Post WWII Europe
advertisement

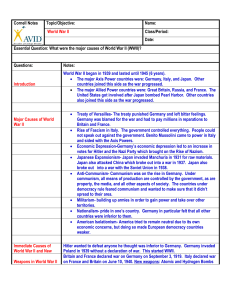
AP Euro Seminar Peyton Lyon 3-16-12 MY PROMPT Analyze the common political and economic problems facing western European nations in the period 1945-1960 and discuss their responses to these problems. The End of WWII The end of WWII left many of Europe's strongest powers in chaos. France, Western Germany, Great Britain, and Italy all faced similar problems. They needed to: -Rebuild their economies -Re-create their democratic institutions -Prevent the growth of Communist parties and ideas Post WWII Europe Common Issues In European Nations Rebuilding the Economy Trade markets all over the world were down in production. Industrial power was very low. Unemployment rates were very high. Opposition to Communism The rising popularity of the communist party within Europe was putting the established government's power at risk. Re-creation of Democratic Institutions Many different political partiers were forming in Europe The rise of the Christian Democratic Party was a key factor in the rebuilding of Europe’s leading nations Outside Help In 1947, U.S Secretary of State, George Marshall, offered economic aid to all European countries. The Marshall Plan Officially known as the European Recovery Program Provided over 13 Billion dollars in aid to Europe The battered economies of Western Europe began to improve European Coal an Steel Community (ECSC) European Economic Community (EC) / Common Market By promoting economic cooperation among individual European nations, it reduced the threat of conflict. French Responses At the end of WWII, France established its Fourth Republic which had a weak executive with too many political parties. Although the Fourth republic was not an effective government, the country made a good economic recovery and industrial production increased 250% But, With the threat of Civil war in the African Colony of Algeria, the Fourth Republic started to collapse. With France on the verge of civil war, they called in retired political man, Charles de Gaulle. He formed the French Popular Movement. By forming the French Popular Movement, France’s political mess was blamed on the presence of too many political parties. The National Assembly gave Charles de Gaulle complete power for 6 months to write a new constitution for France. He finished the Fifth Republic in 1958. French Fifth Republic Greatly increased the power of the President President now had the authority to - Choose the Prime Minister - Dissolve Parliament - Supervise defense and foreign Policy - Submit popular issues to the people - Assume emergency power when necessary De Gaulle invested greatly into Nuclear Arms. He pulled France out of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) In 1962, he granted Algeria its freedom. When De Gaulle came into power, he reformed within the government to make France a major industrial producer and exporter. West German Responses Within Germany in 1945, political parties started to re-emerge. Three major parties developed: The Social Democrats (SDP) The Christian Democrats (CDU) The Free Democrats (FDP) Konrad Adenauer, leader of the Christian Democrats, served as chancellor from 1949-1963 and was considered the “founding hero” of the Federal Republic. The U.S worked with the CDU to ensure that West Germany became a solid part of the Western Alliance. Adenauer wanted to reconcile with France, Germany’s longtime enemy. Western Germany re-armed themselves and joined North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO. Adenauer’s leadership was referred to as an economic miracle. Unemployment rates went from 8% in 1950, to .4% in 1965. Starting in 1953, the German government started making payments to all Holocaust survivors and their families as well as Israel in attempt to repay the crimes in the Nazi era. Western Germany rebuilt its cities, factories, and trade system. By the 1960’s, West Germany had become one of the leading economies in Western Europe. British Response Elections were held in Britain immediately after the war ended. The Labour Party succeeded over Churchill’s Conservative Party. When Clement Attlee was the prime minister, he started the reforms that created a modern Welfare State. British Welfare State Nationalization of the Bank of England Nationalization of coal and steel industries Nationalization of social welfare National Insurance Act - Established a comprehensive social security program and nationalized medical insurance - Enabled the state to subsidize the unemployed, sick and elderly National Health Service - Created a system of socialized medicine that required doctors and dentists to work with state hospitals - Private practices were still allowed - Within a few years, 90% of medical practitioners were participating The British modeled a welfare state to other European countries The British Welfare State The costliness of creating a welfare state, forced Britain to reduce national spending Reducing spending meant unraveling of the British empire. As economic problems continued, the Conservatives returned to power and undertook the Welfare State. They even extended it by instituting a program to improve British housing. Great Britain’s Recovery British recovery from the war was a long process. It moved at a much slower rate than other European countries. Although Britain made a recovery from WWII, it had lost much of its prewar revenues, and was left with debt form its multiple international commitments. Britain was no longer viewed as a World power. Italian Response When WWII ended, Italy rejected and removed the fascist monarchy and set up a republic. Italy was the Western country had faced the most physical destruction, only second to Germany Two regions were established, the successful industrial North, and the rural South. Similar to West Germany, the Christian Democrats, who were allied with the Catholic Church, dominated. Alcide De Gasperi came to power rather than the Communists who wanted power. The alliance between the Catholic Church and the Christian Democrats supplied national unity to Italian politics by providing prime ministers with a coalition government. Economic Italy Italy developed into one of the 10 industrial powers. The Marshal Plan helped the Italian economy to get back onto its feet. Rapid steps of growth took place within Italy Italy started to produce electrical appliances, cars, and everyday machinery, which took the largest leap towards a successful economy. In Conclusion The road to political and economic recovery in Europe was aided largely by the Marshall Plan drawn by the U.S Britain’s position as a European power, was decreased. France, West Germany, Great Britain, and Italy all recovered from the damage in WWII. Germany rebuilt and was on the right track to becoming a strong leading power again. Italy witnessed an economic miracle in its recovery. France was led strongly be De Gaulle to a victorious reconstruction.