NEURON
advertisement

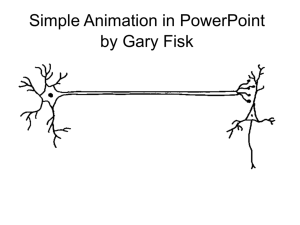
DR. ZAHOOR ALI SHAIKH LECTURE --9 1 Neuron (nerve cell) consists of Three Basic Parts : 1– Cell Body 2– Dendrites 3– Axon 2 Cell Body The nucleus and organelles are present in the cell body. From the cell body many extensions known as DENDRITES project to increase the surface area for receiving the signals from other neurons. Cell Body and Dendrites are Input zone. 3 4 Some neuron have up to 400,000 dendrites. In cell body Graded Potentials (Local potentials) are produced in response to incoming signals. 5 AXON or NERVE FIBER Axon is a single, elongated, tubular extension from the cell body. Axon conducts Action Potential from the cell body and terminates on other cells. 6 AXON Axon Hillock It is the first portion of Axon + Cell body from which axon leaves, it is called Axon Hillock AXON HILLOCK is the place where Action Potential are generated. Action potential are then conducted from Axon Hillock along the axon to its branched endings called Axon Terminals. 7 AXON Axon Terminals – release chemical messengers to other cells with which they come in contact Therefore Axon is the conducting zone of neuron. And Axon Terminals are Output zone. Axon may be less than 1mm or longer than 1meter depending on the area they innervate. 8 REMEMBER Dendrites & cell body – Input zone ( Receive) Axon -- Conducting zone Axon Terminals – Output zone Action Potential are initiated at Axon Hillock 9 10 In neuron, graded potentials ( local potentials) are generated in the Dendrites and Cell body due to chemical signals. If the potential is strong that can initiate Action potential at the Axon Hillock than impulse (AP) is conducted throughout the axon. 11 There are TWO types of conduction: 1– Continuous conduction or Contiguous conduction. 2– Saltatory conduction or Jumping 12 Continuous or Contiguous conduction occurs in UNMYELINATED nerve fibers. Saltatory Conduction occurs in MYELINATED nerve fibers. 13 14 15 16 Conduction depends on Two factors: 1) Diameter of the nerve fiber 2) Axon (Nerve fiber) is Myelinated or Unmyelinated 17 Diameter of Nerve fiber Nerve fiber with small diameter – conducts slowly Nerve fiber with large diameter – conducts fast 18 Myelinated Nerve Fibers Myelinated nerve fibers conduct FAST then Unmyelinated nerve fibers. Why? Myelinated nerve fibers have saltatory conduction. 19 20 SUMMARY Small diameter fiber conduct SLOW Large diameter fiber conduct FAST Myelinated nerve fiber conduct VERY FAST. 21 22 Why Myelinated Nerve Fibers have increased speed of conduction or increase Nerve Conduction Velocity [NCV] ? Because Myelinated fibers are axons covered with myelin sheath, a thick layer composed of lipids. Myelin Sheath is present at regular intervals along the length of nerve fiber. 23 Myelin Sheath acts as insulator. Why ? Because water soluble ions which carry current across the membrane, can not pass. Between the myelinated regions – there is NODE OF RANVIER, where axonal membrane is not covered with myelin sheath and exposed to Extra-Cellular Fluid [ECF]. 24 In Myelinated Fiber, current can flow at NODE OF RANVIER to produce Action Potential. Therefore impulse jumps from node to node, skipping over the myelinated portion of axon. This type of conduction in Myelinated Fiber is called ‘SALTATORY CONDUCTION’ [saltare means to jump]. Saltatory Conduction [in myelinated fibers] is fast than continuous conduction in unmyelinated fibers. 25 26 What is Myelin Sheath ? Myelin Sheath is formed by myelin forming cells in Peripheral Nervous System [PNS], SCHWANN CELLS. Myelin Sheath is not a part of neuron but formed by Schwann Cells that cover the axon. Please Note – In Central Nervous System (CNS) i.e Brain and Spinal cord myelin is formed by OLIGODENDROCYTES. 27 In case of a cut axon in peripheral nerve, there is REGENERATION (Re-growth) of axon due to Schwann cell. In case of CNS ( Brain and Spinal cord), axons which are myelinated by Oligodendrocytes, do not regenerate. 28 In Unmyelinated Fibers, nerve impulse passes along the entire length of nerve fiber. It is slow conduction as compared to myelinated fibers. 29 Structure of neuron – Cell body, Dendrites, Axon. Axon – Action Potential [AP] is generated at axon hillock and AP is conducted by axon. Axon is the conducting zone of neuron. Input Zone – Dendrites and Cell Body. Output Zone – Axon terminals Graded Potential [Local Potential] is generated at dendrites and cell body due to chemical signals. Types of Nerve Conduction - Contiguous Conduction [continuous] occurs in unmyelinated nerve fiber - Saltatory Conduction – occurs in myelinated nerve fiber Factors affecting conduction - Diameter of Nerve Fiber - Myelinated or Unmyelinated Nerve Fiber What is myelin sheath? What is Node of Ranvier? Difference between Contiguous Conduction and Saltatory Conduction? 30 31