IB Physics: Reflection & Refraction Lab Report
advertisement

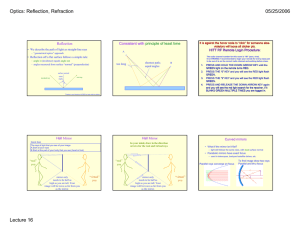
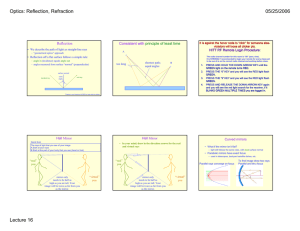
IB Physics – Reflection & Refraction Lab Part 1: Reflection Goal: Determine the relationship between the incident light and reflected light off of a plane (flat) mirror. Procedure: Design a method that will allow you to measure the incident and reflected angles of light on a plane mirror for various angles. Make sure that you do not look directly at the laser – it will burn your eyes! Table I Plane Mirror θi θr Analysis: Make a half page graph of θr and θi. Determine the equation of the trend. Part 2: Refraction Goal: Determine the mathematical description for the refraction of light as it passes from one medium to another. Procedure: Choose a refractive medium (either a hollow plastic container filled with water or a solid plastic semi-circle). Use the double-pin-sighting method to gather data to complete the data table. Table II Refractive medium: ________________ θi θr 0 10 20 30 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 Analysis: Make a half page graph of θr and θi. Make a second half page graph of sin(θr) and sin(θi). Determine the equation of each curve. Questions: 1. What is the general mathematical description for the refraction of light? 2. Why is the semi-circular shape necessary? What would happen if the object had parallel sides? Use drawings to explain. 3. What is the index of refraction for the material? Be careful with this calculation! 4. What is the difference between refraction and reflection? Use a diagram to support your explanation. 5. Explain, including a diagram, how optical fibers transmit light signals long distances without appreciable loss of light intensity. In your explanation, include a discussion of critical angle, total internal reflection, optical density, incident angle and refracted angle.