Uniform-Glossary Redlined
advertisement

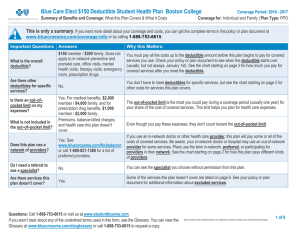
Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms • This glossary defines many commonly used terms, but isn’t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be different from the terms and definitions in your plan or health insurance policy. Some of these terms also might not have exactly the same meaning when used in your policy or plan, and in any such case, the policy or plan governs. (See your Summary of Benefits and Coverage for information on how to get a copy of your policy or plan document.) • Bold text indicates a term defined in this Glossary. • See page 6 for an example showing how deductibles, coinsurance and out-of-pocket limits work together in a real life situation. Allowed Amount The amount the provider agreed to accept as payment for billed amounts or the most common charge for similar services in your area. Also called “eligible expense”, “payment allowance”, or “negotiated rate”. Appeal A request that your plan review a decision that denies a benefit or payment (either in whole or in part). Balance Billing When a provider bills you for the balance remaining on your bill that is not covered by your plan. This amount is the difference between the actual billed amount and the allowed amount. Brand Named Drugs The first drug of its kind and can only be made and sold by the company that invented it. Brand drugs can be either “preferred brand drugs” or “non-preferred brand drug.” Claim A request for payment made by you or your health care provider to your plan for health care or services received. Coinsurance Your cost share for a covered health care service, calculated as a percentage (for example, 20%) of the allowed amount for the service. You generally pay coinsurance after paying any deductible you owe. (For example, if the plan’s allowed amount for an office visit is $100 and you’ve met your deductible, your coinsurance payment of 20% would be $20. The health insurance or plan pays the rest of the allowed amount.) Different coinsurance will apply to care received by a network provider and an outof-network provider. Copayment A fixed amount (for example, $25) you pay for a covered health care service, usually when you receive the service. The amount can vary by the type of covered health care service. Different copayments will apply to care received by a network provider and out-of-network provider. Cost Sharing Your share of costs for services covered by a plan that you must pay out of your own pocket (sometimes called “out-of-pocket costs”). Cost Sharing examples include copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance. Deductible The amount you owe before your plan begins to pay. Most plans have an “overall deductible” and “specific deductibles”. Overall Deductible: the amount you owe during a coverage period (usually one year) for health care services your plan covers before your plan begins to pay. For example, if your overall deductible is $1000, your plan won’t pay anything until you’ve met your $1000 overall deductible for covered health care services subject to the overall deductible. The overall deductible may not apply to all services. Also known as “yearly deductible”, “plan deductible” or “individual/family deductible.” Specific Deductible: the amount you owe for certain covered health care or services your plan covers before your plan begins to pay for that health care or service. For example, if the plan has a $250 specific deductible for hospital stays, you pay the $250 specific deductible and your plan pays on the remaining allowed amount. Diagnostic Test Care to figure out what your health problem is. For example, an x-ray can be a diagnostic test to see if you have a broken bone. Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Equipment or supplies ordered by a health care provider for everyday or extended use. DME may include: oxygen equipment, wheelchairs, crutches or blood testing strips for diabetics. Emergency Medical Condition An illness, injury, symptom or condition that is severe enough (including severe pain), that if you did not get immediate medical attention you could reasonably expect one of the following to result: 1) Your health would be put in serious danger; or 2) You would have serious problems with your bodily functions; or 3) You would have serious damage to any part or organ of your body. Emergency Medical Transportation Ambulance services for an emergency medical condition. Types of emergency medical transportation may include transportation by air, land, or sea. Your plan may not cover all types of emergency medical transportation, or may pay less for certain types. Emergency Room Care Services to check for an emergency medical condition and treat you to keep an emergency medical condition from getting worse. These services may be provided in a licensed hospital’s emergency room or other place that provides care for emergency medical conditions. Excluded Services Your plan does not cover these services. No payment will be made for these services under your plan. You will pay the full cost for these services. Explanation of Benefits A statement from your health plan or issuer showing the payment made; the provider discount (if applicable) and your costs. Formulary A list of drugs your plan covers. a list of drugs covered by your health plan. Not all drugs are on each health plan’s formulary. The list of drugs, or formulary, may include how much you pay for each drug. You may have to pay different amounts for different drugs. Please consult your plan for your formulary list and costs. Generic Drugs A drug that copies a brand name drug. A generic drug is the same as a brand name drug in dosage form, safety, strength, quality, performance and use. Generic drugs usually have the lowest cost share. Grievance A complaint that you communicate to your health insurer or plan. Also called a “complaint”. Habilitation Services Health care services that focus on learning new skills for daily living. For instance, an individual may have been born without the abilities, skills or knowledge and must learn them. Home Health Care Health care services and supplies you get in your home under your doctor’s orders. Services may be provided by nurses, therapists, social workers, or other licensed health care providers. Home health care usually does not include help with non-medical tasks, such as cooking, cleaning or driving. Hospice Services Services that provide comfort and support for persons in the last stages of a terminal illness and their families. Hospitalization Care in a hospital that requires admission as an inpatient. An overnight stay for observation could be outpatient care. Also called “inpatient care”. Medically Necessary Health care services or supplies needed to prevent, diagnose or treat an illness, injury, condition, disease or its symptoms and that meet accepted standards of medicine. Minimum Essential Coverage Health coverage that will meet the individual responsibility requirement under the Affordable Care Act. Minimum essential coverage generally includes plans available through the Marketplace or other individual market policies, Medicare, Medicaid, CHIP, TRICARE and certain other coverage. Minimum Value The Affordable Care Act generally sets certain value standards for plans. For example, “bronze level” individual insurance is designed to pay about 60% of the total cost of certain essential medical services, on average, for a standard population. Plans are subject to a minimum value standard that is similar to that 60% standard, although the benefits covered by the plan may differ from those covered under individual insurance. Also called “Minimum Value Standard”. Network The facilities, providers and suppliers your plan has contracted with to provide health care services. Network Provider A provider who has agreed to accept a lower amount for billed amounts through a contract or agreement with the insurance company. If you plan uses provider levels or tiers, you will pay more to see some providers. Your policy may use the term “in-network”, “preferred provider” or “participating provider” instead of “Network Provider.” Out-of-Network Provider A provider who doesn’t have a contract with your health insurer or plan to provide services to you. You’ll generally pay more to see a non-preferred provider than to see a preferred provider. Check your policy to see if you can go to all providers who have contracted with your plan, or if your plan has a “tiered” network and you must pay extra to see some providers. Your policy may use the term “nonpreferred” or “non-participating” instead of “out-of-network provider.” Out-of-Pocket Limit: The most you pay during a coverage period (usually one year) for your share of the costs of covered services. After you meet this limit, the plan will usually pay 100% of the allowed amount. This limit helps you plan for health care costs. This limit never includes your premium, balanced-billed charges or health care your plan doesn’t cover. Physician Services Health care services a licensed medical physician, including an M.D. (Medical Doctor) or D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine), provides or coordinates. Plan Health benefit coverage issued to you directly (individual plan) or through an employer, union or other group sponsor (employer group plan) that provides coverage for certain health care costs. Also called health insurance plan, policy, health insurance policy or health insurance. Preauthorization The process of obtaining permission from the plan to receive certain drugs, medical treatment, services or supplies before receiving the care. Preauthorization does not apply to emergency care. Preauthorization is not a promise your health plan will cover the cost. Sometimes called “prior authorization”, “prior approval” or “precertification.” Premium The amount you pay for your plan. You and/or your employer usually pay it monthly, quarterly or yearly. Prescription Drugs Drugs and medications that by law require a provider prescribe. Preventive Care Care or services received to avoid illness and improve your health at no cost to you. The goal is to protect, promote, and maintain health and wellbeing. Preventive care may be subject to age requirements and/or medical history. You can ask your provider if the care received is preventive care. Please see www.healthcare.gov/preventive-care-benefits for a complete listing of preventive care or call your plan for more information. Common preventive services include: For Adults Only: screenings (instead of screenings could use “check or checking on blood pressure…”) for blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, tobacco and alcohol use, obesity and other general screenings; shots prevent illness. For Women Only: mammography and breast cancer counseling; cervical cancer screening; contraceptives; and well-women visit. For Children (up to 18 years old) Only: shots to prevent illness; autism screening; obesity services; health screenings; and vision screening Primary Care Provider A physician, including an M.D. (Medical Doctor), D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) or any other provider who your plan allows to be a primary care provider. Your primary care provider coordinates your care and services. Also known as “Primary Care Physician.” Provider A physician, including an M.D. (Medical Doctor) or D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine), other health care professional (including nurse practitioners, physician assistants, chiropractor or any other provider allowed by the plan), hospital, or other health care facility licensed, certified or accredited as required by state law. Referral A written order from your primary care provider for you to see a specialist or get certain health care services. If you don’t get a referral first, the plan may not pay for the services. Rehabilitation Services Health care services that help a person regain skills and the ability needed for daily living that have been lost or impaired because of disease or injury. These services may include physical and occupational therapy, speech-language pathology and psychiatric rehabilitation services in a variety of inpatient and/or outpatient settings. Screening A type of service that includes tests or exams to detect the presence of a condition. Preventive screenings are performed when you have no symptoms, signs or prevailing medical history of a disease or condition. Skilled Nursing Care Services, such as nursing or therapy, performed or supervised by licensed nurses in your home or in a nursing home. Specialist A physician focusing on a specific area of medicine or a group of patients to diagnose, manage, prevent or treat certain types of symptoms and conditions. Specialty Drug A type of prescription drug that, in general, requires special handling or ongoing monitoring by a health care professional, or is relatively difficult to dispense. If the plan’s formulary uses “tiers,” and specialty drugs are included as a separate tier, you will likely pay more in cost sharing for drugs in the specialty drug tier. UCR (Usual, Customary and Reasonable) The averaged billed amount for medical services in an area by available providers. This amount is sometimes used to determine the allowed amount. Urgent Care Care for an illness, injury or condition serious enough that a reasonable person would seek care right away, but not so severe as to require emergency room care.