Mitosis
advertisement

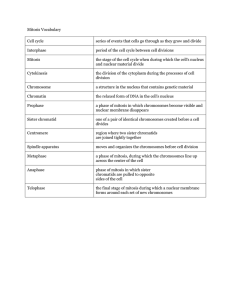
• Prophase – Metaphase – Anaphase – Telophase • Prophase – – – – chromatin begins to tightly coil (condenses) nuclear envelope begins to disappear nucleoli disappear each chromosome is now a complex of sister chromatids – mitotic spindle begins to form – centrosomes move away fro each other • Prometaphase – nuclear envelope fragments – microtubules move through the nuclear area through the center of the cell – each sister chromatid complex is now connected to a microtubules by the kinetochore region of the centromere M-Phase M-Phase • Metaphase – longest phase of Mitosis – centrosomes are now at opposite sides of the cell – chromosomes are located at the metaphase plate (center) – kinetochores of the sister chromatids are now attached to tubules of opposite centrosomes – microtubule complex is now called the spindle M-Phase • Anaphase – shortest phase of Mitosis – sister chromatids are pulled apart as the spindle fibers shorten – the separated chromosomes migrate toward the opposite poles – at the end of anaphase the polar regions of the cell have equivalent amounts and types of chromosomes • Telophase M-Phase – the 2 daughter cell nuclei begin to form – nuclear envelopes begin to form from the parent fragments – chromosomes become less condensed – mitosis is complete with the completion of the 2 nuclei regions M-Phase • Cytokinesis – the cell divides at the cleavage furrow shortly after Mitosis • Pinching in of the plasma membrane – Cell plate forms in plants • Becomes the cell wall