Alkanes
advertisement

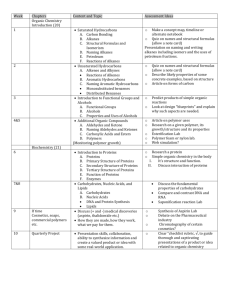
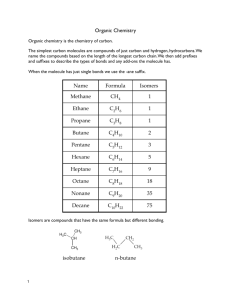
The study of carbon-based compounds and their properties. Historically the distinction between inorganic and organic substances was based on whether or not they were produced by living systems. It was believed that some sort of “life force” was needed to synthesize them. NH4OCN H2N—C—NH2 O urea In 1828, the German chemist Freidrich Wohler (1800-1882) prepared urea from the inorganic salt ammonium cyanate by simple heating. Hydrocarbons: contain only hydrogen and carbon Hydrocarbons can be divided into different types, depending on their bonding. Hydrocarbons Aliphatic Aromatic Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Cyclic Naming Organic Molecules Alkanes - - Carbon chain, no double or triple bonds. All single bonds Alkenes - - Carbon chain, contains double bond(s) Alkynes - - Carbon chain, contains triple bond(s) Naming Organic Molecules There are two parts to the main name of each molecule… prefix: tells the # of carbons in main chain or ring suffix: tells the type of bonding in the chain or ring Prefix: indicates number of carbon atoms in the main chain or ring 1 meth- 6 hex- 2 eth- 7 hept- 3 prop- 8 oct- 4 but- 9 non- 5 pent- 10dec- Suffix: indicates types of bonds present Alkanes: (all single bonds) ___ -ane Alkenes: (double bond) ___ -ene Alkyne: (triple bond) ___ -yne For example… For example… For example… Saturated Hydrocarbons contain only single C-C bonds Unsaturated hydrocarbons: contain double or triple C-C bonds Saturated Hydrocarbons: the ALKANES: chains of carbon connected by single bonds: ALKANES methane, CH4 ALKANES ethane, C2H6 ALKANES propane, C3H8 ALKANES butane, C4H10 ALKANES pentane, C5H12 ALKANES hexane, C6H14 ALKANES octane, C8H18 “Normal” v. Branched “normal” hydrocarbons are straight chains; no branching Branched-chain hydrocarbons – isomers of “normal” hydrocarbons; have same formula, but different structures n-butane 2-methlypropane n-pentane 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpentane Cycloalkanes cyclopentane Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: ALKENES – contain C-C double bonds 2-pentene Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: ALKENES – contain C-C double bonds 2,4-hexadiene Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: ALKYNES – contain C-C triple bonds 1-butyne Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: ALKYNES – contain C-C triple bonds 3-ethyl-1-pentyne Aromatic Hydrocarbons: benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon; has a symmetrical ring structure Aromatic Hydrocarbons: benzene – can be drawn like this… Derivatives of benzene: 1-ethyl-2-methylbenzene Derivatives of benzene: 1,2-dimethyl-4-propylbenzene Functional Groups Functional groups: special groups of atoms attached to a hydrocarbon skeleton; the most common sites of chemical reactivity. Organic halides: a hydrogen is replaced by a halogen fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo- 2-iodobutane Organic halides: a hydrogen is replaced by a halogen fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo- 2,4-dibromo-1-hexene Organic halides: a hydrogen is replaced by a halogen fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo- 1-bromo-2-chlorobenzene Alcohols & phenols: contain the hydroxyl group (-OH) alcohols: at least 1 H on a hydrocarbon is replaced by OH phenols: at least 1 H on an aromatic ring is replaced by OH 2-propanol Alcohols & phenols: contain the hydroxyl group (-OH) alcohols: at least 1 H on a hydrocarbon is replaced by OH phenols: at least 1 H on an aromatic ring is replaced by OH 3-methyl-1-butanol Alcohols & phenols: contain the hydroxyl group (-OH) alcohols: at least 1 H on a hydrocarbon is replaced by OH phenols: at least 1 H on an aromatic ring is replaced by OH 1,2-butanediol ethers: compounds in which an O atom is bonded to 2 organic groups: -C-O-C- methoxymethane (dimethyl ether) ethers: compounds in which an O atom is bonded to 2 organic groups: -C-O-C- methoxypropane (methyl propyl ether) ethers: compounds in which an O atom is bonded to 2 organic groups: -C-O-C- methoxybenzene (methyl phenyl ether) amines: derivatives of ammonia (NH3) in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by organic groups (alkyl or aryl groups) ammonia amines: derivatives of ammonia (NH3) in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by organic groups (alkyl or aryl groups) methylamine amines: derivatives of ammonia (NH3) in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by organic groups (alkyl or aryl groups) trimethylamine amines: derivatives of ammonia (NH3) in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by organic groups (alkyl or aryl groups) 2-aminobutane amines: derivatives of ammonia (NH3) in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by organic groups (alkyl or aryl groups) 1-amino-3-propylcyclohexane *aniline: the simplest aromatic amine aniline *aniline: the simplest aromatic amine 3,5-dichloroaniline *aniline: the simplest aromatic amine N,N-dimethylaniline Carboxylic acids: compounds that contain the carboxyl group (general formula is R-COOH) butanoic acid Carboxylic acids: compounds that contain the carboxyl group (general formula is R-COOH) ethanoic acid Carboxylic acids: compounds that contain the carboxyl group (general formula is R-COOH) 3-methylpentanoic acid Carboxylic acids: compounds that contain the carboxyl group (general formula is R-COOH) benzoic acid