File - chemistryattweed
advertisement

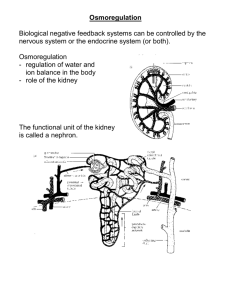
Lesson Review • The Role of the Kidney • It plays a central role in homeostasis, • Function: The primary role of the Kidneys is osmoregulation • Role 2: Excretion of all nitrogenous wastes Fresh Water fish • Fish (bony) living in freshwater are hypertonic to their surroundings. • Hypertonic – they maintain a higher concentration of solutes in their body • Water therefore tends to diffuse into their bodies - need to continuously get rid of the excess water. • Their kidneys produce copious amounts of very dilute urine Salt Water Fish • Their internal body fluids are less concentrated (more dilute) than the surrounding water. • They absorb the water and salts. • The water is retained and the salts are actively excreted, some via the gills and some via the kidneys. • Saltwater bony fish excrete very little urine. • Marine cartilaginous fish (sharks and rays) have their tissues isotonic with the seawater so that there is no net movement of water in or out. Mammalian Excretory System • Main Function: the kidneys of mammals regulate the internal water and salt concentrations in the body and excrete urea, the nitrogenous waste produced by mammals. Kidney Structure Nephrons • Each kidney is made up of about one million small filtering units called nephrons. • It is in these structures that urine is produced. • Each nephron is a convoluted tubule • The nephrons are surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. The Formation of Urine • The kidneys continuously process a large volume of blood to form a small volume of urine. • This involves three processes: filtration, reabsorption and secretion. Filtration • Blood is brought to the kidney by the renal artery. This divides into smaller vessels which form a network of capillaries called a glamorous outside the Bowman’s capsule. • The pressure is very high in the glomerulus and this causes some fluid to be forced out through the walls of the blood vessels into the Bowman’s capsule. • This liquid consists of urea, glucose, amino acids, some hormones, vitamins, salts and water (no plasma proteins or blood cells). • This liquid is known as glomerular filtrate. • Filtration is a non- selective process. • Reabsorption: • Surrounding each nephron is a large capillary network. • As the filtrate travels down the capsule the materials that the body can reuse are reabsorbed into the blood. • Reabsorption is an active process that requires energy. • Secretion: • Secretion is a selective process where by the body actively transports substances from the blood into the nephron. Loop of Henle • Inthe descending part, the walls are permeable to water but not to salt. • Water passes across by osmosis. • In the ascending part the walls are permeable to salt not to water. • Salt passes out passively across a thin walled section and then actively across a thick walled section. • The salt passing out makes the interstitial fluid of the medulla area of the kidney quite concentrated. (This hypertonic medulla helps remove water by osmosis from the descending part and collecting duct). • In the distal tubule – selective reabsorption and secretion again occur to adjust pH of the blood and level of salts particularly sodium and potassium. • The walls of the collecting ducts are permeable to water but not to salt. Water passes out by osmosis and the final filtrate or urine is formed. (due to high salt concentration in the medulla) • Diffusion and osmosis are passive forms of transport that do not require the expenditure of energy. • Diffusion and osmosis involve the movement of substances with the concentration gradient – that is from where there are many particles to where there are few. • Movement of substances against a concentration gradient requires energy. This is called active transport. • In the kidneys both forms of transport are use in the regulation of the body fluid composition. • Passive transport occurs in filtration and the osmosis of water back into the blood. • Active transport occurs in the secretion of substances into the nephron, the active transport of nutrients back into the blood and the selective reabsorption of salts required by the body. • Diffusion and osmosis are both examples of passive transport, relying on the random movement of molecules. Diffusion is too slow for the normal functioning of the body and does not select for useful solutes. • Osmosis only deals with the movement of water and thus would only allow water to move out of the body not nitrogenous waste. – Aldosterone is a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal gland. – Function: Its function is to regulate the transfer of sodium and potassium ions in the kidney. – When sodium levels are low, aldosterone is released into the blood causing more sodium ions to pass from the nephron to the blood. – Water then flows from the nephron into the blood by osmosis. This results in the homeostatic balance of blood pressure. – If there is an increase in blood volume and pressure (resulting from high salt concentrations, which causes water retention), the out put of aldosterone is reduced. Less salt and water is reabsorbed by the nephron tubules and increased amounts of water and salts are lost in the urine. • – Antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin) controls water reabsorption in the nephron. Made in the hypothalamus. – When levels of fluid in the blood drop, the hypothalamus causes the pituitary gland to release ADH. – ADH increases the permeability of the collecting ducts and distal tubules allowing more water to be reabsorbed from the urine into the blood. – The resulting urine is more concentrated. – When there is too much fluid in the blood, sensors in the heart cause the hypothalamus to reduce the production of ADH in the pituitary, decreasing the amount of water reabsorbed in the kidney. – This results in a lower blood volume and larger quantities of more dilute urine. Blood water concentration falls Less water reabsorbed from kidney tubules. Large volume of dilute urine. Pituitary gland releases more ADH Pituitary gland releases less ADH More water reabsorbed from kidney tubules Blood water concentration rises