Powerpoint Format ()
advertisement
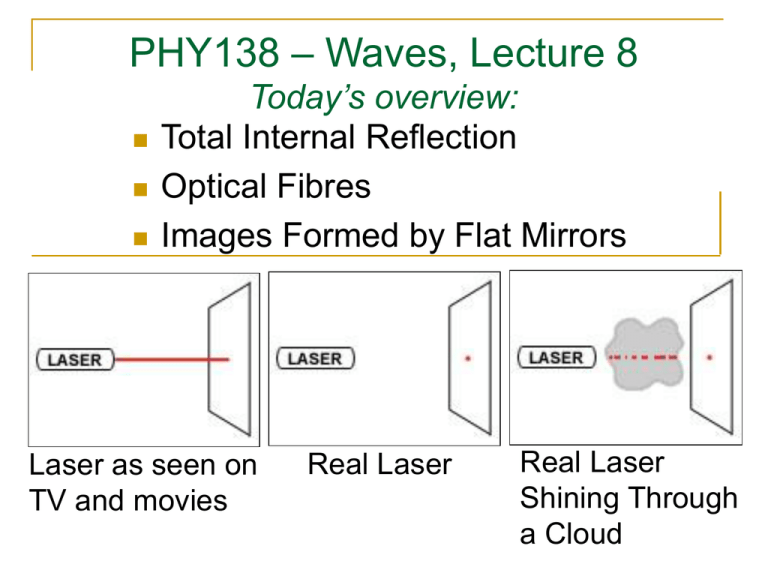
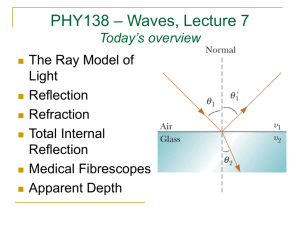
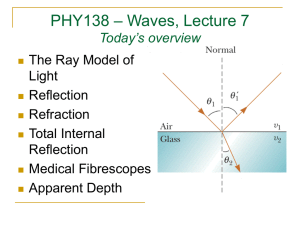
PHY138 – Waves, Lecture 8 Today’s overview: Total Internal Reflection Optical Fibres Images Formed by Flat Mirrors Laser as seen on TV and movies Real Laser Real Laser Shining Through a Cloud Reading Assignment Please read the following from Serway and Jewett before class on Monday: Chapter 26, Sections 26.4 - 26.6 and Context 7 Conclusion on page 1037. A www.masteringphysics.com assignment is due this Friday at 5:00 PM. It is the last Mastering Physics assignment of the semester. (hoot.) air water A fish swims below the surface of the water. An observer sees the fish at: 1. a greater depth than it really is. 2. its true depth. 3. a smaller depth than it really is. Notes from last lecture The index of refraction, n, of air depends on temperature; n decreases as air Temperature increases When a ray enters a layer of different n, it bends If n decreases, the ray bends away from the normal. This is refraction. Refraction effects cause mirages, twinkling of starlight, and “heat currents” off hot highways or other surfaces. Hot air near the ground Temperature Inversion: Hot air above Total Internal Reflection Occurs when n2<n1 θc = critical angle. When θ1 ≥ θc, no light is transmitted through the boundary; 100% reflection n2 sin c n1 An Optical Fibre Quiz 2 An observer O, facing a mirror, observes a light source S. Where does O perceive the mirror image of S to be located? (5 = none of the points shown.) mirror O 1 3 S 4 2 Virtual Image in a flat mirror Light rays emerging from an object obey the law of reflection for the specular surface of a mirror Our mind imagines that the rays emerge from points beyond the mirror. This thing beyond the mirror is called an image. No light rays actually pass through the image, so it is “virtual”. It is convenient to describe the size and location of the image as if it were an actual thing. How an image is formed