Body Fluid Regulation and Excretory System
advertisement

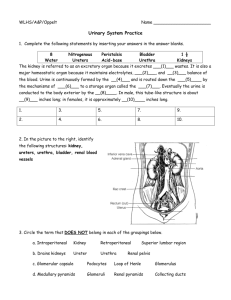
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretory System Body Fluid regulation Retaining or eliminating certain ions (such as Na+, Cl-, K+, HCO3-) and water (in and out must be equal) Osmosis – movement of water from greater concentration to less concentration (toward higher solutes!!) Aquatic animals Marine invertebrates (mollusks and arthropods) and cartilaginous fish (sharks) have body fluids isotonic to sea water Bony fish – have some salt, prone to water loss Salt water bony fish Drink water constantly Freshwater bony fish – hypertonic Never drink water, constantly eliminate excess Terrestrial animals Lose water by evaporation, respiration, sweat and feces Drink water occasionally to replace what is lost Birds and reptiles can drink salt water because they have a salt gland near the eyes Humans conserve water by producing a hypertonic urine Nitrogenous waste products Amino acid metabolism – broken down for energy or converted to fats, carbs for storage amino groups are removed and excreted as ammonia, urea, or uric acid, depending on species Ammonia – little or no energy needed in conversion by adding H (NH3) Toxic and needs a lot of water to wash away Excreted by bone fish, aquatic invertebrates, amphibians Nitrogenous waste continued Urea – excreted by terrestrial amphibians and mammals Less toxic than ammonia and needs less water to remove from body Requires energy Produced in liver Uric acid – insects, reptiles and birds Not very toxic, poorly soluble in water Requires most energy, but conserves most water White stuff in bird droppings Excretory organs Planarians Excretory tubules Flame cells – contain beating cilia, propels fluid through tubules and out of body Earthworms Nephridia – tubule with ciliated opening and excretory pore Urine contains metabolic wastes, salts and water Insects Malpighian tubules – attached to gut Uric acid flows from hemolymph into tubules water flows from salt gradient but is usually reabsorbed Urinary system in humans Kidneys – size of fist, lower back, right slightly lower than left. Urine – product Kidney ureter urinary bladder urethra In males, urethra also carries sperm 3 parts Renal cortex – outer region, nephrons Renal medulla – renal pyramids Renal pelvis – inner hollow changer, urine collects here and carried to bladder via ureter Kidney stones (renal calculus), can block renal pelvis or ureter Nephron Over 1 million in each kidney Produce urine Primarily found in renal cortex Structure: Glomerular capsule proximal convoluted tubule loop of the nephron distal convoluted tubule collecting duct (delivers urine to renal pelvis) Glomerulus – capillary bed Urine formation – 3 processes Glomerular filtration at the glomerular capsule Tubular reabsorption at the convoluted tubules Tubular secretion at the convoluted tubules Figure 38.9 Urine formation and homeostasis Hypertonic urine – more concentrated than blood occurs as result of reabsorption of water ADA – antidiruetic hormone – post. Pituitary Water reabsorption at collecting duct Aldosterone – adrenal glands Excretion of K+, reabsorption of sodium Renin – enzyme, stimulates adrenal gland to relsease aldosterone due to low blood volume ANH – atrial natriuretic hormone – atria of heart due to increase in blood volume, blocks uptake of renin Acid- base balance Kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate ions and excrete hydrogen ions as need to maintain the normal pH of the blood. Urine pH = 6 Excess of H+ excreted Ammonia provides a buffer for H+