World History CH 2
advertisement

World History CH 2
Section 1 Ancient Kingdoms of the
Nile
The land: Its Geography and its
Importance
Egypt Lies in North Africa with the Mediterranean Sea
to the North and the Red sea to the East
Today Desert covers most of Egypt.
In Ancient times, however, the landscape was much
different
12,000 years ago the area was covered in swampland,
that supported a large variety of animals
The most dominate feature of Egypt has been the Nile
for more than 5,000 years
The world and Africa
The Nile River
The nile river is the longest river in the world stretching
4,160 and it flows South to North
During the ancient times the Nile was “broken” by six
great cataracts, or rapids.
These Cataracts were difficult if not impossible to
navigate and flowed through channels of cut out rock
The Nile River Continued
The Ancient Egyptian Civilization was built between
the Nile Delta and the First great Cataract
{The Flow of the Nile South to North made it possible to move
goods upland}
The Winds from the north made it possible to move
goods up river inland using sails
{The Egyptian farmers planed their work around the annual
summer flooding of the Nile}
They would harvest their crops before the floods came
and the floods left fertile soil behind
They would dig canals to carry water to their fields and
they were able to grow several crops a year
Other Natural Advantages
The ability to travel both ways on the Nile was what
allowed upper and lower Egypt to unite into one
kingdom
{The Valleys location also gave the advantage of geographic
Isolation}
With the Mediterranean to the North and the Red sea
to the East and desert to the West they were naturally
protected from invasion
{The only way into Egypt was through the Isthmus of Suez in
the North East}
This land bridge allowed for a trade route and exchange
of ideas between Africa and Asia
Early steps toward civilization
By 12,000 BC the hunter-gatherers had moved into the
Nile river valley
By 3,800 BC they had started to mine Copper, to make
tools and jewelry, and mix with tin to make Bronze
They had also learned to glaze pottery
By 3,000 BC they had developed a form of writing
called Hieroglyphics using 600 signs or symbols
{At first they carved these pictures into stone but later developed
paper from the Papyrus plant }
They sliced the stem of the plant into long thin strips
and pressed them together making sheets of paper
Continued
Hieroglyphics were finally translated when in the
1800s the French Army found the Rosetta Stone
the Rosetta stone is a stone with three different
languages carved into it
Each passage says the same thing once in
hieroglyphics, once in Greek and once in an
Egyptian writing called demotic
{They used the Greek text to decode the hieroglyphics
and figure out how to decode all other hieroglyphics}
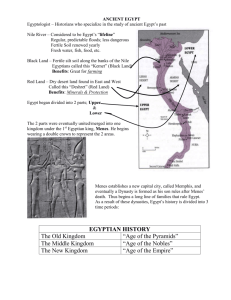
The Egyptian Kingdoms
Over the centuries two distinct cultures developed
along the Nile river
They formed two distinct kingdoms. Lower Egypt in
the North and Upper Egypt in the South
Sometime after 3200 BC the two kingdoms were united
under King Menes
King Menes founded a dynasty, or family of rulers
Menes and his successors gained new land and
improved irrigation and trade, making Egypt wealthier
They were considered political and religious leaders and
built temples and tombs in their honor
cointinued
The kings of the Egypt took the title of Pharaoh which
means “great house”
These Pharaohs held absolute power and were also
judges, high priests, and generals of the armies
From the time of King Menes to almost 300 BC some
30 dynasties ruled Egypt
This time span is divided into three Kingdoms
The Old Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom
The New Kingdom
The Old Kingdom
This existed from 2600 BC to 2180 BC
Many developments in science and art took place
during this time
They Egyptians of the old kingdom built the Great
Sphinx and the largest of the pyramids
The society was split into two classes
The Lower classes were peasants and farmers who
served in the army and worked on building projects
They made the Pyramids (not slaves) and canals for the
crops
Built in the old kingdom
continued
The upper class included the Pharaoh, the royal
family, priests, scribes, and Govt Officials
The upper class gradually became a small but
powerful hereditary group of nobles
{Toward the end the Pharaohs became weaker and the
nobles stronger}
For more than 100 years after the fall of the Old
Kingdom there were civil wars dividing Egypt
Rivals fought for control of the land
The Middle Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom began in 2050 BC when a new
line of Pharaohs reunited Egypt
This new era was the “golden age” for Egypt marked
by stability and prosperity
However at this time the nobles and the priests were
weakening the power of the Pharaoh
Around 1780 a people called the {Hyksos came in and
were able to take over using the Chariot and compound bow}
The Hyksos were able to take over but there is little
evidence of how they did and weather or not they were
violent, but they did rule for more than 100 years
Pyramids of the middle kingdom
The Hyksos
Little is known about the Hyksos which means
outsiders and they remained outsiders
Some Historians think that they were brutal and
destroyed the cities of Egypt
Others think that they were able to take over
with their superior technology but were fair to
the conquered Egyptians
This invasion and 100 year occupation by these
outside forces led to the second intermediate
period and The New Kingdom
The Hyksos, chariot, and bow
The New Kingdom
Eventually the leaders in upper Egypt drove the Hyksos
out of the country and a line of strong pharaohs united
Egypt
This new ruling group ran Egypt out of Thebes and
Pharaohs ruled with absolute power
These new Pharaohs used the technology of the
Chariot to create a strong army and conquered land in
the Eastern Mediterranean
Egyptian became an empire which when weaker
Pharaohs ruled, the conquered lands tried to break
away
The New Kingdom Continued
One of the New Kingdom rulers was {Hatshepsut one of
the first ever known Female rulers}
She reigned as Co-Pharaoh from 1503 BC to 1482 BC
with her stepson Thutmose III
Hatshepsut was a strong ruler who kept Egypt's
borders secure and built trade with other countries
She was able to rule due to Thutmose II’s Skin disease
leading to his death before Thutmose III was of age to
rule allowing Hatshepsut to rule in his stead
From 1380 to 1362 BC Amenhotep IV Ruled Egypt
and tried to bring Social and Religious changes
Hatshepsut’s Temple
Amenhotep IV
Before Amenhotep the Egyptians were polytheistic
meaning that they believed in many different gods
{Amenhotep believed in only one god or monotheism}
The one god that he believed in was the sun god Aton
and in recognition of Aton, Amenhotep changed his
name to Akhenaton or “he who is pleasing to Aton”
This caused struggle with the priests who did not like
their decreased role and decreased wealth
He was unable to change his peoples religious beliefs
and after his death the priests were able to take control
back and reestablish polytheism
Amenhotep/Akhenaton
Egypts Decline
After the death of Akhenaton few strong Pharaohs
ruled Egypt
Ramses II was one of those leaders who kept the
empire together and ordered the construction of
temples and monuments
A series of invasions including the Assyrians and the
Nubians led to the downfall of the Egyptian imperial
power
By the 300’s BC the rule of Egypt by Egyptians came
to an end
The Great Temple of Ramses II
Review
What Direction does the Nile river flow?
What made it possible to move goods up river?
Why did geographic isolation benefit the
Egyptians?
Why were we eventually able to read
Hieroglyphics?
Name the outside invaders that came in and
took over Egypt for a while.
What was special about Hatshepsut?