Carbon Allotropes & Covalent Networks: Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene
advertisement
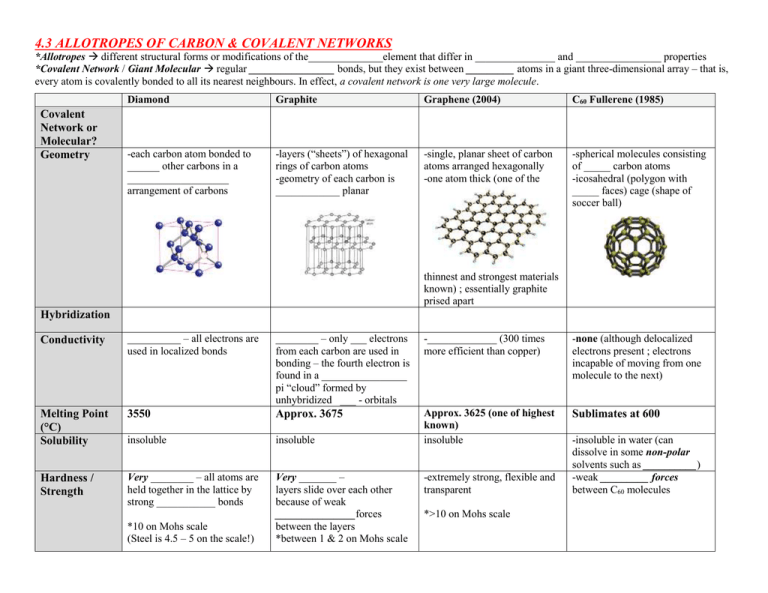
4.3 ALLOTROPES OF CARBON & COVALENT NETWORKS *Allotropes different structural forms or modifications of the______________element that differ in _______________ and ________________ properties *Covalent Network / Giant Molecular regular ________________ bonds, but they exist between _________ atoms in a giant three-dimensional array – that is, every atom is covalently bonded to all its nearest neighbours. In effect, a covalent network is one very large molecule. Covalent Network or Molecular? Geometry Diamond Graphite Graphene (2004) C60 Fullerene (1985) -each carbon atom bonded to ______ other carbons in a ___________________ arrangement of carbons -layers (“sheets”) of hexagonal rings of carbon atoms -geometry of each carbon is ____________ planar -single, planar sheet of carbon atoms arranged hexagonally -one atom thick (one of the -spherical molecules consisting of _____ carbon atoms -icosahedral (polygon with _____ faces) cage (shape of soccer ball) thinnest and strongest materials known) ; essentially graphite prised apart Hybridization Conductivity __________ – all electrons are used in localized bonds ________ – only ___ electrons from each carbon are used in bonding – the fourth electron is found in a ________________ pi “cloud” formed by unhybridized ___ - orbitals -_____________ (300 times more efficient than copper) -none (although delocalized electrons present ; electrons incapable of moving from one molecule to the next) Melting Point (°C) Solubility 3550 Approx. 3675 Sublimates at 600 insoluble insoluble Approx. 3625 (one of highest known) insoluble Hardness / Strength Very ________ – all atoms are held together in the lattice by strong ___________ bonds Very _______ – layers slide over each other because of weak _______________forces between the layers *between 1 & 2 on Mohs scale *10 on Mohs scale (Steel is 4.5 – 5 on the scale!) -extremely strong, flexible and transparent *>10 on Mohs scale -insoluble in water (can dissolve in some non-polar solvents such as __________) -weak _________ forces between C60 molecules Some Uses -heavy-duty cutting tools (e.g., saws, polishing tools, dental drills) -pencil ‘lead’ -machine lubricant -potential to replace metals -inclusion complexes (enclosed used in the aerospace industry -LCD screens atoms or small molecules within fullerene cage) potentially used as gene and drug carriers, and in superconductivity -inhibit HIV related enzymes Other Examples of Covalent Networks: Silicon Geometry *Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), Quartz / Silica *Quartz: same as diamond structure Silicon Carbide (SiC / Moissonite) Conductivity Hybridization Melting Point (°C) Solubility Semiconductor *Silica = sand (amorphous…no ordered structure) Solid – none ; Molten - conducts 1400 1710 2700 -insoluble -insoluble -insoluble Hardness Some Uses 7.0 on Mohs scale -electronic components -computer chips 7.0 on Mohs scale -use in optical and scientific instruments -electronics (e.g. quartz watch) 9 - 9.5 on Mohs scale -diamond alternative - SiC powder = an abrasive - car parts -bulletproof vests Periodic Table of Videos: Buckyballs (fullerenes): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ljF5QhD5hnI Graphene: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=prKi2TI0TVw Carbon / allotropes of Carbon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QuW4_bRHbUk Silicon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a2aWO5cL410 semiconductor







