Cellular Respiration
advertisement

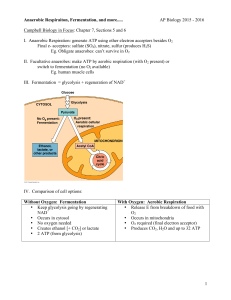
Cellular Respiration Do Now : Why do we need to breathe? Equation Oxygen + Glucose Carbon dioxide + Water + ATP 2 6 12 6 Reactants 2 2 Products 2 Kinds of Cellular Respiration • Aerobic: Occurs in the presence of oxygen • Anaerobic: Occurs when no oxygen is present. Aerobic Respiration 3 stages 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain Glycolysis • First stage in cellular respiration • Only stage that does not require O2 Requires 2ATPs to start. End Product = 4 ATP Net Gain: 2 ATP One cell can produce thousands of ATP molecules in a few milliseconds!!! REVIEW: What is the purpose of glycolysis? To break down glucose Krebs Cycle • CO2 is released as a waste gas • Requires O2 • Occurs in mitochondria • Produces 2 ATPs Electron Transport Chain • ADP is converted into ATP • Up to 34 ATPs can be produced Aerobic respiration yields a net total of 3638 ATPs Question: Which step of aerobic respiration produces the most ATPs (most efficient step)? ETC- Electron Transport Chain Question : In what part of the cell aerobic respiration takes place? Mitochondria AIM : Fermentation Do Now Discuss photosynthesis and explain its importance to an organism. In your answer, be sure to: • identify the organelle where this process occurs • identify two raw materials necessary for this process • identify one energy-rich molecule that is produced by this process • state how organisms use the energy-rich molecule that is produced • state how a gas produced by this process is recycled in nature Fermentation • Anaerobic process: occurs in absence of O2. • Recycles NAD+ ,so that glycolysis can continue producing 2ATPs for every round. • Does not produce any ATP 2 kinds of fermentation: 1. Alcoholic Fermentation 2. Lactic Acid Fermentation www.kyleskitchen.net www.healthstones.com Alcoholic Fermentation + 2 Ex: Yeast in Bread Lactic Acid Fermentation + Produced in muscle cells during exercise when body is no longer able to supply O2 to cells.