Vertebrates: Fish to Reptiles Ch
advertisement

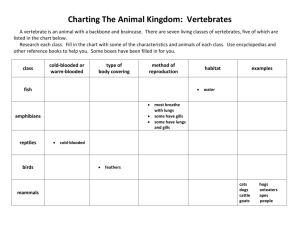
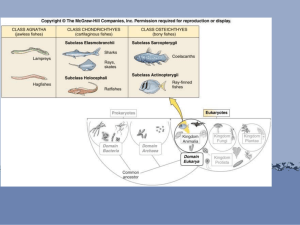
Vertebrates: Fish to Reptiles Ch. 34 Phylum: Chordata Characteristics common of all chordates • __________________________ – later modified into the brain and spinal cord – Other animal phyla = ventral nerve cord • ___________– a flexible, internal, support structure (in most vertebrates by cartilage or bone early in development) • _______________– used in respiration (only present in embryos of land chordates) • __________________________– disappears in some (e.g. humans) 3 subphyla of the chordates: Subphylum: __________________ • 3 classes of animals • Biggest are marine tunicates (sea squirts) • Lack ___________________ and notochord as adults but have all chordate characteristics as larvae Subphylum __________________ (Lancelets) • Small marine animals • Most common is amphioxus – small eel-like creature Subphylum __________________– key feature is a flexible spinal column made of vertebrae extending from anterior to posterior Characteristics: • __________________ (individual segment of backbone) • __________________symmetry • Dorsal, hollow nerve cord (anterior = brain) • __________________skeleton • 2 pairs of jointed appendages • Organ systems (e.g. heart – 2 to 4 chambers and closed circulatory system and respiratory – lungs or gills) – coelom contains digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs • Body covering: skin often 2layers and forms scales, feathers, glands • __________________ (“cold-blooded) or __________________ (warm-blooded) 1 5 main classes of vertebrates Ectothermic (body temp changes with environment) • __________________– Jawless Fish, Cartilaginous Fish, Bony Fish • __________________– Salamanders, Frogs and Toads • __________________– Crocodiles and Alligators, Turtles, Lizards and Snakes Endothermic (constant body temp independent of environment) • __________________ • __________________ Question1: What characteristics distinguish chordates from other animals? Answer1: Question2: What basic characteristics distinguishes vertebrates from the other chordates? Answer2: Fish – 4 classes Class __________________– (E.g. Lamprey) • Snake-like bodies, no paired fins, true jaws, or scales • Most are __________________– using sucker-like mouth and teeth to “chew” a hole in host and suck blood/body fluids • Cartilaginous skeleton Class: __________________– Hagfish • Marine animals feeding on worms and dead animals • a.k.a. “slime eels” because they use slime as a defense mechanism • Use ‘__________________instead of a jaw to eat Cartilaginous Fish – evolution of movable jaws Class: __________________ • Sharks, rays, skates • Moveable upper and lower jaws • Skeleton is entirely __________________ • 2-chambered hearts • No __________________or muscled operculum (gill cover) therefore they must swim continuously so they don’t sink and can breath • Skates and Rays – flattened bodies feeding on mollusks and crustaceans • Stingrays – poisonous stingers in tail • Electric rays - produce electric charge to stun prey • Rays – young are born live (__________________) • Skates – egg laying (__________________) 2 • • • Sharks – most are meat eaters and active hunters Very tough scales Main hunting senses: • olfactory sacs – to smell prey • __________________– detect vibration of prey Bony fish Class: __________________ • __________________and overlapping scales for protection • Jaws are present with many teeth in mouth • Most of the body is muscle • Most have a swim bladder – help float by increasing/decreasing amount of gas • Respiration by gills supported by bony gill arches and covered by an operculum • Circulation consists of __________________heart, arterial and venous systems, and four pairs of aortic arches • Complex nervous system of brain, olfactory lobes, optic lobes, spinal cord, lateral line… • Sexes are separate- usually __________________fertilization • Bony fish vary greatly in size and shape Question1: List the general characteristics of bony fish. Answer1: Question2: What structures aid in maintaining balance and controlling the direction of movement in bony fish? Answer2: 3 Class ____________________ – frogs, toads, salamanders, newts • Shows vertebrate evolution: ____________________ • First land vertebrates for 75 million years before reptiles • Parts of life are on both land and water – Fully aquatic embryos and larvae – Most need water for ____________________ – sperm released into the water to fertilize the eggs - external fertilization – Adults need ____________________ environments • Thin skin with ____________________ glands • 3 chambered heart (2 atria, 1 ventricle) • 2 pairs of limbs on lateral edge – better for swimming • Respiration is by ____________________ (nostrils connected to the mouth), gills, and ____________________ We will study the frog – a good representative and anatomy resembles most vertebrates _____– dry, rough, warty skin and can live away from water but need water to reproduce Frog Features - External Features • Short, broad body, 2 forelimbs and 2 muscular hind-limbs • Eyes – ____________________ – upper, lower, and ____________________ (allows the frog to see underwater) • ____________________ – ‘ear’ • 2 nostrils at upper tip of head – Why? Circulatory System • _______________________ – 2 atria and 1 muscular ventricle (CO2 and O2-rich blood not separated) • Closed system with ____________________ Know the flow of blood through the frog Respiratory System • In adults – use of ____________ • ____________ – external gills which are then absorbed as the lungs form – The skin (thins, moist, and with many blood vessels) plays a small role in respiration but is the main organ of respiration during ____________________ 4 Nervous System • Central nervous system – _____________________________ • ____________________ nervous system – nerves separate from the spinal cord • Lobes of the brain 1. ____________________ (smell) 2. ____________________ (sight) 3. _______________(interprets sensory info and voluntary muscle action) 4. ____________________ (balance and coordinates movement) 5. ____________________ – (controls involuntary muscle action) Excretory System • Most ____________ is excreted by skin • Other wastes excreted by ____________ which filter the blood to form urine • Urine is carried from the ureters (tube) to the bladder and then to the ______________ before leaving the body – Cloaca – a common opening to expel ____________________ Reproductive System • ____________________ fertilization • Mating – ____________________ – male clasps the female with forelimbs and as eggs leave female body, the male releases sperm over the many eggs • Tadpoles (fish-like with gills, no legs or protection from the mother) • ____________________ – develops legs, absorbs tail and gills, and develops lungs, 3-chambered heart – This may take 3 months to 3 years depending on the type of frog 5 Question1: An ecologist studying a local frog species observed that the population declined in years with droughts in the spring but was not affected by droughts at other times of the year. How would you explain this observation? Answer1: 6 Class ____________________ – lizards, crocodiles, turtles, snakes Characteristics: • Well suited for life on land -do not require water for reproduction – ____________________ fertilization with thick, leathery eggs • No ____________________ • Dry, scaly skin – protect against water loss • 2 pairs of legs (except snakes) • Well developed respiratory system – protected by ____________________ • Well developed excretory system producing a semisolid paste for urine – ____________________ • ____________________ – 2 atria and 1 partly divided ventricle (less mixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood) Crocodiles and Alligators - 2.5 meters to 7 meters long Differences: • ____________________ — Alligators tend to have wide, U-shaped, rounded snouts, while crocodiles tend to have longer, more pointed, V-shaped snouts. • ____________________— The fourth tooth on the lower jaw sticks up over the upper lip on crocodiles, so you can see it when their mouths are closed. In alligators, this fourth tooth is covered up. • ____________________ — Crocodiles also have special glands in their tongues that can get rid of excess salt, so they tend to live in saltwater habitats. Alligators have these glands, too, but they don't work as well as the crocodiles', so alligators prefer to live in freshwater habitats. • With 23 species of crocodilians, though, these general rules don't always apply— there are exceptions! Turtles • ____________________ • Turtles live primarily in the water, while tortoises are land dwellers • Herbivore or carnivores (though they have no teeth) • Some marine turtles can be up to 2 meters long and over 500kg Lizards • Well distributed • Range from small (gecko) to very large (_________________ more than 100kg) 7 Snakes • Body – ________________________________________ • ____________________ detects odor • May or may not be venomous – Venomous – ____________________ – poisons attack nervous tissue – ____________________ – break down red blood cells • Others may be constrictors Question1: Name two characteristics of reptiles that are important adaptations for life in arid climates. Answer1: 8