Latest New
advertisement

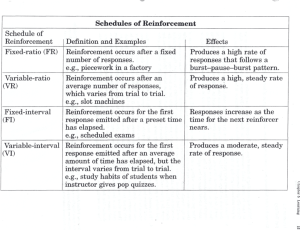
fixed interval reinforcement Answer : provides reinforcement on a fixed time schedule fixed ratio reinforcement Answer : provides reinforcement after a fixed number of behaviors hierarchy of needs theory Answer : Abraham Maslows hierarchy that assumes human needs are arranged in a hierarchy of importance human relations approach Answer : an approach to motivation that suggests that favorable employee attitudes result in motivation to work hard human resource approach Answer : an approach to motivation that assumes employees want and are able to make genuine contributions to the organization hygiene factors Answer : factors that are extrinsic to the work itself and include factors such as pay and job security learning Answer : a relatively permanent change in behavior or behavioral potential resulting from direct or indirect experience motivation factors Answer : factors that are intrinsic to the work itself and include achievement and recognition need for achievement Answer : the desire to accomplish a task or goal more effectively than in the past need for affiliation Answer : the need for human companionship need for power Answer : the desire to control the resources in ones' environment need based theories of motivation Answer : theories that assume that need deficiencies cause behavior organizational behavior modificaiton OB mod Answer : the application of reinforcement theory to people in organizational settings outcome Answer : anything that results from performing a particular behavior performance to outcome expectancy Answer : an individuals perception of the probability that performance will lead to certain outcomes positive reinforcement Answer : a reward or other desireable consequence that a persona receives after exhibiting behavior process based perspectives on motivaiton Answer : perspectives that focus on how people behave in thier efforts to satisfy thier needs punishment Answer : an unpleasant or aversive consequence that results from behavior reinforcement Answer : consequence of behavior reinforcement thoery Answer : theory based on the idea that behavior is a function of its consequences schedules of reinforcement Answer : schedules that indicate when or how often managers should reinforce certain behaviors scientific management Answer : one of the first approaches to management focused on the efficiency of individual workers and assumed that employees ar emotivated by money social learning Answer : occurs when people observe the behaviors of others recognize their consequences and alter their own behavior as a result valence Answer : the degree of attractiveness or unattractiveness a particular outcome has for a person variable interval reinforcement Answer : varies the amount of time between reinforcements variable ratio reinforcement Answer : varies the number of behaviors between reinforcements empowerment Answer : the process of enabling workers to set their own work goals make decisions and solve problems within their sphere of responsibility and authority job characteristics approach Answer : identifies five motivational properties of tasks and three psychological states of people job design Answer : how organizations define and structure jobs job enlargement Answer : involves giving workers more tasks to perform job enrichment Answer : entails giving workers more tasks to perform and more control over how to perform them job specialization Answer : as advocated by scientific management it can help improve efficiency but it can also promote monotony and boredom participation Answer : the process of giving employees a voice in making decisions about thier own work goal acceptance Answer : the extent t which a person accepts a goal as his or her own goal commitment Answer : the extent to which a person is personally interested in reaching a goal goal specificity Answer : the clarity and precision of a goal indirect compensation - benefits Answer : refers to nonwage or salary compensation such as paid time off and insurance coverage MBO - management by objectives Answer : a collaborative goal setting process through which organizational goals cascade down throughout the organization performance management system PMS Answer : comprises the processes and activities involved in performance appraisals performance measurement Answer : the process by which someone evaluates an employees work behaviors by measurement and comparison with previously established standards perquisites Answer : special privileges awarded to selected members of an organization usually top managers self efficacy Answer : the extent to which people believe they can accomplish their goals even if they failed to do so in the past surface value Answer : the objective meaning or worth a reward has to an employee symbolic value Answer : the subjective and personal meaning or worth a reward has to an employee all channel network Answer : in this type of network all members communicate with all other members accomodation Answer : occurs when the parties goals are compatible and the interaction between groups is relatively unimportant to the goals attainment chain network Answer : in this type of network each member communicates with the person above and below except for the individuals on each end who each communicate with only one person affinity group Answer : collections of employees from the same level in the organization who meet on a regular basis to share information capture emerging opportunities and solve problems channel noise Answer : a disturbance in communication that is primarily a function of a medium avoidance - negative reinforcement Answer : the opportunity to avoid or escape from an unpleasant circumstance after exhibiting behavior circle network Answer : in this type of network -each member communicates with the people on both sides but with no one else collaboration Answer : occurs when the interaction between groups is very important to goal attainment and the goals are compatible communication fidelity Answer : the degree of correspondence between the message intended by the source and themessage understood by the receiver command group Answer : a relatevely permanent formal group with functional reporting relationships usually included in the organization chart cosmopolite Answer : an individual who inks the organization to the external environment and may also be an opinion leader in the group communication and decision making Answer : the stage of group development where members discuss their feelings more openly and agree on group goals and individual roles in the group decoding Answer : the process by which the reciever of themessage interprets its meaning competition Answer : occurs when the goals are incompatible and the interactions between groups are important to meeting goals encoding Answer : the process by which the message is translated from an idea or thought into transmittable symbols gatekeeper Answer : an individual who has a strategic position in the network that allows him or her to control information moving in either direction through a channel isolate Answer : an individual who tends to work alone and to interact and communicate little with othes isolated dyad Answer : two people who tend to work alone and to interact and communicate little with others conflict stimulation Answer : the creation and constructive use of conflict by a manager jargon Answer : the specialized or technical language of a trade profession or social group control and organization Answer : the stage of group development when the group is mature members work together and are flexible adaptive and self correcting friendship group Answer : a group that is relatively permanent and informal and draws its benefits from the social relationships among its members medium Answer : the channel or path through which the message is transmitted goal compatibility Answer : the extent to which the goals of more than one person or group can be achieved at the same time semantics Answer : the study of language forms source Answer : the individual group or organization interested in communicating something to another party group composition Answer : the degree of similarity or difference among group members on factors important to the groups work group performance factors Answer : factors that affect the success of the group in fulfilling its goals including composition size norms and cohesiveness verification Answer : the final stage of the creative process in which the truthfulness of the insight is determined interest group Answer : a group that is relatively temporary and informal and is organized around a common activity or interest of its members wheel network Answer : in this type of network information flows between the person at the end of each sopke and the person in the middle linking role Answer : a position for a person or group that serves to coordinate the activities of two or more organizational groups mutual acceptance group Answer : the stage of group development that is characterized by members sharing information about themselves and getting to know each other norm Answer : a standard against which the appropriateness of a behavior is judged management teams Answer : consist of manages from various areas they coordinate work teams problem solving teams Answer : temporary teams established to attack specific problems in the workpplace job centered leader behavior Answer : behavior that involves paying close attention to the work of subordinates explaining work procedures and demonstrating a strong interest in performance product development teams Answer : combinations of work teams and problem solving teams that create new designs for products or services that will satisfy customers needs ohio state leaderships studies Answer : these studies defined leader consideration and initating structure behaviors as independent dimensions of leadership quality circles Answer : small groups of employees from the same work area who regularly meet to discuss and recommend solutions to workplace problems employee centered leader behavior Answer : behavior that involves attempting to build effective work groups with high performance goals work teams Answer : include all the people working in an area are relatively permanent and do the daily work making decisions regarding how the work of the team is done hersey and blanchard model Answer : model that identifies different combinations of leadership presumed to work best with different levels of organizational maturity on the part of followers least preferred coworker - LPC scale Answer : scale that presumes to measure a leader's motivation vroom's decision tree approach to leadership Answer : this model attempts to prescribe how much participation subordinates should be allowed in making decisions impression management Answer : a direct and intentional effort by someone to enhance his or her own image in the eyes of others consideration behavior Answer : behavior that involves being concerned with subordinates feelings and respecting subordinates ideas Path goal theory of leadership Answer : theory that suggests that effective leaders clarify the paths - behaviors- that will lead to desired rewards - goals influence Answer : the ability to affect the perceptions attitudes or behaviors of others LPC theory of leadership Answer : theory that suggests that a leaders effectiveness depends on the situation leadership substitutes Answer : individual task and organizational characteristics that tend to outweigh the leaders ability to affect subordinates satisfaction and performance trait approach Answer : an approach that attempted to identify stable and enduring character traits that differentiated effective leaders from non leaders initiating structure behavior Answer : behavior that involves clearly defining the leader subordinate roles so that subordinates know what is expected of them organizational politics Answer : activities carried out by people to acquire enhance and use power and other resources to obtain thier desired outcomes personal power Answer : resides in the person regardless of the position he or she fills michigan leadership studies Answer : these studies defined job centered and employee centered leadership as opposite ends of a single leadership continuum superleadership Answer : occurs when a leader gradually and purposefully turns over power responsibility and control to a sel managing work group transformational leadership Answer : the set of abilities that allows the leader to recognize the need for change to create a vision to guide that change and to execute that change effectively incremental innovation Answer : continues the technical improvement and extends the applications of radical and systems innovations acceptance theory of authority Answer : the theory that the managers authority depends on the subordianates acceptance of the managers right to give directives and to expect compliance with them behavioral approach Answer : approach to leadership that tries to identify behaviors that differentiate effective leaders from nonleaders uses rules of thumb suboptimizing and satisficing in making decisions change agent Answer : a person responsible for managing a change effort Cognitive style is determined by Answer : how people gather and evaluate information Groupthink is Answer : likely to occur when the group values getting along more than getting things done Experts predict that the predominant style of organization in the future will be Answer : skills-oriented The 4I framework of a learning organization consists of intuiting, interpreting, integrating, and Answer : institutionalization Which of the following is the foundation of all organization cultures? Answer : History of the company and its founders What triggers the fight or flight response? Answer : Stress Process consultants wil Answer : guide and coach on workflow, informal relationships, and communication Which type of firm is likely to use a territorial departmentalization structure? Answer : Large service firm The Delphi technique is best suited for Answer : decision making for groups that are difficult to bring physically together What is cognitive dissonance? Answer : When attitudes or beliefs held by a person are contradictory A team member in the role of process observer contributes by Answer : helping the group look at how it's functioning According to attribution theory, Answer : information on causation is gathered on three dimensions of behavior Which of the following is a frequently used research method for organizational behavior? Answer : Interviews Which of the following accurately describes social loafing? Answer : It is also known as freeloading. According to Myers-Briggs typology, a sensation-type individual is best described as someone who Answer : prefers routine and order when gathering information Problem recognition, immersion, incubation, insight, and verification describe what organizational process? Answer : Creative decision making Individual styles are likely to come into conflict during which stage of group development? Answer : Storming All of the following are ways to become a learning organization EXCEPT Answer : focus development efforts on senior management Which of the following is the most effective technique for preventing and reducing stress? Answer : Power napping Max Webber Answer : classical organization theory was concerned with structuring organizations effectively Max Webber Answer : proposed the development of what he called the bureaucratic form of organization structure individual processes Answer : include individual differences -attitudes personalities perception attribution, employee motivation learning reinforcement and work stress informal learning Answer : is learning by imitation. normally on a uncounscious level where the learner picks up the skills by another employee who masters the skill formal learning Answer : learning by means of rewards and punishments such as incentives bonuses or reprimands and punishment technical learning Answer : is based on conscious learning where a consciously learning method has been chosen cyclic process Answer : where the employee is doing - then reflecting then thinking then deciding and this process continues with re-doing planning Answer : is the process of determining the organizations desired future position and deciding how best to get there organizing Answer : the process of designing jobs grupong jobs into manageable units and establishing patterns of authority amoung jobs and groups leading Answer : is the process of motivating members of the organization to work together toward the organizations goals controlling Answer : is the process of monitoring and correcting the actions of the organization and its people to keep them headed toward their goals Mintzberg, Henry Answer : defined basic managerial roles such as interpersonal roles - informational roles critical managerial skills interpersonal roles Answer : figurehead role - leader role - liasion role - are involved primarily with interactions with other people informational roles Answer : involve some aspect of information processng - monitor - disseminator - spokesperson decision making entrepreneur - disturbance handler resource allocator negotiater role The four management functions include all of the following EXCEPT _____. Answer : staffing _____ studies behavior as it relates to concerns such as absenteeism, turnover, productivity, and performance. Answer : organizational behavior According to the text, the best approach for obtaining knowledge about human behavior is_____. Answer : a systematic approach What behavioral science discipline has made the MOST significant contributions to understanding individual behavior? Answer : Psychology _____ has helped us understand differences in fundamental values, attitudes, and behavior between people in different countries. Answer : Anthropology ____ means that organizations are becoming more heterogeneous in terms of gender, race, and ethnicity. Answer : Workforce diversity The _____ assumption assumes that people who are different will want to assimilate. Answer : melting-pot Which of the following groups will NOT increase as a percentage of the workforce? Answer : white males A(n) _____is a situation in which an employee must define right and wrong conduct. Answer : ethical dilemma Individual level independent variables include _____. Answer : perception Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of physical ability? Answer : Looks According to your text, which is the most likely explanation for the higher absentee rate for women? Answer : Traditionally, women have had the responsibility of caring for home and family. _____ is the learning concept of reinforcing closer and closer approximations to the desired new behavior. Answer : Shaping An example of _____ is when an employee receives a one-week suspension from work and is fined $200 for stealing company property. Answer : punishment Eliminating any reinforcement that is maintaining an unwanted behavior is called _____. Answer : extinction All of the following are TRUE about both positive and negative reinforcement EXCEPT: Answer : Both positive and negative reinforcement tend to weaken behavior and decrease it subsequent frequency. A slot machine is an example of _____ reinforcement. Answer : intermittent For a salesperson who is paid commission, reinforcement occurs on a _____ schedule. Answer : variable-ratio The application of reinforcement concepts to individuals in the work setting is referred to as _____. Answer : behavior modification The belief that "discrimination is wrong" is a value statement. Such an opinion is the _____ component of an attitude. Answer : cognitive Leon Festinger would propose that the desire to reduce dissonance would be determined by all of the following EXCEPT _____. Answer : the extent to which attitudes are widely held by society. If attitudes and behavior are inconsistent, individuals will most likely _____ Answer : change either their attitudes or behavior _____ describes a positive feeling about your job resulting from an evaluation of its characteristics. Answer : satisfaction Job _____ measures the degree to which a person identifies psychologically with his or her job and considers his or her perceived performance level important to self-worth. Answer : involvement _____ commitment refers to an employee's obligation to remain with an organization for moral or ethical reasons. Answer : Normative _____ refers to an individual's involvement with, satisfaction with, and enthusiasm for the work she does. Answer : Employee engagement Steve is unhappy with his job. He takes every possible vacation and sick day and sometimes shows up for work late. He is expressing his dissatisfaction with a _____ response. Answer : neglect People with positive _____ believe in their inner worth and basic competence. Answer : Core self-evaluations Quietly continuing to do your work, even though you're dissatisfied, is an example of _____ response to dissatisfaction. Answer : loyalty According to the Myers-Briggs type Indicator, people who are classified as _____ are conceptualizers. Answer : ENTPs In the book Profiles of Genius, thirteen key executives were interviewed and tested and all were found to be _____ types. This result is particularly interesting because this type represents only about five percent of the population. Answer : intuitive thinking Which dimension of the Big Five model refers to an individual's propensity to defer to others? Answer : Agreeableness Individuals with a positive _____ like themselves, see themselves as effective, capable, and in control of their environment. Answer : core self-evaluations Individuals who are high in the _____ dimension of personality manipulate more, win more, are persuaded less, and persuade others more. Answer : Machiavellianism According to Rokeach, _____ values refer to desirable end-states of existence. Answer : terminal Which of the following is NOT one of Hofstede's five dimensions of national culture? Answer : language proficiency _____ is the degree to which people in a country prefer structured over unstructured situations. Answer : Uncertainty avoidance John Holland argues that job satisfaction is highest and turnover lowest where _____. Answer : personality and occupation are in agreement personality and occupation are in agreement Answer : Perception Which one of the following is NOT a factor that influences perception? Answer : Medium Because it is impossible for us to assimilate everything we see, we engage in _____. Answer : selective perception The internment of Japanese-Americans during World War II is an example of _____. Answer : profiling Which is NOT one of the steps in the rational decision making model? Answer : Selecting the decision that satisfices Decision makers operate within the confines of _____ i.e., they construct simplified models that extract the essential features from problems without capturing all their complexity. Answer : bounded rationality _____ is an increased commitment to a previous decision in spite of negative information. Answer : Escalation of commitment In spite of the fact that short-term stock price changes are essentially random, a large proportion of investors believe that they can predict the direction that prices will move. This is an example of _____. Answer : randomness error Which of the following is NOT an organizational constraint on decision-making? Answer : Personality Decisions made so as to provide the greatest good for the greatest number are based on _____. Answer : utilitarianism Which of the following is NOT a key element in motivation? Answer : Environment _____ is the drive to become what one is capable of becoming in Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Answer : Self-actualization Which of the following were considered higher-order needs by Maslow? Answer : social, esteem, and self-actualization needs A Theory X manager would assume employees would _____. Answer : need to be controlled Two-factor theory suggests that extrinsic factors such as _____ cause dissatisfaction. Answer : working conditions Individuals with a high need to achieve prefer all of the following EXCEPT _____ Answer : a high degree of risk According to the goal-setting theory of motivation, goals should be _____. Answer : difficult but attainable Manager's can increase an employee's _____ through enactive mastery, vicarious modeling, verbal persuasion, and arousal. Answer : self-efficacy _____ exists when an individual perceives that the ratio of their inputs to outcomes is dissimilar to the ration of relevant others. Answer : Equity tension The degree to which organizational rewards satisfy an individual's personal goals or needs and the attractiveness of those potential rewards for the individual is the ____ relationship. Answer : Rewards-personal goals The _____ says that internal rewards are obtained by individuals when they learn that they personally have performed well on a task that they care about. Answer : job characteristics model ____ (or cross-training) is the periodic shifting of an employee from one task to another. Answer : Job rotation _____ may be implemented by combining tasks, forming natural work units, establishing client relationships, expanding jobs vertically, and opening feedback channels. Answer : Job enrichment Susan works from 6 a.m. to 3 p.m. each day, while other employees in her office work from 10 a.m. to 7 p.m. It appears that Susan's employer offers a _____ option. Answer : flextime Writers, attorneys, analysts, and employees who spend the majority of their time on computers or on the telephone are natural candidates for _____. Answer : telecommuting _____ is a participative process that uses the entire capacity of employees and is designed to encourage increased commitment to the organization's success. Answer : Employee involvement A _____ is a group of employees and supervisors who meet regularly to discuss their quality problems and recommend solutions. Answer : quality circle Piece-rate plans, merit based pay, bonuses, profit sharing, gainsharing, and employee stock ownership plans are all forms of _____ programs. Answer : variable-pay _____ is an incentive plan where improvements in group productivity determine the total amount of money that is allocated. Answer : Gainsharing The three most popular types of _____ are modular plans, core-plus options, and flexible spending accounts. Answer : flexible benefits _____ is a generic term that covers a broad range of feelings that people experience. Answer : Affect Six universal _____ are anger, fear, sadness, happiness, disgust, and surprise. Answer : emotions _____ is a field of study that examines the extent to which emotions, whether positive or negative, serve a purpose. Answer : Evolutionary psychology _____ is a mood dimension consisting of nervousness, stress, and anxiety at the high end, and relaxation, tranquility, and poise on the low end. Answer : Negative affect _____ occurs when people associate two events, when there is no real connection. Answer : Illusory correlation _____ refers to an employee's expression of organizationally desired emotions during interpersonal transactions at work. Answer : Emotional labor Jane is concerned that her company is selling products of very poor quality. However, when meeting with customers, Jane feels obligated to be positive and express confidence about the quality of the product. Jane is likely experiencing _____. Answer : emotional dissonance People who exhibit _____ know their own emotions and are good at reading others' emotions may be more effective in their jobs Answer : emotional intelligence _____, one of the dimensions of emotional intelligence, is awareness of one's feelings. Answer : Self-awareness People in good moods use _____, or rules of thumb, to make decisions. Answer : heuristics The _____ stage in group development which is characterized by uncertainty. Answer : forming The _____ model is effective at describing decision-making within temporary groups, particularly those with deadlines. Answer : punctuated-equilibrium ____ groups are defined by the organization's structure. Answer : Formal _____ refers to the attitudes and behaviors that are consistent with a role Answer : Role identity _____ describe how others believe you should act in a given situation. Answer : Role expectations Which is NOT a common class of norms appearing in most work groups? Answer : Termination What is the relationship between size and group performance? Answer : Increases in group size are inversely related to individual performance. Which is NOT a weakness of group decision-making? Answer : Groups offer increased diversity of views. Which of the following best describes brainstorming? Answer : A process for generating ideas. Which of the following does NOT explain the current popularity of teams? Answer : Teams enable organizations to better utilize employee talents. _____ is an attribute of work teams which results in a level of performance that is greater than the sum of the individual inputs. Answer : Synergy _____ teams go farther than problem-solving teams in getting employees involved in work-related decisions and processes. Answer : Self-managed Which is NOT one of the three primary factors that differentiate virtual teams from face-to-face teams? Answer : Increased social rapport Which of the following is NOT one of the key factors in creating effective teams? Answer : demographics Which of the following statements is true concerning the climate of trust? Answer : Interpersonal trust among team members reduces the need to monitor each others behavior. Teams are most effective when staffed with people who are _____. Answer : Organizational demographics _____ illustrates a process loss as a result of using teams. Answer : Social loafing The _____ initiates a message by encoding a thought. Answer : sender The chief means of conveying messages is _____ communication. Answer : oral The _____ communication network is best illustrated by an unstructured committee. Answer : all-channel Grapevine studies have shown that ____ percent of employees hear about matters first through rumors on the grapevine. Answer : 75 Electronic communication includes all of the following EXCEPT: Answer : telephone calls. _____ refers to the amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode. Answer : Channel richness Jake tells his boss only what he believes the boss wants to hear. He is engaging in _____. Answer : filtering Which of the following is NOT a barrier to effective communication? Answer : Channel richness Tannen's research indicates that men use talk to ___, while women use it to _____. Answer : emphasize status; create connection In _____ cultures, the words themselves are the primary conveyors of meaning. Answer : low-context Which of the following statements is TRUE? Answer : All managers are not leaders. _____ theory states that people are born with certain characteristics that predispose them to being leaders. Answer : Trait When organized around the Big Five, _____ is the most important trait of effective leaders. Answer : extraversion _____ is the extent to which a person is likely to have job relationships that are characterized by mutual trust, respect for employees' ideas, and regard for their feelings. Answer : consideration Fiedler's contingency model assumes that an individual's leadership style is _____. Answer : fixed Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership theory differs from other leadership theories most clearly because it _____. Answer : focuses on the followers According to LMX theory, which of the following is NOT true of those individual's who fall into the outgroup? Answer : They are trusted. A _____ leadership style, identified by House in path-goal theory, leads to greater satisfaction when tasks are ambiguous or stressful than when they are highly structured and well laid out. Answer : directive The leader-participation model was developed by _____. Answer : Vroom and Yetton Leaders demonstrate _____ when they use language to influence followers' perceptions of the world, the meaning of events, beliefs about causes and consequences, and visions of the future. Answer : framing Which of the following is NOT true of charismatic leaders? Answer : They are focused on their personal needs. A charismatic leader's _____ is key to follower acceptance. Answer : vision A _____ leader has five essential qualities: (1) individual capability; (2) team skills; (3) managerial competence; (4) the ability to stimulate others to high performance; and (5) a blend of personal humility and professional will. Answer : level-5 _._____ leaders know who they are, know that they believe in and value, and act on those values and beliefs openly and candidly. Answer : Authentic Which of the following is NOT a dimension of trust? Answer : Distance A ______ is a senior employee who sponsors and supports a less-experienced employee. Answer : mentor Which of the following is true concerning online leadership? Answer : Effective on-line leaders need to develop the skill of deciphering the emotional components of messages. Which of the following is NOT a substitute for leadership? Answer : Professional orientation of employees ____ research emphasizes style; whereas research on ____ focuses on tactics for gaining compliance. Answer : Leadership; power A has ____ power over B if A can dismiss, suspend, or demote B, assuming that B values his or her job. Answer : Coercive Avoidance of ______ is why most organizations develop multiple suppliers rather than give their business to only one. Answer : dependency _____ is the only power tactic that is effective across organizational levels. Answer : _____ is the only power tactic that is effective across organizational levels. Most studies confirm that the concept of _____ is central to understanding sexual harassment. Answer : Power ______ occurs when people within organizations use whatever influence they can to taint the facts to support their goals and interests. Answer : Politicking Which of the following is NOT an individual factor related to political behavior? Answer : Level of trust _____ is the process by which individuals attempt to control the impressions others form of them. Answer : Impression management _____ are more likely to engage in impression management, molding their image to fit the situation. Answer : High self-monitors Each of the following is a question your text suggests to analyze ethical questions except: Answer : Is the action legal? Conflict must be _____ by the parties to it. Answer : perceived The traditional view of conflict argues that conflict _____. Answer : indicates a malfunctioning within the group The _____ view of conflict argues that some conflict is absolutely necessary for a group to perform effectively. Answer : interactionist _______ conflicts are almost always dysfunctional. Answer : Relationship During the _____ stage of the conflict process, conditions are present that create opportunities for conflict to arise. Answer : potential opposition or incompatibility Assertiveness is _____. Answer : the degree to which one party attempts to satisfy his/her own concerns Labor-management negotiations over wages exemplifies _____ bargaining. Answer : distributive _____ bargaining builds long-term relationships and facilitates working together in the future. Answer : Integrative During which phase of the negotiation process do the parties exchange their initial proposals or demands? Answer : Definition of ground rules Which of the following is correc Answer : In negotiations, Brazilians are likely to use physical contact. Work specialization is also referred to as ___ Answer : division of labor At an Alcoa aluminum tubing plant in upstate New York, production is organized into five departments: casting; press; tubing; finishing and inspecting, packing, and shipping. This is an example of _____ departmentalization. Answer : process The ____ is characterized by highly routine operating tasks achieved through specialization. Answer : bureaucracy The ____ violates the unity-of-command concept. Answer : matrix structure The ____ is also called the network or modular organization. Answer : virtual organization The boundaryless organization relies heavily on _____. Answer : information technology The _____ is a structure characterized by extensive departmentalization, high formalization, a limited information network, and centralization. Answer : mechanistic model Which of the following is NOT a determinant of an organization's structure? Answer : Industry Changes in corporate strategy precede and lead to _____. Answer : changes in an organization's structure Which of the following generalizations about organizational structures and employee performance and satisfaction is MOST true? Answer : There is no evidence that supports a relationship between span of control and employee performance. Institutionalization is the process through which _____. Answer : an organization takes on a life of its own Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of organizational culture? Answer : Formalization A strong culture builds all of the following EXCEPT ____. Answer : quality Culture is most likely to be a liability when _____. Answer : the environment is dynamic Which of the following is NOT a way that culture is created? Answer : Founders poll early employees to determine the appropriate cultural values. All of the following serve to sustain a culture EXCEPT _____. Answer : formalization _____ is the process that adapts employees to the organization's culture. Answer : Socialization Which of the following is NOT a common form by which culture is transmitted to employees? Answer : Selection Which of the following is NOT identified that managers can create a more ethical culture? Answer : Set aggressive performance goals. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a spiritual organization? Answer : Censorship of employee expression The objective of effective _____ is to match individual characteristics such as ability and experience, with the requirements of the job. Answer : selection _____ tests assess the applicant's ability in an authentic situation. Answer : Performance simulation Which of the following was NOT specifically suggested by your author as a general category of employee skills? Answer : Financial _____ skills training includes learning how to be a better listener and how to be a more effective team player. Answer : Interpersonal ____ training includes job rotation, apprenticeships, understudy assignments, and formal mentoring programs. Answer : On-the-job Performance evaluation serves a number of purposes, including determining who gets merit increases and other rewards. This is an example of which of the following functions of performance evaluation? Answer : Basis for reward allocations _____ evaluation provides performance feedback from the full circle of daily contacts that an employee might have. Answer : 360-degree John's performance evaluation rates him on a scale of 1 to 5 for characteristics such as job knowledge and cooperation. John's company is using a _____ performance evaluation system. Answer : graphic rating scale Even the most prestigious of schools has experienced grade inflation. In 1970, the average GPA of students at Princeton was _____, while it was _____ in 2000. Answer : 2.99, 3.40 Flextime, job sharing, and part-time work are examples of _____ for managing work-life conflicts. Answer : time-based strategies _____ are responsible for initiating and managing change within an organization. Answer : Change agents Stan is trying to implement a new organizational structure at his company. A group of key employees is resisting the change. In an attempt to "buy off" the leaders, Stan is giving them a key role in the change decision. He doesn't really value their opinion, but wants their endorsement. Stan is using the change strategy of _____. Answer : cooptation Refreezing involves _____ Answer : making a new change permanent John Kotter's _____ for implementing change builds on Lewin's three-step model. Answer : 8-step plan What of the following best describe action research? Answer : a change process based on the systematic collection of data and then selection of a change action based on what the analyzed data indicate _____ is a paradigm that values human and organizational growth, collaborative processes, and a spirit of inquiry. Answer : Organizational development _____ uses high-interaction group activities to increase trust and openness among team members. Answer : Team building ____ seeks to identify the unique qualities and special strengths of an organization and build on these to improve performance. Answer : Appreciative inquiry When errors are detected in _____, the correction process relies on past routines and present policies. Answer : single-loop learning According to Kolb's Learning Style Type, which of the following describes the convergent learning style? Answer : Abstract conceptualization, active experimentation, problem-solving According to the garbage can model of decision making, the four factors that need to connect to make a decision are problems, participants, solutions, and Answer : choice opportunities Which of the following is true about stress? Answer : Employees with external locus of control perceive situations to be more stressful than employees with internal locus of control. classical organization theory Answer : an early approach to management that focused on how organizations can be structured most effectively to meet thier goals conceptual skills Answer : skills used to think in the abstract controlling Answer : is the process of monitoring and correcting the actions of the organziation and its members to keep them directed toward their goals decision making roles Answer : key roles include the entrepreneur, the disturbance handler the resource allocator and the negotiator diagnostic skills Answer : skills used to understand cause and effect relationships and to recognize the optimal solutions to problems ethics Answer : an individuals personal beliefs about what is right and wrong or good and bad Hawthorne Studies Answer : conducted between 1927 and 1932 led to some of the first discoveries of the importance of huma behavior in organizations human relations movement Answer : the beginning of organizational behavior was based on the assumption that employee satisfaction is a key determinant of performance informational roles Answer : key roles include the monitor the disseminator and the spokesperson interpersonal roles Answer : key roles include the figurehead the leader and the liasion interpersonal skills Answer : skills used to communicate with understand and motivate individuals and groups leading Answer : is the process of getting the organizations members to work together toward achieving the organizations goals organization behavior Answer : the study of human behavior in organizational settings of the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organization itself organizing Answer : is the process of designing jobs grouping jobs into units and establishing patterns of authority between job and units planning Answer : is the process of determining an organizations desired future position and the best means of getting there rightsizing Answer : the process of optimizing the size of an organizations workforce through downsizing expanding and or outsourcing scientific management Answer : one of the first approaches to management focused on the efficiency of individual workers and assumed that employees are motiviated by money situational perspective Answer : theory that suggests that in most organizations situations and outcomes are contingent on or influcence by other variables social responsibility Answer : an organizations obligation to protect and contribute to the social environment in which it functions technical skills Answer : the skills necessary to accomplish specific tasks within the organization theory X Answer : described by Douglas McGregor is an approach to management that takes a negative and pessimistic view of workers theory Y Answer : described by Douglas McGregor is an approach to management that takes a positive and optimistic perspective on workers assimilation Answer : the process through which memb ers of a minority group are forced to learn the ways of the dominant group collectivism Answer : the extent to which people emphasize the good of the group or society individualism Answer : the extent to which people place primary value on themselves long term orientation Answer : people who focus on the future masculinity assertiveness or materialism Answer : the extent to which the dominatnt values in a society emphasize aggressiveness and the acquisition of money and material goods over concern for people relationships among people and the overall quality of life pluralistic organization Answer : an organization that has diverse membership and takes steps to fully involve all people who differ from the dominant group power distance Answer : the extent to which less powerful persons accept the unequal distribution of power primary dimensions of diversity Answer : factors that are either inborn or exert extraordinary influcene on early socialization age ethnicity gender physical abilities race and sexual orientation short term orientation Answer : people with focus on the past or present stereotypes Answer : judgements about others that reinforce beliefs about superiority and inferiority uncertainty avoidance Answer : the extent to which people prefer to be in unambiguous sitatuions valuing diversity Answer : the act of putting an end to the assumption that everyone who is not a member of the dominant group must assimilate aggreeableness Answer : a person's ability to get along with others attitudes Answer : a persons complexes of beliefs and feelings about specific ideas situations or other people authoritariansism Answer : the belief that power and status differences are appropriate within hierarchical social systems such as organizations big five personality traits Answer : a set of fundamental traits that are especially relevant to organizations burnout Answer : a sense of exhaustion that develops when someone experiences too much stress for an extended period of time cognitive dissonance Answer : the anxiety a person experiences when he or she siimultanously possesses two sets of knowledge or perceptions that are contradictory or incongruent conscientiousness Answer : the number of goals on which a person focuses contributions Answer : what the individual's contributes to an organization including effort skills ability time and loyalty creativity Answer : the ability to generate new ideas or to conceive of new perspectives on existing ideas dysfunctional behaviors Answer : work related behaviors that detract from organizational performance emotional intelligence - EQ Answer : the extent to which people are self aware can manage thier emotions can motivate themselves express empathy for others and possess social skills extraversion Answer : the quality of being comfortable with relationships the opposite extreme introversion is characterized by more social discomfort general adaption syndrome GAS Answer : a cycle through which stress occurs alarm resistance and exhaustion incubaiton Answer : the stage of less intense conscious concentration during which a creative person lets the knowledge and ideas acquired during preparation mature and develop individual differences Answer : personal attributes that vary from one person to another inducements Answer : the tangible and intangible rewards provided by organizations to individuals insight Answer : the stage in the creative process when all the scattered thoughts and ideas that were maturing during incubation come together to produce a breakthrough job satisfaction Answer : the extent to which aperson is gratified or fulfilled by his or her work locus of control Answer : the extent to which people believe their circumstances are a function of their own actions versus external factors beyond their control machiavellianism Answer : a behavior which causes people to behave to gain power and to control the behavior of others negative affectivity Answer : people who are generally downbeat and pessimistic see things in a negative way, and seem to be in a bad mood negative emotionality Answer : characterized by moodiness and insecurity openness Answer : the capacity to entertain new ideas and to change as a result of new information organizational citizenship Answer : the extent to which a person's behavior makes a positive overall contribution to the organization organizational commitment Answer : a persona identification with and attachment to an organization perception Answer : the set of processes by which an individual becomes aware of and interprets information about the environment performance behaviors Answer : the total set of work related behaviors that the organization expects the individual to display personality Answer : the relatively stable set of psychological attributes that distinguish one persona from another person job fit Answer : the extent to which the individuals contributions match the inducements offered by the organization positive affectivity Answer : people who are upbeat and optimistic have an overall sence of well being and see things in a positvie light preparation Answer : usually the first tage in the creative process includes education and formal training psychological contract Answer : a person's set of expectations regarding what he or she will contribute to the organization and wht the organization will provide in return risk propenjsity Answer : the degree to which a person is willing to take chances and make risky decisions selective perception Answer : the process of screening out information that we are uncomfortable with or that contradicts oru beliefs self efficacy Answer : the extent to which people believe they can accomplish their goals even if they failed to do so in the past self esteem Answer : the extent to which a person believes he or she is a worthwhile and deserving individual stereotyping Answer : the process of categorizing or labeling people on the basis of a single attribute stess Answer : an individuals response to a strong stimulus stressor Answer : a strong stimulus that results in stress turnover Answer : occurs when people quit their jobs type a individuals Answer : people who are extremely competitive highly committed to work and have a strong sense of time urgency type b individuals Answer : people who are less competitive less committed to work and have a weaker sense of urgency verification Answer : the final stage of the creative process in which the validity or turthfulness of the insight is determined workplace behavior Answer : a pattern of action by the members of an organization that directly or indirectly influences organizational effectiveness avoidance -negative reinforcement Answer : the opportunity to avoid or escape from an unpleasant circumstance after exhibiting behavior classical conditioning Answer : a simple form of learning that links a conditioned response with an unconditioned stimulus continuous reinforcement Answer : behavior that is rewarded every time it occurs dual structure theory Answer : identifies motivation factors which affect satisfaction and hygiene factors which determine dissatisfaction effort to performance expectancy Answer : a persons perception of the probability that effort will lead to performance equity Answer : the belief that one is being treated fairly in relation to others inequity is the belief that one is being treated unfairly in relation to others ERG theory Answer : theory that describes existence relatedness and growth needs expectancy theory Answer : theory that suggests people are motivated by how much they want something and the liklihood they perceive of getting it extinction Answer : decreases the frequency of behavior by eliminating a reward or desirable consequence that follows that behavior Which of the following is an element of the informal organization? Answer : a. values Which of the following statements is true concerning change? Answer : Global competition is the leading force driving change at work. Power distance is: Answer : d. the degree to which a culture accepts unequal distribution of power. In organizational justice, distributive justice: Answer : a. concerns the fairness of outcomes individuals receive. Which of the following is not a basic proposition of interactional psychology? Answer : . A person is changed by situations, rather than changing situations. Type theory states that introverts: Answer : c. have excellent social skills but prefer the internal world of ideas, thoughts, and concepts. Identify the five major barriers to social perception. Answer : c. selective perception, stereotyping, first-impression error, projection and self-fulfilling prophecies Cognitive dissonance is caused by a conflict between: Answer : b. attitudes and behavior. The correspondence between attitudes and behaviors doesn't depend on: Answer : d. selective perception. Which of the following individual qualities is not required in ethical decision making? Answer : Dependence on a supervisor to always tell you what is right. Which of the following is a level of cognitive moral development? Answer : a. the premoral level Herzberg's hygiene factors relate to: Answer : . both job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction. The manifest needs as identified by McClelland include Answer : achievement, affiliation, and power. In studying motivational theories, we are learning that: Answer : c. achievement is more of a motivator for Americans than for other nationalities. Classical conditioning is: Answer : modifying behavior so that a conditioned stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus and elicits an unconditioned response. ________ results from inaccurate definition of the expected job performance. Answer : b. Invalidity 5 A process of self-motivation and evaluations by a manager, peers, and possibly customers is known as? Answer : b. 360 degree feedback 6 In attribution theory, a non-performing employee's internal attribution might include: Answer : b. lack of commitment. Silence as a response has: Answer : b. value for the listener who needs to sort out thoughts. 3 Problem solving and decision making are often examples of Answer : d. two-way communication. Which of the following statements about barriers to communication is TRUE? Answer : c. They include gender differences and language. The most simplistic name for two or more people having common interests or objectives is a ________. Answer : b. group The "interpersonal glue" that helps work groups stay together is known as: Answer : c. group cohesion. Teams are very useful when: Answer : b. the tasks are interrelated. Responsibilities of a team leader, in contrast to a manager, include: Answer : d. hands-on skills of direct involvement and full membership in the team. Escalation of commitment: Answer : is simply hanging on to a poor decision. ________ is a deterioration of mental efficiency, reality testing, and moral judgment resulting from in-group pressures. Answer : b. Groupthink Which tactic is an American manager most likely to use when dealing with a tardy employee? Answer : c. If you don't start reporting on time for work, I will have to cut your pay. ________ is the belief that one has the ability to do a job well. Answer : b. Self-determination The main difference between a leader and a manager is that: Answer : leaders are advocates for change, and managers for the status quo. On the Leadership Grid, a manager who has a medium concern for people and production is a(n): Answer : b. organization man manager. Which of the following ideas are associated with Fiedler's contingency theory? Answer : Leaders are classified using an assessment tool called Least Preferred Coworker (LPC) scale. According to the Situational Leadership model, a ________ style is characterized by high task behavior and high relationship behavior. Answer : d. selling Which of the following is one of the competencies that make up emotional intelligence? Answer : a. empathy A dynamic follower is one who: Answer : b. practices self-management. ________ conflict occurs when a person experiences conflict among the multiple roles in his or her life. Answer : c. Interrole Which of the following statements best describes our understanding of the "avoidance approach" to conflict? Answer : d. It is all right to use this approach when issues seem trivial. 6 In order to create a conflict-positive organization, there are many interrelated steps to follow. They include which of the following? Answer : a. Empower employees to feel confident and skillful. Scientific management emphasized: Answer : b. work simplification. Which of the following job core characteristics does NOT directly relate to meeting the needs of a critical psychological state? Answer : c. rate of pay The mechanics approach to job design emphasizes: Answer : c. a lower chance of mental overload. The idea of placing human consideration at the center of job design is called: Answer : d. anthropocentric. The characteristics which appropriately impact the design of an organization's design processes are known as: Answer : b. contextual variables. In comparing the organizational design needs of the small organization and the large organization, which of the following is a consideration for the small organization? Answer : c. more centralization In Perrow's study of the impact of technology on organization design, he considered all but which of the following elements? Answer : d. The span of control in an organization as a whole. 6 There are several things that can assist a large organization to decentralize, including: Answer : specialization of products/market/technology. The most visible and accessible level of culture is: Answer : c. artifacts. Which statement is TRUE about espoused values? Answer : . They are what members say they are. Which one of the following is NOT one of the five major elements in a managing culture? Answer : d. How well leaders know their employees. Change and acquisition is: Answer : a. when the newcomer begins to master the demands of the job. It is the position of the authors, Nelson and Quick, that: Answer : c. adapting, flexibility, and responsiveness are desirable hallmarks in change management. Powerful external forces for change do not include: Answer : d. bureaucratic guidelines. 5 Which of the following is NOT one of the steps in Lewin's change model? Answer : a. freezing Which of the following is true of Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory? Answer : Maslow believed that humans were creative beings seeking self-actualization. All of the following are factors that are necessary in the communication process EXCEPT Answer : A) trust Job rotation is used primarily to Answer : keep employees from getting bored Which of the following is NOT thought to be a determinant of personality? Answer : emotional intelligence Which of the following is considered an unethical political tactic to gain power in an organization? Answer : Playing territorial games Information technology Answer : All of the following disciplines have contributed to the foundations of the field of organizational behavior EXCEPT What do denial, stereotyping, and projection have in common? Answer : They are all ways to deal with sensory information The office grapevine is an example of Answer : information communication The following are true about making good business decisions EXCEPT Answer : an estimated 20 percent of decisions made in organizations fail What is considered a standard response for routine problems? Answer : programmed decision A manager trying to motivate an employee should Answer : give ample feedback A manager trying to motivate an employee should Answer : By observing leaders and socialization Which of the following is the least effective method of influencing others? Answer : coalition formation cross functional teams are Answer : used most often for the purpose of product development decision criteria are used to Answer : evaluate alternatives Who developed the situational leadership model? Answer : Paul Hersey and Kenneth Blanchard What is the trend in work space design? Answer : Creating public spaces for employees to use for various purposes The question "To whom do you go to for information about what's going on?" is commonly asked Answer : during a social network analysis Employees resist change most often because of the Answer : fear of an adverse outcome What is a common result of information overload? Answer : increased work stress Which of the following is true of heuristics? Answer : Heuristics lead to biases in judgment. According to the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), Bill is a thinking-type. When reviewing a vendor proposal with his boss, he will most likely Answer : express his opinion Which of the following is true about gender differences in leadership? Answer : It is difficult to judge the truth about stereotypes of gender differences. According to Kolb's Learning Style Type, which of the following describes the accommodative learning style? Answer : Concrete experience, active experimentation, adaptive Power granted to a person by an organization is an example of Answer : position power What is a dependent variable? Answer : The factor that an experiment or hypothesis tries to explain or predict that is affected by some other factor Which of the following is NOT true about stress? Answer : Women respond more intensely to stress than men and have a higher risk of heart attack and stroke. Which of the following statements accurately describes situational leadership? Answer : There is no one best way to influence group members. A mechanistic organization Answer : emphasizes specialization and control Which of the following is true about job enrichment? Answer : It increases employee responsibility. Which is a major contributing factor to the transformational leader? Answer : chharisma The most important challenge facing the field of organizational behavior is Answer : managing workforce diversity Which of the following has become a significant source of workplace conflict? Answer : rudeness and incivility Empowerment is a strategy focused on improving all of the following EXCEPT Answer : bureaucracy What is an organigraph? Answer : A map that gives an overview of a company's functions and the way people organize themselves at work Which of the following statements is true about Herzberg's two-factor theory? Answer : Intrinsic factors are related to job satisfaction. Accounting firms, consulting firms, and hospitals are examples of Answer : professional bureaucracies Which of the following is a difference between men's and women's communication styles? Answer : Women prefer to communicate to build rapport, and men use communication to display knowledge and skill. Being "in the zone" is also known as Answer : the experience of flow Which of the following is true about Total Quality Management (TQM)? Answer : Relies on bottom-up, participative decision making in planning and execution A leader with Machiavellian tendencies would likely Answer : manipulate others for his or her personal gain Which of the following statements accurately describes Vroom's expectancy theory? Answer : It is one of the most widely accepted theories of motivation. Advances in information technology have Answer : increased access to information and made delayering possible What type of power will help a leader establish a power base? Answer : Power as an expert What is the relationship between stress and job performance? Answer : Moderate stress correlates with high performance. Outsourcing means that a company Answer : hires other companies to do some of its work What is an affinity group? Answer : An employee-involvement group made up of professional-level workers The only way a person can influence someone else is to Answer : communicate Which is true about flat organization structures? Answer : Customer problems can be solved quickly. A person with a high achievement need Answer : prefers tasks of intermediate difficulty What differentiates a team from a group? Answer : Shared versus individual accountability Reinforcement theory Answer : has operant conditioning at its foundation Determining the tasks to be done, who should do them, and who reports to whom is an example of which management function? Answer : Organizing Which of the following statements is true about group dynamics? Answer : Groups go through predictable stages to become productive. According to the triarchic theory of intelligence, Answer : wisdom, street smarts, and common sense are important factors of intelligence As a rule of thumb, in the absence of information, what do many employees do? Answer : Create and spread rumors Which of the following describes people with a directive style of decision making? Answer : Has a low tolerance for ambiguity and seeks rationality The following are all conditions that favor social learning EXCEPT Answer : need for power Which of the following is true about virtual teams? Answer : They benefit companies that are spread out in a wide geographic area. The contingency approach to organization design affirms that Answer : organizations are more effective when they are structured to fit the situational demand Which of the following is true about employee recognition? Answer : Employees welcome praise as much as a paycheck. A strategy, or method, for increasing organizational effectiveness by bringing about planned change is called Answer : organizational development Nonverbal communication has the main purpose of Answer : expressing the communicator's emotions behind the message If an employee misperceives an event that occurs in the workplace, it is likely that he or she has Answer : strong attitudes about that event Which organization structure is best suited to leveraging specialization? Answer : Functional The nominal group technique is Answer : a group decision-making approach that generates creative alternatives independently According to the Holmes and Rahe "Social Adjustment Rating Scale," which of the following is considered the most stressful event? Answer : Death of a spouse Which of the following is NOT a technique to enhance creativity? Answer : Forming homogeneous work groups Which of the following is a disadvantage of a bureaucratic organizational structure? Answer : Bureaucratic controls can suppress initiative and decision making at lower levels. In order to build teamwork, a manager should avoid which of the following? Answer : Supervising the group closely Which of the following is an accurate description of Emotional Intelligence (EI)? Answer : A person's EI predicts performance better than IQ. Which of the following statements is true about organizational behavior? Answer : Organizational behavior is a study of individuals, groups, and structure. Openly discussing the worst-case possibilities of a situation is a way a company can Answer : reduce the negative consequences of rumors What does the P stand for in the equation B = ƒ(P x E)? Answer : Person All of the following accurately describe Alderfer's ERG theory EXCEPT Answer : Alderfer reworked Herzberg's theory to align with empirical research According to the Leadership Grid®, which is the best leadership style? Answer : Team management According to equity theory model, Answer : employee satisfaction is dependent on how fairly the employee believes he or she is treated in comparison to others Who created the three-step model for change that includes unfreezing, movement, and refreezing? Answer : Kurt Lewin Leadership is the domain of which group of employees? Answer : All employees Which of the following is true about conflict? Answer : Conflict can be both positive and negative. Which of the following accurately describes organizational change? Answer : Individuals' ability to learn to deal with change is a major part of managing change.