anticonvulsants
advertisement
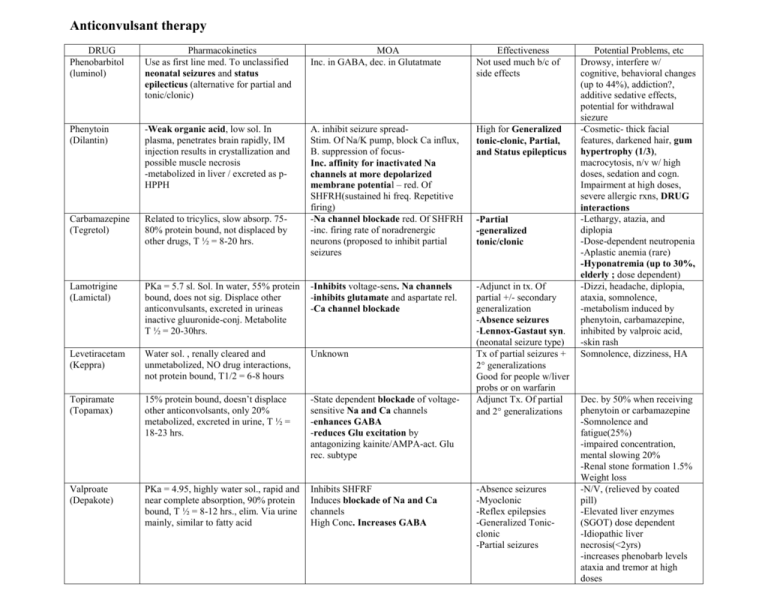
Anticonvulsant therapy DRUG Phenobarbitol (luminol) Pharmacokinetics Use as first line med. To unclassified neonatal seizures and status epilecticus (alternative for partial and tonic/clonic) MOA Inc. in GABA, dec. in Glutatmate Effectiveness Not used much b/c of side effects Phenytoin (Dilantin) -Weak organic acid, low sol. In plasma, penetrates brain rapidly, IM injection results in crystallization and possible muscle necrosis -metabolized in liver / excreted as pHPPH High for Generalized tonic-clonic, Partial, and Status epilepticus Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Related to tricylics, slow absorp. 7580% protein bound, not displaced by other drugs, T ½ = 8-20 hrs. A. inhibit seizure spreadStim. Of Na/K pump, block Ca influx, B. suppression of focusInc. affinity for inactivated Na channels at more depolarized membrane potential – red. Of SHFRH(sustained hi freq. Repetitive firing) -Na channel blockade red. Of SHFRH -inc. firing rate of noradrenergic neurons (proposed to inhibit partial seizures Lamotrigine (Lamictal) PKa = 5.7 sl. Sol. In water, 55% protein bound, does not sig. Displace other anticonvulsants, excreted in urineas inactive gluuronide-conj. Metabolite T ½ = 20-30hrs. -Inhibits voltage-sens. Na channels -inhibits glutamate and aspartate rel. -Ca channel blockade Levetiracetam (Keppra) Water sol. , renally cleared and unmetabolized, NO drug interactions, not protein bound, T1/2 = 6-8 hours Unknown Topiramate (Topamax) 15% protein bound, doesn’t displace other anticonvolsants, only 20% metabolized, excreted in urine, T ½ = 18-23 hrs. -State dependent blockade of voltagesensitive Na and Ca channels -enhances GABA -reduces Glu excitation by antagonizing kainite/AMPA-act. Glu rec. subtype -Adjunct in tx. Of partial +/- secondary generalization -Absence seizures -Lennox-Gastaut syn. (neonatal seizure type) Tx of partial seizures + 2 generalizations Good for people w/liver probs or on warfarin Adjunct Tx. Of partial and 2 generalizations Valproate (Depakote) PKa = 4.95, highly water sol., rapid and near complete absorption, 90% protein bound, T ½ = 8-12 hrs., elim. Via urine mainly, similar to fatty acid Inhibits SHFRF Induces blockade of Na and Ca channels High Conc. Increases GABA -Partial -generalized tonic/clonic -Absence seizures -Myoclonic -Reflex epilepsies -Generalized Tonicclonic -Partial seizures Potential Problems, etc Drowsy, interfere w/ cognitive, behavioral changes (up to 44%), addiction?, additive sedative effects, potential for withdrawal siezure -Cosmetic- thick facial features, darkened hair, gum hypertrophy (1/3), macrocytosis, n/v w/ high doses, sedation and cogn. Impairment at high doses, severe allergic rxns, DRUG interactions -Lethargy, atazia, and diplopia -Dose-dependent neutropenia -Aplastic anemia (rare) -Hyponatremia (up to 30%, elderly ; dose dependent) -Dizzi, headache, diplopia, ataxia, somnolence, -metabolism induced by phenytoin, carbamazepine, inhibited by valproic acid, -skin rash Somnolence, dizziness, HA Dec. by 50% when receiving phenytoin or carbamazepine -Somnolence and fatigue(25%) -impaired concentration, mental slowing 20% -Renal stone formation 1.5% Weight loss -N/V, (relieved by coated pill) -Elevated liver enzymes (SGOT) dose dependent -Idiopathic liver necrosis(<2yrs) -increases phenobarb levels ataxia and tremor at high doses Ethosuximide (Zarontin) Lipophilic but rel. water soluble, complete absorption from GI tract, absence of Protein binding, Met. In liver, T ½= 18-72 hrs after chronic tx Lorazepam (Ativan) BZD PKa = 1.3 and 11.5, insol. In water, 90% protein bound, rapidly absorbed, rapid penetration into CSF, T ½ = 825hrs., biotransformed to inactive glucuronide and excreted via urine Blocks Ca channels of thalamic interneurons that appear to interrupt the neuronal hypersynchrony of thalmocortical pathways seen in absence seizures -Agonist action on BZD binding site of GABA rec. complex -at sedating and antistatus doses, blocks Ca channels and SHFRF DOC for Absences seizures N/V, headache Status epilepticus -Sedation, anterograde amnesia, dysarthria, -Withdraw seizures following abrupt cessation of chronic therapy