Step Toss Jump Pitch Ski Stretch Walk Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Arts Behaviors) Assemble Dot Illustrate Press Stamp Blend Draw Melt Roll Stick Brush Build Drill Fold Mix Mold Rub Sand Stir Trace Carve Color Form Frame Nail Paint Saw Sculpt Trim Varnish Construct Hammer Paste Shake Wipe Cut Handle Pat Sketch Wrap Dab Heat Pour Smooth Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Drama Behaviors) Act Display Express Pass Show Clasp Emit Leave Perform Sit Cross Enter Move Proceed Start Direct Exit Pantomime Respond Turn Verbs for stating specific learning outcomes (Laboratory Science Behaviors) Apply Demonstrate Keep Prepare Specify Calibrate Dissect Lengthen Remove Straighten Conduct Feed Limit Replace Time Connect Grow Manipulate Report Transfer Convert Increase Operate Reset Weigh Decrease Insert Plant Set