world history test
advertisement

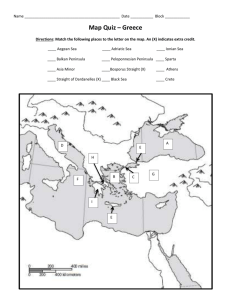
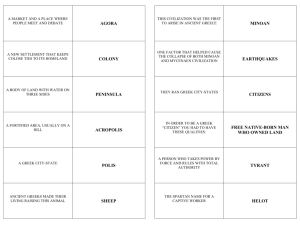
WORLD HISTORY TEST NAME__________________________ CHAPTER 5 – The Greek City-States DATE________________PER_______ MATCHING a. b. c. d. e. frescoes polis acropolis agora oracles ab. ac. ad. ae. bc. hoplite tyrants aristocracies democracy helots _____1. Rulers who seized power with popular support _____2. Government in which all citizens vote on decisions _____3. Predictors of the future _____4. Non-aristocratic soldiers _____5. Officials who supervised Spartan kings _____6. “Slaves of the state” in Sparta _____7. Non-Athenian residents of Athens _____8. “High city,” a feature of each city-state _____9. Government ruled by a few wealthy families _____10. Literally “rule by the people” _____11. Greek word for a city-state _____12. Elected rulers in Athens bd. be. cd. ce. de. ephors archons metics direct democracy representative democracy MATCHING a .Minoans b. Mycenaeans c. Illiad d. Odyssey e. Homer ab. ac. ad. ae. bc. Draco Solon Peisistratus Cleisthenes Marathon _____13. Epic poem about the Trojan War _____14. Archon who ended debt-slavery _____15. Ruler who set up a direct democracy in Athens _____16. Poet believed to be the author of the Greek epics _____17. Athenian lawgiver _____18. Greek defeat during the Persian Wars _____19. Earliest Greek civilization _____20. Tribal, warlike people who later conquered Crete _____21. Alliance of Greek cities led by Athens _____22. War caused by a rebellion of Greek cities _____23. Early Greek victory over Persia _____24. Epic which takes place after the Trojan War bd. be. cd. ce. de. Thermopylae Pericles Delian League Peloponnesian War Persian Wars MULTIPLE CHOICE _____25. Although we do not know that much about them, we can tell that the Minoans contributed ___________________________ to Greek civilization a)an established sea trade b)an early form of writing c)the art of glassblowing d)none of these _____26. Most Greek city-states developed around a a)temple b)fort c)seacoast d)river _____27. The purpose of the Olympic games was to a)honor Zeus b)strengthen city-states c)prepare for war d)choose a king _____28. City-states run by groups of nobles were known as a)hoplites b)tyrants c)democracies d)aristocracies e)none of these _____29. In Sparta, the ephors a)supervised the kings b)ran the army c)oversaw taxes d)made trade policy e)none of these _____30. Athenians would have preferred spending money on a)private homes b)public buildings c)a strong army d)personal decoration _____31. The Persians were defeated at Salamis by a superior a)Athenian army b)Spartan army c)Athenian navy d)Spartan navy e)Spongebob Squarepants _____32. Greece’s geography led its people to become a)farmers and herders b)nomadic tribes c)hunters and traders d)artisans and traders e)none of these _____33. Most city-states featured an agora, or a)fort b)temple c)store d)citadel e)none of these _____34. The Greek myths a)explained the laws of Greece b)told stories about the history of Greece c)told stories about gods and goddesses d)were a dictionary of linear B _____35. Spartans’ lives were based around a)government service b)the military c)religion d)philosophy e)Crabby Patties _____36. The Delian League was under the leadership of a)Sparta b)Troy c)Persia d)Corinth e)none of these _____37. The Peloponnesian War was won by a)Athens b)Sparta c)Persia d)Egypt e)none of these