Mendel - Hazlet.org
advertisement

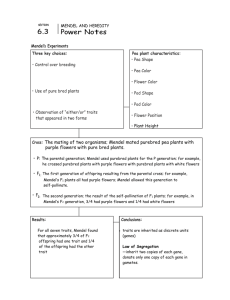
Mendel & Heredity Chapter 11.1 The Origins of Genetics Heredity The passing of traits from parents to offspring is known as heredity. What are some examples of traits that are passed from your parents? Even before the structure of DNA was discovered people were interested in how genes on DNA were passed from generation to generation. Gregor Mendel Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk born in 1822. Mendel is known today as the father of modern genetics. Mendel performed experiments on different varieties of pea plants. Mendel used pea plants because there are many different traits, they grew quickly and they can self-pollinate. Seven traits Mendel studied Flower color – (purple & white) Seed color – (yellow & green) Seed shape – (round & wrinkled) Pod color – (green & yellow) Pod shape – (smooth & wrinkled) Flower position – (middle & top) Plant height – (tall & short) Mendel’s Observation Mendel’s first observation came from a monohybrid cross a cross that involves one pair of contrasting traits. For example crossing a plant with purple flowers with one with white flowers. In order to make sure he had truebreeding purple & white plants Mendel self-pollinated each for many generations. Three Steps of Mendel’s Experiments. Step 1: Mendel crossed the two different true-breeding plants & called it the P (or parental) generation. Step 2: The offspring from the P generation were then crossed and called the F1 Generation. Step 3: The offspring from the F1 generation were then crossed and called the F2 Generation. Mendels Results After the P generation was crossed Mendel noticed that all of the offspring exhibited one type of color, the other color “disappeared”. In the F2 generation the color that “disappeared” came back in a ratio of about one in every four. Calculating Mendel’s ratios. Mendel noticed that he had 705 purple flowers and 224 white flowers in his F2 generation. 705/224 = 3.15 224/224 = 1 A ratio of about 3:1 Do your own: 787 tall plants & 277 short. Review Questions Why did Mendel use pea plants? What was the ratio Mendel noticed in his F2 generation? What is the following ratio of pod color 428 green & 152 yellow. How did Mendel make sure that his P generation were true-breeding?