Coaching & Mentoring PPT
advertisement

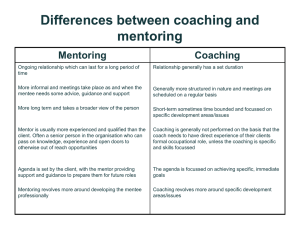
Welcome to the Team Oriented Coaching and Mentoring BEST Consulting Successful Consulting, Level II Workshop Series Presentation by Rick Sell Facilities Location of: – Restrooms – Telephones and Messages – FAX Machines – Smoking Areas – Water and Sodas – Snacks Workshop Groundrules This is a workshop and is designed to be informal, however: – Respect others and their opinions; give them the space to successfully learn and grow. – Turn those phones off and put your beepers on vibrate - PLEASE? – Resist those that are trying to summon you until the break. Workshop Overview Caveat We will not severely differentiate between coaching and mentoring due to the reasonable assumption that there are no overriding major fundamental differences between the two. For the purposes of this workshop the following semantic rules will apply: Synonymous words: – – Performer, worker, co-worker, employee, team member, individual Project team leader, team leader, supervisor, manager, management Introductions Who am I? – Rick Sell – Now it’s your turn! Introductions …and you are? – How long with BEST Consulting, how – – – – long in consulting in general? Current assignment and skill sets Hobbies/outside activities or interests Last movie seen;would you recommend? Important: What are your expectations of this course? Workshop Agenda Work, Learn, Have Fun! – – – – – Session: 4 hours Introductions Course Overview Discuss Topics Breaks - What Breaks!!! Workshop Overview What this workshop is: – A practical and pragmatic approach to coaching and mentoring team members in a performance environment . What this workshop is not: – This workshop will not make you an expert coach/mentor, although it will lay a foundation for continued improvement. Workshop Overview Workshop Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Define a workplace performance environment. Explain the need for coaching and/or mentoring in a variety of organizational settings. List a variety of situations where coaching and/or mentoring can be effective. Apply strategies to improve interpersonal communication in the workplace. Implement techniques to improve your success when giving and receiving performance feedback. Workshop Overview Workshop Objectives (con’t) Upon completion, you will be able to: Define the steps of an effective Coaching and Mentoring Model that can be used in hierarchical and team-driven environments. Execute strategies for dealing both with substandard performers. Develop or improve a system for accurately documenting all team member coaching and mentoring activities. Instructional Materials Student Manual is provided as a valuable desk-top reference. Case Studies and Student Exercises are an integral part of this course, and essential events in your learning process - Please Participate? Student Activity: Self-Assessment Goal: To provide you with an idea of how well you perform in each area. An opportunity to define your style Provide a baseline for improvement. Why Coach/Mentor? Learning Objectives After completing this subject, you will be able to: – Define the performance environment – Define performance coaching and mentoring – Describe the characteristics of an effective coach/mentor. – Explain the importance of coaching/mentoring in improving workplace effectiveness. – Identify and eliminate excuses for not coaching or mentoring. Examining The Performance Environment Formal evaluated, defined, and documented organizational program containing: – Project Management Plan Project performance goals (expected outcomes) Performance baseline criteria – Continued Performance Improvement Plan – Individual (Team Member) Performance Plan: Performance behavior expectations Education and Training plan Why Coach/Mentor? Shifts in Behavioral Expectations Axiom Change is inevitable; people are adverse to change Roles and behavior are changing to match new demands in the workplace. Organizations are moving from Hierarchical to Team Structure. Why Coach/Mentor? What is Coaching and Mentoring? It’s what we do all the time - we just don’t put a name to it! Influencing, helping, instructing, motivating, leading. Why Coach/Mentor? What does Coaching and Mentoring Involve? Any activity in which a coach/mentor and an individual work toward individual performance improvement. Influencing, helping, instructing, motivating, leading. What are some other skills practiced by successful coaches and mentors? Why Coach/Mentor? Characteristics of an Effective Coach/Mentor – – – – – – Excellent communication skills Motivated Enthusiastic Goal oriented Creative Patient What are some other characteristics of successful coaches and mentors? Why Coach/Mentor? Benefits of Coaching/Mentoring? Success, Success, Success Win-win situation Improved perception of the consultants who take on active roles of coach and/or mentor. Increased business opportunities through success. Why Coach/Mentor? Excuses for Failing to Coach/Mentor Excuses are used by “others”, not consultants. Excuses are nothing more than internal roadblocks. Excuses are a roadmap for failure. Opportunities for Coaching/Mentoring Learning Objectives Upon completion of this subject, you will be able to: – Realize the cost of failing to coach/mentor. – Recognize opportunities for coaching and/or mentoring team members. – Develop a strategy for orienting new team members. – Explain the importance of developing team members performance. When: Opportunities for Coaching/Mentoring – Anytime a new team member comes on board. – You (team leader) are off-site – The individual appears to be too dependent on you and other team members. – When changes take place in the workplace. – New processes, policies, procedures implemented. – A team member is failing, or is displaying the behavior to potentially to fail. Goal: Opportunities for Coaching/Mentoring – Build teams. – Coach/mentor yourself “out of a job”. – Empower team members; allowing them to be independent. – Minimize impact of changes in the workplace. – Smooth implementation of new processes, policies and procedures. – Eliminate the need for formal counseling and retraining. Opportunities for Coaching/Mentoring Develop and Document an Orientation Process The program has to be used to be effective. Show genuine personal interest in new people. Publish the Orientation Procedures. Develop and Use an Orientation Checklist. Evaluate, Train, and Assign “buddies”, then continually re-evaluate. Opportunities for Coaching/Mentoring The Cost of Failing to Coach/Mentor Failure, Failure, Failure Lost team members Lost revenues Lost time Lost confidence in your credibility by management and other team members Coaching/Mentoring Process Learning Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Develop a systematic approach to coaching and mentoring, using the formal eight-phase model. Set effective goals and objectives with your team members. Identify resources for individual development. Construct an Action Plan for individual development. Coaching/Mentoring Process The Model: Eight-Phased Approach Phase 1 - Establish Goals Phase 2 - Collect Performance Data Phase 3 - Analyze Performance Phase 4 - Review and Modify Performance Goals as Needed Phase 5 - Identify Developmental Resources Phase 6 - Develop an Action Plan Phase 7 - Implement Strategies Phase 8 - Evaluate Performance Coaching and Mentoring for Better Relationships Learning Objectives After completing this subject, you will be able to: Apply the Communication Process. Explain how coaching and mentoring can aid in building better relationships. Use your knowledge of communication to improve interpersonal relationships in the workplace. Learn to avoid the “Nine Deadly Sins” that affect relationships. Build stronger relationships with your team members, peers, and boss. Coaching and Mentoring for Better Relationships The Communication Process Communication is the transmission of information and meaning from one individual or group to another. Contains the Communication Model. Building solid two-way communications in your team cannot be overemphasized. Communication Model Sender has idea Sender has idea Sender encodes message How may the sender encode a message? Verbally or nonverbally By speaking, writing, gesturing Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message What kinds of channels carry messages? Letter, memo, telephone, TV, report, computer picture, voice, body--Others? Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise How does a receiver decode a message? Hearing, reading, observing Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise What is noise? Anything that disrupts the process ? Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise Receiver understands message Feedback travels to sender Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Receiver understands message Noise How can a communicator provide for feedback? Ask questions, watch responses, don’t exchange. dominate Feedback travels to sender Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise What kind of feedback is better? Descriptive rather than evaluative. Receiver understands message Feedback travels to sender Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise Possible additional feedback travels to receiver Receiver understands message Feedback travels to sender Noise Sender has idea Sender Channel encodes carries message message Receiver decodes message Noise Possible additional feedback travels to receiver Receiver understands message Feedback travels to sender Sender has idea When is communication successful? Possible additional feedback travels to receiver Receiver understands message Feedback travels to sender Sender has idea When the message is understood as the sender intended it to be. Possible additional feedback travels to receiver Receiver understands message Try your skill ... Select the definition or explanation of the following parts of the communica-tion process. 1. Encoding is the process of: a. Creating a meaningful dialogue. b. Selecting and organizing symbols to represent a message. Understanding the meaning of a message. c. Try your skill ... Select the definition or explanation of the following parts of the communica-tion process. 1. Encoding is the process of: Creating a meaningful dialogue. b. Selecting and organizing symbols to represent a message. Understanding the meaning of a message. a. c. Try your skill ... 2. Decoding is the process of: Avoiding noise and interference. b. Selecting and organizing symbols for feedback. c. Interpreting the meaning of communicated symbols. a. Try your skill ... 2. Decoding is the process of: Avoiding noise and interference. b. Selecting and organizing symbols for feedback. c. Interpreting the meaning of communicated symbols. a. Coaching and Mentoring for Better Relationships Learning Objectives After completing this subject, you will be able to: Apply the Communication Process. Explain how coaching and mentoring can aid in building better relationships. Use your knowledge of communication to improve interpersonal relationships in the workplace. Learn to avoid the “Nine Deadly Sins” that affect relationships. Build stronger relationships with your team members, peers, and boss. Coaching and Mentoring for Better Relationships Nine Deadly Sins that Affect Relationships Failing to Communiciate Effectively. Playing Games. Playing Favorites. Getting Involved with Individuals Personal Problems. Becoming Personally Involved with Team Members. Ignoring Performance Gaps. Treating Team Members Unfairly. Failing to build a Sound Foundation. Displaying a Lackadaisical Attitude. Coaching and Mentoring for Better Relationships Peer Relationships Do: – Be very sensitive to the individual and their needs. – Allow an individual to correct their own mistakes, but monitor closely. Do Not: – Stand idly by while an individual is making a mistake. – Jump in and try to help too quickly, but don’t allow the problem get out of hand. – Set yourself up as a “know it all”. Reminder: An individual does not necessarily have to be on your immediate team for you to help. Effective Feedback Strategies Learning Objectives Upon completing this subject, you will be able to: Recognize various types of feedback. Identify strategies for giving and receiving feedback. Give praise effectively. Give criticism constructively. Develop an environment that encourages the use of feedback. Effective Feedback Strategies Importance of Feedback? Positive communication; review the communication model. An effective tool for building relationships. Potentially destructive if not used carefully. Team members must be coached and mentored in feedback strategies. Know what message you are trying to send. All important: Timing, Timing, Timing! EffectiveHow Feedback Strategies to Give Feedback Written correspondence. Write it and then live with it for a period. Verbal communication. Practice before you deliver! Nonverbal communication. Watch that body language! Actions/Inactions. Timing, Timing, Timing! Trappings. Think about how do you present yourself? Effective Feedback Strategies Approaches to Feedback Focus on the individual’s behavior, not the person’s personality. Avoid globalizing behavior. (always,never) Use “I” instead of “you” language. Effective Feedback Strategies Using Feedback Effectively - Ask yourself: Is this the right time? Is this the right place? Is this the appropriate person? What is the best way to communicate my message? Is the feedback well thought out and valid? What problems might feedback create? Will my feedback damage the relationship? If yes, how? Effective Feedback Strategies Positive Feedback (Praise) Giving: – Team members require positive motivation. – Be specific about what you liked. – Feedback should be given right after the performance. (Timing,Timing,Timing) Receiving: – Be courteous, say “thank you”. – Ask for clarification if you need it. Effective Feedback Strategies Giving Negative Feedback (Criticism) Tell the person exactly what you observed. Explain exactly how you feel about the behavior and the impact. Solicit feedback. Show support and solicit possible solutions from the individual. Get a commitment to improve behavior. Reaffirm the individual’s worth. Effective Feedback Strategies Approaches to Feedback Focus on the individual’s behavior, not the person’s personality. Avoid globalizing behavior. (always,never) Use “I” instead of “you” language. Effective Feedback Strategies Receiving Negative Feedback Listen, do not interrupt. Ask for clarification or more information. Try to be objective. (Yes, it is hard!!!) Decide if the comments are valid. Now its your turn: Be polite and provide appropriate feedback. Say “thank you”. Effective Feedback Strategies Encouraging Feedback Build a system which encourages feedback. Feedback empowers team members. Gives them buy-in to the process. Allow team members to fail. Remember: Feedback (communication) is a twoway street! Managing Team Members Performance Learning Objectives After completing this subject, you will be able to: Determine what motivates performers. Recognize signs of negative behavior. Define strategies for dealing with substandard performers. Identify techniques to assist and reward above-average performers. Managing Team Members Performance What motivates performers? Coach/Mentor = Motivator You are the motivator, its your responsibility to find out. Simplest method? Ask! Remember the individual, they all have separate needs, wants, and desires. Managing Team Members Performance Performance Level Know what the performance gap is. Address performance gaps after determining what factors affect team members. Allocate your resources to address each group of performers separately: poor, average, superstar. Managing Team Members Performance Indicators of Performance Does the individual meet established standards and goals? Are there complaints from other workers about this individual? What are the current quality and quantity levels? How much initiative and enthusiasm does the individual exhibit? Managing Team Members Performance Behavioral Performance Indicators “They Won’t” – They are not motivated. “They Can’t” – They lack the ability. – Outside factors impede them. – Inadequate team leader guidance. “They Don’t Know How” – Lack of technical or job knowledge. Managing Team Members Performance 80/20 rule Having 80% of your time taken up by the 20% of poor performers. You must be very careful not to neglect other performers while trying to “fix” a broken one. Managing Team Members Performance Managing Substandard Performers Identify substandard performers early. Develop an Action Plan for improved performance. Superstars are potentially poor performers because they can be extremely disruptive to the team. You must be proactive in your approach to managing all performers, but especially substandard individuals. Summary Where your expectations met, if not, why not? Do you have any further questions? Now is the time. Your suggestions, comments, and constructive feedback are honestly solicited.