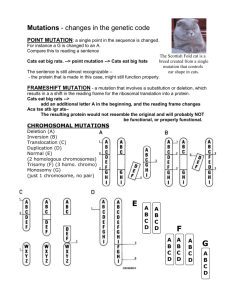
Mutations

Welcome to Genetic Mutations!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6zMIl
7x2WSY
Share out!
Today’s objective:
SWBAT explain how genetic mutations occur
SWBAT distinguish between the 3 types of genetic mutations
GENETIC DISORDERS ARE CAUSED
BY GENETIC MUTATIONS!!!!!!
A. Introduction to Mutations
-A mutation is a change in DNA sequence
(order of nucleotides).
-Mutations are important because they increase genetic variation.
Mutations in Body Cells
-Mutations in body cells cannot be passed on to your children, however, they can cause cancer or other problems in your body.
A cancer cell.
Cancer as a result of mutations in body cells:
A person with skin cancerThis is why it’s important to always wear sunscreen!
Cancer as a result of mutations in body cells:
Tongue cancer and lung cancer are often caused by changes in body cells as a result of smoking, so don’t smoke!!!
Mutations in Reproductive (Sex)
Cells
-Mutations in sex cells (sperm and egg cells) can lead to changes in the DNA sequence which can be passed down to a person’s children.
Mutations in sex cells
-X-men and X-women would be a result of mutations in sex cells. These people inherited mutated (changed)
DNA from their parents:
Good vs. Bad Mutations
Mutations can be good as well as bad. A good mutation could lead to a change in a protein that allows an animal to run faster or see better. A bad mutation could lead to a change in a protein that causes a genetic disease such as Sickle Cell Anemia or
Hemophilia.
TURN AND TALK
WHAT IS A MUTATION?
WHAT IS THE MAIN DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN MUTATIONS IN SEX CELLS
AND MUTATIONS IN BODY CELLS?
B. Gene Mutations
There are 3 main types of gene mutations:
1. POINT MUTATIONS
SUBSTITUTIONS
2. SILENT MUTATIONS
3. FRAMESHIFT
MUTATIONS
INSERTIONS
DELETIONS
1. Point mutation
-Point mutation-a change in one base pair in a DNA sequence.
Example: AUG=Met
AAG=Lys
-A point mutation can cause an amino acid to change, which will change the structure of the protein being made.
POINT MUTATION
Picture of A Point Mutation
Normal mRNA
Protein
Replace G with A
Stop
Point mutation mRNA
Protein
Stop
Point mutations in our lives!
-Sickle cell anemia is a blood disease caused by a point mutation.
A single nucleotide is changed from “A” to “T” which causes the amino acid to change from glutamic acid to valine:
Normal: ACT CCT G A G GAG
Amino Acids:
Thr – Pro – Glu – Glu
Sickle cell:
ACT CCT G T G GAG
Amino acids:
Thr – Pro – Val – Glu
Point mutations in our lives!
-People with sickle cell anemia often experience a lot of pain and swelling and have trouble exercising.
Sickle cells also can’t carry
Oxygen as effectively as normal
Cells.
2. SILENT MUTATION
A TYPE OF
MUTATION THAT
RESULTS IN A
CHANGE IN
CODON BUT
DOES NOT
CHANGE THE
AMINO ACID
CREATED.
Codons can code for the same Amino acid!
Silent Mutations
Single nucleotide mutation that does not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of the protein made
THINK PAIR SHARE
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN
A POINT MUTATION AND A SILENT
MUTATION?
3. Frameshift mutation
-Frameshift mutation- Adding or deleting nucleotides to a DNA sequence.
-A frameshift mutation is much worse than a point mutation because it causes the entire
DNA sequence to be shifted over!
Example: DNA: ATTAAACCG
Delete this T
ATAAACCG
2 types of Frameshift mutations:
INSERTION DELETION
FRAME-SHIFT MUTATIONS:
Insertion: Nucleotide added –
Entire DNA sequence changed
Deletion: Nucleotide missing –
Entire DNA sequence changed
V. Frameshift mutation
Deletion of U
Frameshift mutation mRNA
Protein
Frameshift Mutations
Crohn’s Disease is caused by a frameshift mutation.
It causes inflammation to the digestive tract.
THINK PAIR SHARE
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN A POINT MUTATION AND A
FRAMESHIFT MUTATION?
Difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation.
BRAIN POP VIDEO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=efstlgo ynlk
GUIDED PRACTICE-
WHITEBOARDS
Is this a point mutation or a frameshift mutation?
It’s a point mutation because only one nucleotide changed!
Questions:
THE DOG BIT THE CAT
THE DOG BIT THE CAR
Point or frameshift?
Point!
Questions
THE DOG BIT THE CAT
THE DOB ITT HEC AT
Point or frameshift?
-frameshift
GUIDED PRACTICE
WHAT IS THE NAME OF THE TYPE OF
MUTATION THAT RESULTS IN A
CHANGE IN CODON BUT DOES NOT
CHANGE THE AMINO ACID?
SILENT MUTATION
A TYPE OF
MUTATION THAT
RESULTS IN A
CHANGE IN
CODON BUT
DOES NOT
CHANGE THE
AMINO ACID
CREATED.
GUIDED PRACTICE
What type of frame-shift mutation is shown below?
Answer
INSERTION-
Frameshift
GUIDED PRACTICE
What type of frame-shift mutation is shown below?
Answer
DELETION-
Frameshift
WHAT TYPE OF MUTATION IS
SHOWN BELOW?
Answer
POINT
BEFORE THE MUTATION, A DNA
CODON CODES FOR THE AMINO
ACID VALINE. AFTER THE MUTATION,
THE DNA CODON STILL CODES FOR
VALINE.
WHAT TYPE OF MUTATION IS THIS?
Answer
SILENT
Objective
Today’s objective:
SWBAT explain how genetic mutations occur
SWBAT distinguish between the 3 types of genetic mutations
Rate 1-5 on how confident you feel with these objectives
1- Poor
5- Excellent