Section 8.7 Mutations

KEY CONCEPT
Mutations are changes in DNA that can affect phenotype
What are Mutations?
• Mutations are changes to DNA
Mutations can be caused by several factors.
1. Errors in DNA Replication or Meiosis
.
2. Mutagens - environmental factors such as
- Radiation
- Chemicals in environment
Rachel Carson author of Silent Spring
How Mutations affect Phenotype
The effect mutations have on an organism’s physical characteristics depends on:
1. The number and type of genes involved
2. Type of cell the mutation occurs in
Mutations in:
• Somatic cells – affect only the organism they occur in
• Sex cells – may be passed to offspring
Two Categories of Mutations:
1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication
2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis
Types of Chromosomal Mutations
• Translocation
• Duplication
• Nondisjunction
• Deletion
• Inversion
TRANSLOCATION
(think “transfer location”)
• The exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes.
• DUPLICATION
.
• Chromosomal mutations may occur during crossing over in
– Gene duplication results from unequal crossing over.
• NONDISJUNCTION
• Homologous chromosomes don’t separate in
Anaphase I
• Sister chromatids don’t separate in
Anaphase II
• Deletion – section of chromosome containing one or more genes is removed
• Inversion – a section of a chromosome flips its position
Single Gene Mutations
• Usually occur in DNA replication
• Affect one gene and protein made from it
Types of Gene Mutations Example
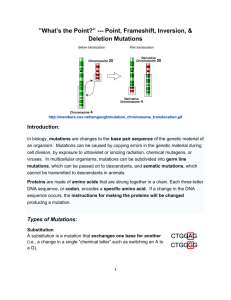
Frameshift The insertion or deletion of a number of bases that is not a multiple of 3. Alters the reading frame.
Deletion
One or more bases are deleted. This alters the reading frame
Insertion
One or more bases added to sequence..
Point
A single base change in DNA sequence. One base is substituted for another Types of point mutations are: nonsense, missense, or silent.
Nonsense
A change in the DNA sequence that results in the coding for a stop codon instead of an amino acid. Full protein not made.
Missense
Change in DNA sequence that results in a codon that requests the wrong amino acid.
This type of mutation can be harmful, others harmless
Silent
A change in the DNA sequence that does not change the protein sequence.
Frameshift Mutation
• A cat sat on my hat Ac ats ato nmy hat
• Due to the insertion or deletion o 1-2 bases
• This changes the amino acid sequence which changes the protein made
• .
Type of Frameshift Mutation
.
Deletion - one or more bases are deleted; shifts the reading frame
Type of Frameshift Mutation
Insertion - one or more bases are added; shifts the reading frame
Point Mutation
• A point mutation substitutes one nucleotide for another.
mutated base
Types of Point Mutations
Nonsense point mutation
• Change codes for a STOP codon
• Full protein not made
• “NO” STOP
Missense Point Mutation
*
Codes for wrong amino acid
* May be harmful or beneficial – depends…
Silent point mutation
Change in the DNA sequence that does not result in a different amino acid or protein being made.
DNA changes but its expression (phenotype) does not.
Mutations affect the DNA
But they may or may not affect phenotype.
• Chromosomal mutations tend to have a big effect.
• Some gene mutations change phenotype.
– Protein not made
– May change protein shape or the active site.
blockage no blockage
Results of mutations may be:
• Harmful – needed protein isn’t made
• Have NO EFFECT – are not harmful or helpful
• Beneficial are favored by natural selection – rarely occurs
• Mutations in body cells do not affect offspring
.
• Only Mutations in sex cells affect offspring.
• Natural selection often removes mutant alleles from a population when they are less adaptive /have no survival advantage.
Transcription is similar to Replication
•
• SIMILARITIES
• Replication (making DNA) andTranscription (making RNA) both
* Make a nucleic acid
* Occur in the nucleus (eukaryotes)
* Occur in all living organisms
* Require a number of enzymes to carry out process
* Involve complimentary base pariring
• DIFFERENCES
• The two processes have different end results.
• _ Replication produces DNA; Transcription produces RNA
– Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies an individual gene on the DNA.
– Replication makes one copy; transcription can make many copies.