Fiber Evidence
advertisement

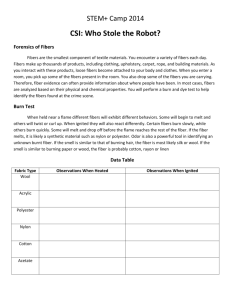
Chapter 6: Fibers Fibers • Fiber: is the smallest unit of a textile material woven or twisted together to form a thread or yarn. • Fibers (like hair) are among the most common items left at a crime scene. • Class evidence- mass produced by textile difficult to trace back • Probative value- can create connection btwn a victim and suspect. Activity 6.1 pg. 129 • Collection and observing fibers from your shirt and pants. Sources & Types of Fibers • Fibers can occur naturally (plant and animal fibers) Or • Fibers can also be man-made (synthetic). Types of Fabric Weave In a weave, the lengthwise yarn is called the warp. The crosswise yarn is called the weft or woof. Types include: Plain Twill Satin 5 Woven Fabric PLAIN Simplest and most common weave Warp and weft pass under each other alternately Design resembles a checkerboard 6 Woven Fabric TWILL Create by passing the warp yearn over one to three weft yearns before going under one Makes a diagonal weave Design resembles a stair steps Denim is the most obvious example 7 Woven Fabric SATIN The yarn interlacing is not uniform Creates long floats Interlacing weave passes over four or more yarns Satin is the most obvious example 8 Knitted Fabric Knitted fabrics are made by interlocking loops into a specific arrangement. It may be one continuous thread or a combination. Diagram: 9 Blends use of different fabrics & colors to create the warp and weft patterns. Fabric Observation • Laboratory Activity 6.1 • Pg. 131 Fibers All fibers are made of polymers which are long chains of repeating units. The word polymer means many (poly) units (mer). The repeating units of a polymer are called monomers. 12 Fiber Morphology Investigators use: 1. fiber cross section 2. chemical structure 3. synthetic polymers for forensic analysis Fiber Cross Section • The cross section of a manmade fiber can be manufacturer-specific • Unusual cross sections increase fiber association. Cross-sectional views of nylon carpet fibers as seen with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) Types of Fibers • Synthetic Polyester Rayon Nylon Acetate Acrylic Spandex • Natural Silk Cotton Wool Mohair Cashmere 15 Natural Fibers Many different natural fibers that come from plants and animals are used in the production of fabric. Cotton fibers are the plant fibers most commonly used in textile materials The animal fiber most frequently used in the production of textile materials is wool, and the most common wool fibers originate from sheep. http://www.fireflydiapers.com/articles/diaperarticle_naturalfibersabsorb.htm Natural Fibers • Wool--animal fiber from sheep, may also be goat (mohair), rabbit (angora), camel, mink, beaver • wool: composed of polypeptide keratin chains of amino acid. Wool Fibers (400X) • main bond is sulfur which accounts for the smell of wool when burned 17 Chemical structure: Natural fibers • Silk: composed of proteins, only 2 amino acids • Silk--animal fiber produced by silkworms (cocoon) Cotton • #polymers is glucose # smell like burning leaves # 40% of all fabric is cotton # 60% of all clothes and furniture # low probative value because its too common • Linen: made from flax plant # Contains cellulose (fibers are longer than cotton) # often blended with other fibers because it is brittle. Synthetic Fibers More than half of all fibers used in the production of textile materials are synthetic or man-made. Nylon, rayon, and polyester are all examples of synthetic fibers. *nylon and polyester are the most common Cross-section of a man-made fiber Fibers under a microscope Images: http://www.trashforteaching.org/phpstore/product_images/YarnWS.JPG http://www.fbi.gov/hq/lab/fsc/backissu/july2000/deedric3.htm#Fiber%20Evidence http://www.jivepuppi.com/images/fiber_evidence.jpg Synthetic Fibers Made from cellulose • Rayon--first man-made fiber; • Acetate:– made from a reaction with acetic acid. Synthetic Fibers (Made from derivatives of petroleum, coal and natural gas) • Acrylic- used in carpets • Spandex--elastic properties 23 Forensics of Fiber Analysis • Cross transfers of fiber often occur in cases in which there is person-to-person contact • More contact= more fiber transferred Forensic Analysis • What can be used to identify and compare fibers as forensic evidence? See book pg. 135 1. fiber cross section 2. View through microscope 3. Burn test 4. Thermal decomposition 5. Refractive index 6. Chemical test Microscopic Examination • A compound microscope: uses light • The comparison microscope (two compound microscopes joined by an optical bridge) is used for more precise identification. • phase-contrast microscope, reveals fiber structure • Scanning electron microscope converts the emitted electrons into a photographic image for display. This affords high resolution and depth of focus. Fiber Comparison Can you tell the difference(s) between the cotton on the left and the rayon on the right? Spectrometer • The spectrometer, which separates light into component wavelengths. • By passing light through something to produce a spectrum, the analyst can read the resulting lines, called "absorption lines." • specific wavelengths are specific to molecules of the substance. Fiber Evidence Collection • Fibers are gathered at a crime scene with tweezers, tape, or a vacuum. • They generally come from clothing, drapery, wigs, carpeting, furniture, and blankets. • For analysis, they are first determined to be natural, manufactured, or a mix of both. Steps of Fiber Analysis • The first step in fiber analysis is to compare color and diameter. • Dyes can also be further analyzed with chromatography, which uses solvents to separate the dye's chemical constituents. Fiber Color • Color influences the value given to a particular fiber identification. • Often several dyes are used • How color is applied and absorbed along the length of the fiber are important comparison characteristics. • Color-fading and discoloration can also lend increased value to a fiber association. Fiber Analysis Testing Fibers 1) Burn Test: look @ how a fiber burns, its odor, and appearance of ash. 2) Thermal decomposition: how a fiber breaks down when heated. *it returns to its monomer (initial building block) * ex: Acetate acetic acid litmus test will turn paper blue to red • Thermal Decomposition of fiber activity 3) Chemical test: test the solubility and decomposition of a fabric using a strong acids (Hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid) or strong bases (NaOCl, acetone, NaOH) – this determines the fabrics polymers. 4) Density: m/v (pg. 148). Density of water is 1.00 g/ml. Olefin is the only fabric that will float in water. 5) Refractive index: bending of light as it passes from air into a solid or liquid -- investigators measure the refractive index of an unknown sample with liquids of a known refractive index. --place sample in different liquids until Becke line is no longer visible liquid w/ high index A same index as fabric B liquid w/ low refractive index C 6) Fluorescence: some fibers will fluoresce when exposed to UV light --- laundry soap and some bleach has whiting agents that cause blue light to be reflected making it appear whiter. 7)Dyes: investigators use a fabric to see if it accepts a particular dye to identify and compare it to an unknown sample 8) Chromatography: separation of dyes by thin layer chromatography (TLC) Rf value = distance of pigment distance of solvent front Other test used in Fiber Analysis 9) FTIR: Fourier Transform Infrared • based on the absorption and wavelength of light in a fabrics polymer. • can be used on a single fiber • Non-destructive 10) PGS-MS: Pyrolysis Gas Chamber-Mass Spectrometry • Burns and separates each combustion product of sample • Match results of chromatogram & products to known • Can be used in short length fibers but is destructive. Fiber Forensics FYI- do not copy • analyst gets only a limited number of fibers to work with—sometimes only one. • Fibers are sent to the lab for analysis. • Fibers from scene are compared to victim Copy### • Any inconsistency (one property does not match) is sufficient to cancel association Fiber Transfer and Persistence • Fibers can be used as trace evidence due to fiber transfer. • How easy the fiber is transferred is affected by: • • • • • • • Area of contact the amount of pressure used Any friction due to side to side contact Number of passes or contacts Kind of clothing donor/recipient was wearing Fiber type, length and texture History of the garment. • How long transfer fibers remain on victim is fiber persistence. • Time of wear and movement • What is covering the fabric • Type of activity • Weather condition ** fiber persistence decreases exponentially with time of wear. Types of Fibers - Key Acrylic Yarn Cotton Yarn Nylon Rope Polyester Yarn Rayon Rope Wool Yarn