Electron Configuration notes
advertisement

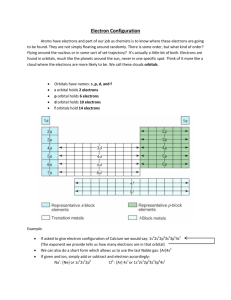
Electron Configuration Where do the electrons really hang out?? In those crazy orbitals!! EC = The arrangement of electrons around a nucleus. Let’s use the orbital shapes to place electrons. Helium Oxygen Not sure about you… I think that is a royal pain! There is an easier way- Electron Configuration! There are seven energy levels (we only worry about the first 4). Within the levels are subshells (s, p, d, f) Each subshell can accommodate a certain number of orbitals Each orbital can contain 2 electrons Electron Configuration 3 Rules: Aufbau Principle Pauli Exclusion Principle Hund’s Rule Molecular Orbital diagrams… Helium Oxygen Aufbau Principle Electrons enter the lowest energy level first Different levels within a principal energy level can overlap the energy levels of an adjacent principal level The filling of atomic orbitals does not follow a simple pattern. Aufbau PrincipleHere’s the pattern!! 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 2p 3p 3d 4p 4d 4f 5p 5d 5f Pauli Exclusion Principle An atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons 1 or 2 electrons may occupy an orbital When an orbital contains 2 electrons, they must have an opposite paired spin Pauli Exclusion Principle Because of their magnetic moments, we generally represent electrons using a single barbed arrow. The tip of the arrow points to the magnetic north of the electron Hund’s Rule When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy (s, p, d, f), one electron enters each suborbital until all orbitals contain 1 electron with the same parallel spin The second electrons then add to each orbital so that their spins are paired. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle “The more precisely the position is determined, the less precisely the momentum is known in this instant, and vice versa.” It is impossible to know the velocity and position of the electron at the same time. Lets do the EC for using the rules! (Show MO and EC) Fluorine Sodium Do WS Level 1 using MO diagrams Some things to note Valence electrons are those in the outer s and p orbitals. Shared and unpaired electrons can be determined by looking at the outermost, incomplete orbital. We can just use Aufbau– it is a little easier Oxygen 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 2p 3p 3d 4p 4d 4f 5p 5d 5f Silicon Calcium Now try the Level 2 WS Work on your Valence electron WS for 10 minutes! Compare answers, discuss what you may be doing wrong. Questions for me? Warm Up Can we tell which element by looking at the EC? 1s22s22p63s23p5 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 3d10 How did you do Count the number of electrons 1s22s22p63s23p5 = 17 electrons, Chlorine 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 3d10= 30 electrons, Zinc Did you write this in your notes? Valence electrons are those in the outer s and p orbitals. Shared and unpaired electrons can be determined by looking at the outermost, incomplete orbital. Molecular Orbital DiagramsUse lines to show orbitals Li 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 2p 3p 3d 4p 4d 4f 5p 5d 5f Phosphorus Vanadium Go over some on the Valence electron WS We can also use the periodic table to determine EC. Try some more of the WS using the periodic table method… Get out a half sheet of paper… I will project the quiz as soon as the bell rings. Be sure you write very neat!! Noble Gas Configuration… Write the noble gas in the period above the element… add the rest of the electron configuration. Example: Long form for Phosphorus: 1s22s22p63s23p3 Noble Gas Configuration for Phosphorus Nobel gas above P = Ne [Ne] 3s23p3 You need to be careful which periodic table you use for this!! The Web-Elements PT works well… Now you try! Write the noble gas configuration for V (atomic #23) La (atomic #57) Lr (atomic #103) Now you try! V (atomic #23) La (atomic #57) Lr (atomic #103) Now you try! Write the noble gas configuration for V [Ar] 4s23d3 La [Kr]6s24f1 Lr [Xe] 7s24f146d1 Molybdenum (42) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s14d5 Th (90) [Rn] 7s25f2 Ground, Excited or Impossible? Ground- If the electrons are in the orbitals that you would expect them to be in. Excited- If some of the electrons are in a higher energy level. Impossible- If the orbital doesn’t exist and/or the EC doesn’t make any sense. Ground, Excited or Impossible? Chlorine- 17 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p5 1s22s22p63s13p34s24p1 1s22s22p63s13p42d2 Ground, Excited or Impossible? Zinc- 30 electrons a. 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d86s2 b. 1s22s22p63s23p64s13d44p7 c. 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 3d10 You try… Write the electron configuration for carbon… Write an electron configuration for an excited atom. Write an impossible EC… Have your neighbor check your work. Questions on the HW? What happens with Ions?? Ions gain or lose electrons… What is the electron configuration for the magnesium cation? What about S2- When removing electrons … Remove the last electrons that were placed… Unless there are electrons in the d orbital…then remove the last s electrons first. Isoelectronic… Different atoms that have the same electron configuration. Na1+ Ne F1- Identify the atoms An element that has a 2- charge that is isoelectronic with Neon. Identify the atoms An atom that has lost 3 electrons and is isoelectronic with He Identify the atoms An element that has a 2- charge that is isoelectronic with Neon. An atom that has lost 3 electrons and is isoelectronic with He An atom that has gained one electron and has the same EC as Cu. Test


![The electronic configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008974852_1-8381577ce936fbfa611892c1a5f109cd-300x300.png)

