ckfinder/userfiles/files/Grade 7 Revision guide weather and climate
advertisement

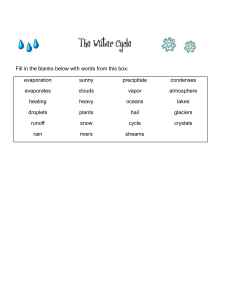
Grade 7: Weather and Climate Revision Guide Name : _______________________ Class: ________________________ What is our climate system? The atmosphere covers the Earth. It is a thin layer of mixed gases which make up the air we breathe. Atmosphere This thin layer also helps the Earth from becoming too hot or too cold. Oceans Oceans cover about 70 percent of Earth's surface. Their large size and thermal properties allow them to store a lot of heat. Land Land covers 27 percent of Earth's surface and land topography influences weather patterns. Ice Ice is the world's largest supply of freshwater. It covers the remaining 3 percent of Earth's surface including most of Antarctica and Greenland. Ice plays an important role in regulating climate, because it is highly reflective. Biosphere The biosphere is the part of Earth's atmosphere, land, and oceans that supports any living plant, animal, or organism. It is the place where plants and animals, including humans, live. Key Terms Weather = describes the day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere. Weather can change quickly - one day it can be dry and sunny and the next day it may rain. Climate = Describes average weather conditions over longer periods and larger areas. What causes weather? Because the Earth is round and not flat, the Sun's rays don't fall evenly on the land and oceans. The Sun shines more directly near the equator bringing these areas more warmth. However, the polar regions are at such an angle to the Sun that they get little or no sunlight during the winter, causing colder temperatures. These differences in temperature create a restless movement of air and water in great swirling currents to distribute heat energy from the Sun across the planet. When air in one region is warmer than the surrounding air, it becomes less dense and begins to rise, drawing more air in underneath. Elsewhere, cooler denser air sinks, pushing air outward to flow along the surface and complete the cycle. What is the Water Cycle? Earth has a limited amount of water. So, that water keeps going around. We call it the water cycle. The water cycle begins with evaporation. Evaporation is when the sun heats up water in rivers, lakes or the ocean. Then turns it into water vapour or steam. The water vapour or steam leaves the body of water and goes into the air. Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water out of their leaves. Condensation is when water vapor in the air gets cold and changes back into water to form clouds. Think of it this way, when you open a cold soda on a hot summer day, your soda will start to sweat as water droplets form on the outside of the can. Precipitation occurs when so much water has condensed that the air can't hold it anymore. This is how we get rain or snow. Collection happens when the precipitation falls and is collected back in the oceans, lakes and rivers. When it falls to the ground, it will soak into the earth and become ground water. This is the water cycle and it just keeps repeating. The Bare Bones: What causes weather – a summary 1. The sun heats Earth – but unevenly. 2. Earth in turn warms the air, which rises. 3. Rising air leads to wind, because air from a colder place flows in to replace. 4. The Sun’s heat also causes water to evaporate, giving water vapour. 5. When the air rises it cools. So the water vapour condenses, giving clouds of water droplets. Droplets join to make larger drops, which fall as rain.