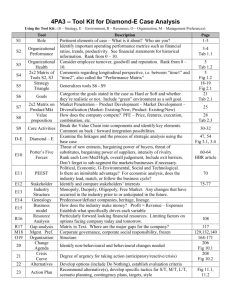
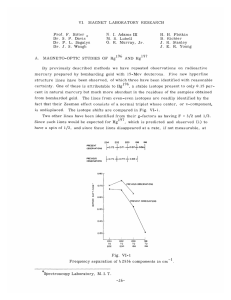
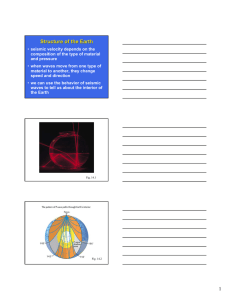
Ch. 29
advertisement

Chapter 29 Serway & Jewett Ch. 29 1 B-field from magnet Ch. 29 E-field from pt charge 2 Electric dipole Ch. 29 Magnetic dipole 3 Repel Attract Attract Ch. 29 Repel 4 Ch. 29 5 Ch. 29 6 Magnetic Force on positive and negative charges Ch. 29 7 Right-hand rule for vector cross products a b c Ch. 29 8 Assume the pictured electron beam initially moves in the vertical direction and then bends to the right in the plane of the picture. Which ways does B point? Ch. 29 9 Ch. 29 10 Ch. 29 11 090104 Ch. 29 12 Ch. 29 13 Table 29-1, p.899 Exotic astrophysical phenomena may be addressed with future multi-Petawatt lasers The minimal requirements for photon-bubble instability could potentially be met with a properly configured 10 ps PetaWatt laser experiment. HEDP Task Force Neutron Star Te ~ 10 keV Trad ~ 10 keV B ~ 10 Gigagauss @ n ~ 10-1-10-3 g/cm3 B ~ 106 T Ch. 29 PetaWatt Laser Te ~ 1 keV Trad ~ 1 keV B ~ 100 Megagauss @ n ~ 10 g/cm3 B ~ 104 T 14 Active Figure 29.19 Ch. 29 (SLIDESHOW MODE ONLY) 15 Active Figure 29.23 v=E/B Ch. 29 (SLIDESHOW MODE ONLY) 16 Quick Quiz 29.10a Three types of particles enter a mass spectrometer like the one shown in your book as Figure 29.24. The figure below shows where the particles strike the detector array. Rank the particles that arrive at a, b, and c by speed. (a) a, b, c (c) c, b, a Ch. 29 (b) b, c, a (d) All their speeds are equal. 17 Quick Quiz 29.10b Rank the particles that arrive at a, b, and c by m/q ratio. (a) a, b, c (b) b, c, a (c) c, b, a (d) All their m/q ratios are equal. Ch. 29 18 Ch. 29 19 Fig 29-7, p.901 Ch. 29 20 Fig 29-8, p.901 Quick Quiz 29.4 The four wires shown below all carry the same current from point A to point B through the same magnetic field. In all four parts of the figure, the points A and B are 10 cm apart. Rank these situations according to the magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on the wires, from greatest to least? Ch. 29 21 Ch. 29 22 Fig 29-10b, p.902 Ch. 29 23 Fig 29-13a, p.904 Torque =rF Ch. 29 24 Fig 29-13, p.904 Magnetic Moment Perpendicular to the surface! Ch. 29 25 Fig 29-15, p.905 Hall Effect Ch. 29 26 Fig P29-48, p.922 Ch. 29 27 Fig P29-53, p.922