1330953540project1
advertisement

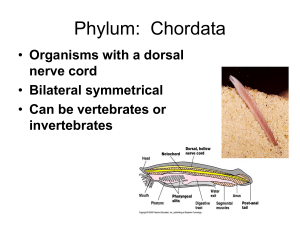
Chordata Aubrey Irwin Agnatha • • • • •• Oldest Class of Vertebrates* Jaw-less animals Cylinder, eel-shaped body The notochord persists in the adult The skeleton is composed of cartilage Example: Lampreys Chondrichthyes • • • • • • Cartilaginous fish Skeletons made of cartilage Internal jaws are present Paired appendages Three semicircular canals Example: Sharks Osteichthyes •• • • • Bony fish Skeletons made of bone Operculum (a flap on each side of the head that covers the gills). The movements of these flaps allow the fish to breathe without moving. Most bony fish are carnivorous, few are herbivores that feed on algae and aquatic plants, and some are filter feeders Example: Ray-finned fish Amphibia • • • • • • 1st vertebrates adapted to live both on land and water Reproduce in water or moist land Glandular skin that lacks the keratinized scales Most have complex life cycles Surrounded by several gelatinous layers Example: Salamanders Reptilia • • • • • • • Able to retain moisture Live on land Produce eggs that do not have to develop in water Improved Skelenton Shelled eggs Scaly skin Examples: Turtles Aves • • • • • Birds Presence of feathers Appendages modified as wings High metabolic rate Bones that are lightened by numerous air spaces Mammalia • • • • • • Have hair/fur Mammary glands Three middle ear bones Warm Blooded Lungs are present Example: Tigers Three Groups • Vertebrates • Tunicates • Lancelets Overview/Characteristics • All have tails, hollow nerve cord, notochord, and pharyngeal slits at some point of life or development. Vertebrates • • • • • Large Active Well developed brains in hard skull Segmented backbone Example: Humans Tunicates • Urochordates • Free swimming/sessile • Example: Sea squirts Lancelets • • • • • Cephalochordates Small Eel-like Found in shallow tropical oceans Example:Lancelet