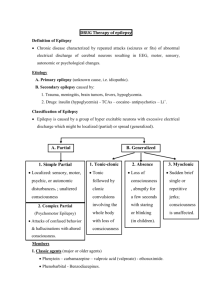
epilepsy

1) Lamotrigine all True Except :
a) Adjunctivetherapy
b) Enzyme inducer ( no effect on liver enzyme) c)Life threatening dermatitis d) Inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters .
3) regarding Pramipexole all true Except :
a) safelyusedinrenalinsufficiency b) used as monotherapy in milled cases of PD c) neuroprotective d) may cause mental disturbance
4) levodopa in combination w/ carbidopa : (choose ! correct )
a)daily dose of levodopa
Levodopa can causes all the AE EXCEPT: MCQ
a) Arrhythmia b) Glaucoma c)Retroperitoneal fibrosis d)Mood change
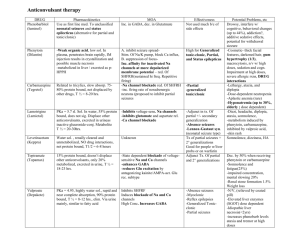
DOC of febrile seizures: MCQ
a)Diazepam
Carbamazepine is DOC in: MCQ
a)Partial complex seizures
Phenytoine
: Woman is using phynitoin, if she get pregnant, what is the best thing to do??
a) abrupt stop of phynitoin b) gradual stop c) decrease dose .....
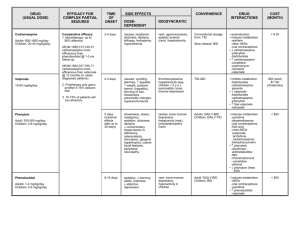
Anti-epileptic drugs:I think MCQ
a)Suppress but not cure seizures
b)Drugs combination commonly used initially c)Abrupt withdrawal recommended in non responding patients
d)Their plasma level must be monitored weekly
5) selegiline T or F:
a) ↓ on & off phenomenon b) ↓ nigral damage by toxins c) Lack cheese reaction d)Dependence upon chronic use
Lamotrigine: a- Can work by inhibiting the transmission of excitatory amino acids b- Can be used as monotherapy for treatment of Grand-mal seizures c- Can cause weight gain
d- Is an enzyme inhibitor.
Regarding antiepileptic drugs a- They relieve the symptoms but they don’t cure the disease (T) b- Plasma levels should be monitored daily (F) c- Sudden withdrawl is advised if the drug doesn’t relieve the symptoms (F) d- We should start treatment with combination of drugs (F)
Pramipexole : aHas a neuroprotective effect (T) bCan be used as a monotherapy in severe Parkinson disease (F) cCauses mental disturbances (T) dDose should be adjusted in renal failure (T) yo has abscense seizure with some attacks of generalize tonic clonic the DOC is; b. Ethosoximid
Doesn't treat status eplyptic is a.Valproic acida b. Clonazepam c. Diazepam d. Phenobarbitone
e. Phenytoin
1) Which one of the following antiepileptic drugs is effective in manicdepressive illness ? a) Ethosuximide b) Phenobarbital c) Carbamazepine d) Phenytoin
2) Adverse effects of phenytoin may includes ; a) Ataxia b) Hirsutism c) Gum hyperplasia d) Hyponatremia
3) Which one of the following is not an adverse effect of sodium valporate ? a) Hepatitis b) Loss of hair c) Anorexia d) Tremor
4) Regarding carbamazepine : a) Its plasma half-life decreases after chronic use . b) It is not effective in complex partial seizure c) Can be used in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia d) Causes megaloblastic anaemia
5) Lamotrigine :
a) blocks sodium channels b) is used as monotherapy for partial seizures c) is not effective in absence seizures d) may cause life-threating dermatitis
6) The drug of choice for febrile convulsions is : a) Phenytoin b) Diazepam c) Primidone d) Carbamazepine
7) Regarding the mechanism of action of vigabatrin : It a) inactivates Na+ channels . b) inhibits the activated Ca+ channels. c) inhibits GABA aminotransferase . d) potentiates GAD enzyme.
8) Topiramate : a) potentiates the inhibitory effect of GABA . b) is effective in the treatment of generalized tonic-clonic seizures c) has no adverse effect on the CNS . d) is safely used during pregnancy .
9) The following statements regarding the treatment of epilepsy are true,
except : a) The choice of drug depends on the cause of epilepsy and not on
the seizure type . b) Monotherapy is preferred initially . c) Treatment must not be for life . d) Avoid sudden withdrawal of drugs .
10) An epileptic woman controlled by phenytoin , she became pregnant .
which of the following measures is most appropriate? a) Medical termination of pregnancy . b) Withdraw phenytoin therapy . c) Gradually reduce phenytoin dose to the lowest effective level . d) Substitute phenytoin with a combination of carbamazepine and
sodium valporate .
11) Which of the following is the drug of choice for the treatment of absence seizures associated with generalized tonic-clonic seizures ? a) Ethosuximide. b) Sodium valporate. c) Carbamazepine. d) Phenytoin.
1.
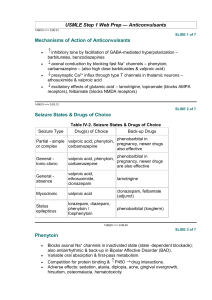
The mechanism of action of antiepileptic drugs is : a) Enhancement of GABA-ergic (inhibitory) transmission
b) inhibition of excitatory (usually glutamate-ergic) transmission c) Modification of ionic conductance d) All of the above .
2.
which of the following has an impotent effect on the T-type calcium channels in thalamic neurons? a) Carbamazepine b) Lamotrigine c) Ethosuximide d) Phenytoin .
3.
The drug which does not produce a voltage-dependent inactivation of sodium channels is : a) Lamotrigine b) Carbamazepine c) Phenytoin d) Vigabatrine .
4.
The antiepileptic drug, which produce inhibition of the central effects of excitatory amino acids is : a) Ethosuximide b) Lamotrigine c) Diazepam d) Tiagabine .
5.
The drug which is not used for partial and generalized tonic-clonic seizures is : a) Carbamazepine b) Valproate c) Phenytoin d) Vigabatrine .
6.
The drug which is used for absence seizures is : a) Sodium valproate b) Phenobarbital c) Carbamazepine d) Phenytoin .
7.
The drug which is used for myoclonic seizures is: a) Primidone b) Carbamazepine c) Clonazepam d) Phenytoin .
8.
The most effective drug in status epilepticus in adults is : a) Carbamazepine b) Ethosuximide c) Diazepam d) Zonisamide .
9.
Regarding phenytoin:
a) It effects on Ca 2+ currents, reducing the low-threshold (T-type) current b) It blocks Na + channels c) It inhibits GABA-transaminase, which catalyzes the breakdown of GABA d) None of the above .
10.
Phenytoin is used in the treatment of: a) Petit mal epilepsy b) Grand mal epilepsy c) Myoclonic seizures d) None of the above .
11.
Dose-related adverse effect caused by phenytoin is: a) Physical and psychological dependence b) Gingival hyperplasia c) Exacerbated grand mal epilepsy d) Steven-Johnson syndrome .
12.
Granulocytopenia , GI irritation and facial hirsutism are possible adverse effects of: a) Phenobarbital b) Ethosuximide c) Phenytoin d) Carbamazepine .
13.
which of the following does not induce hepatic microsomal enzymes ? a) Carbamazepine b) Phenytoin c) Phenobarbital d) Sodium valproate .
14.
The drug of choice for partial seizures is: a) Carbamazepine b) Diazepam c) Ethosuximide d) Phenytoin .
15.
The mechanism of action of Carbamazepine appears to be similar to that of: a) Benzodiazepines b) Sodium valproate c) Phenytoin d) Ethosuximide .
16.
Which of the following is also effective in treating trigeminal neuralgia? a) Carbamazepine b) Phenytoin c) Vigabatrine d) Lamotrigine .
17.
The most common adverse effects of Carbamazepine are: a) Diplopia, ataxia, and nausea b) Gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism
c) Sedation, physical and psychological dependence d) All of the above .
18.
Phenobarbital causes : a) Physical and phychological dependence b) Exacerbated petit mal epilepsy c) Sedation d) All of the above .
19.
Lamotrigine can be used alone in the treatment of all the following except : a) Partial seizures b) Absence c) Myoclonic seizures d) Generalized tonic - clonic seizures .
20.
The mechanism of action of vigabatrine is : a) Direct action on the GABA receptor-chloride channel complex b) Inhibition of GABA aminotransferase c) NMDA receptor blockade via the glycine binding site d) Inhibition of GABA neuronal reuptake from synapses .
21.
The mechanism of topiramate’s action is: a) Reduction of excitatory glutamate-ergic neurotransmission b) Inhibition of voltage sensitive Na + channels c) Potentiation of GABA-ergic neuronal transmission d) All of the above .
22.
The drug of choice in the treatment of petit mal (absence seizures) is: a) Phenytoin b) Ethosuximide c) Phenobarbital d) Carbamazepine .
23.
adverse effects of ethosuximide are all the following except : a) Gastric upset such as anorexia, pain, nausea and vomiting b) Exacerbated grand mal epilepsy c) Fatigue , Dizziness and headache d) Aggressive behavior .
24.
Sodium valproate is very effective against all the following except : a) Absence seizures b) Myoclonic seizures c) Generalized tonic-clonic seizures d) Partial seizures .
25.
The drug of choice in the treatment of myoclonic seizures is: a) Sodium valproate b) Phenobarbital c) Phenytoin d) Ethosuximide .
26.
Which of the following antiepileptic drugs may produce teratogenicity? a) Phenytoin b) Valproate c) Topiramate d) All of the above .
27.
The most dangerous effect of antiepileptic drugs after large overdoses is: a) Respiratory depression b) Gastrointestinal irritation c) Alopecia d) Sedation
8.c
9.b
10.b
11.b
12.c
13.d
Answers
:
1.d
2.c
3.d
4.b
5.d
6.a
7.c
14.a
15.c
16.a
17.a
18.d
19.d
20.b
21.d
22.b
23.d
24.d
25.a
26.d
27.a
1Topiramate t or f
-
Weight loss
-
Safe on pregnancy
-
Potentiantes GABA
2Carbidopa is compined to levadopa to :
-
Increase it’s T ½
-
Decrease it’s therapeutic use
-
Decrease central adverse effects
-
Increase oral bioavailability
-
MATCHING
-
1) (The drug with its adverse effect)
a) Gum hyperplasia. 2
b) Hepatotoxicity. 5
c) Physical dependence1
d) Hyponatremia 4
1. Diazepam 2. Phenytoin 3. Gabapentine 4. Carbamazepine 5. Valporic acid
1 – Na valporate 2- Diazepam 3- Phenytoin 4- Carbamezapine
a- Absence seizures and others b- Febrile c- Osteomalacia d- Partial seizure