urinary
advertisement

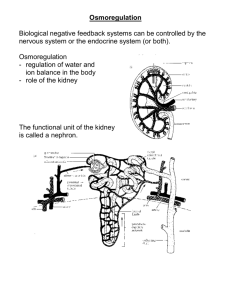
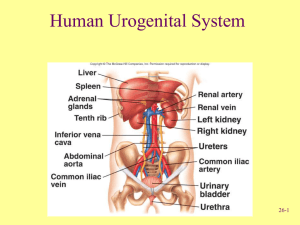
Urinary System Urinary System Basic Anatomy • Kidneys -filter blood • • • of toxins, regulate water, pH, salt content of blood (also helps regulate blood pressure, produces erythropoietin) Ureters - carry urine to bladder Bladder - stores urine Urethra - allows urine to pass out of body Kidneys • Are located posterior • to digestive organs in a retroperitoneal position (behind peritoneal membrane) Covered by transparent membrane called the renal capsule Renal Blood Supply • Renal artery carries • • blood from aorta into kidneys at the hilus (see diagram) Renal vein carries blood from kidneys to inferior vena cava Blood vessels branch into tiny capillaries inside the kidneys Cross-section of Kidney • Cortex (outer portion • of kidney) Medulla (inner portion of kidney) The Nephron Nephron Functional unit of kidney (1 million per kidney): Composed of: • Glomerulus: ball of capillaries involved in filtration of blood- keeps large particles (blood cells, large proteins) out of the filtrate (filtrate becomes urine) • Renal tubules: involved in reabsorption - (putting needed substances back into the blood) and secretion (moving wastes from blood to the filtrate to be excreted in urine) Components of a nephron Areas of the Nephron 1) Glomerulus (surrounded by Bowman’s capsule) filtration 2) Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) reabsorption 3) Loop of Henle (descending and ascending limbs) 4) Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) - secretion * The filtrate drains into the collecting duct (not part of the nephron) and is carried out of the kidneys to the ureters 1 Bowman’s capsule 2 4 3 3 A Nephron Collecting duct The Nephron Concentration of Urine • ADH (antidiuretic • • • hormone - released from pituitary gland) enhances the reabsorption of water in the collecting ducts Triggered when blood pressure and volume are low Makes urine very concentrated Urine is dilute when ADH is not present No With ADH ADH ADH vs. No ADH No ADH ADH present Renin-Angiotensin System • Renin – enzyme secreted by juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys in response to low blood pressure/volume • Leads to a cascade of reactions that results in production of angiotensin II, a vasoconstrictor • Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone production from adrenal glands • Blood pressure increases Aldosterone • Released from the adrenal • • glands on top of the kidneys Leads to conservation of sodium (and sometimes water) and the excretion of potassium Raises blood pressure by increasing blood volume Bladder • Holds urine (made of • • smooth muscle) Stretch receptors in wall of bladder trigger urge to urinate (occurs after about 200ml of urine collect) - maximum capacity is about 800-1000ml Micturition (urination) occurs when it is “convenient” to go (see animation) Micturition Reflex Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) • Infection of the urinary tract • • • (most commonly urethra) by bacteria (usually E.coli from digestive tract) More common in women (shorter urethra and proximity of urethra to anus) Infections could spread to bladder (cystitis) or kidney (pyelonephritis) if not treated Risk increases if urine flow is obstructed or if catheters are used frequently Kidney Stones